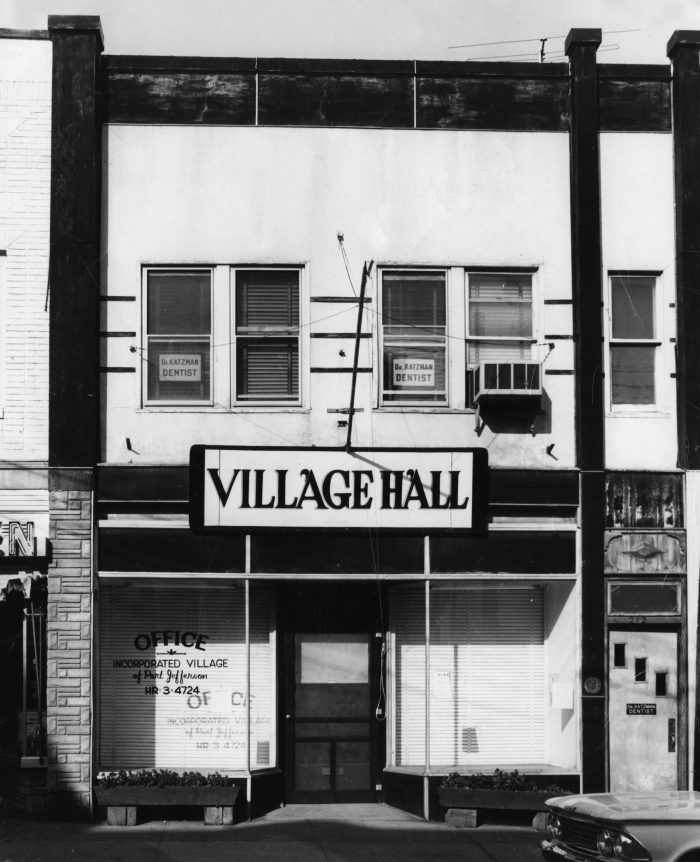
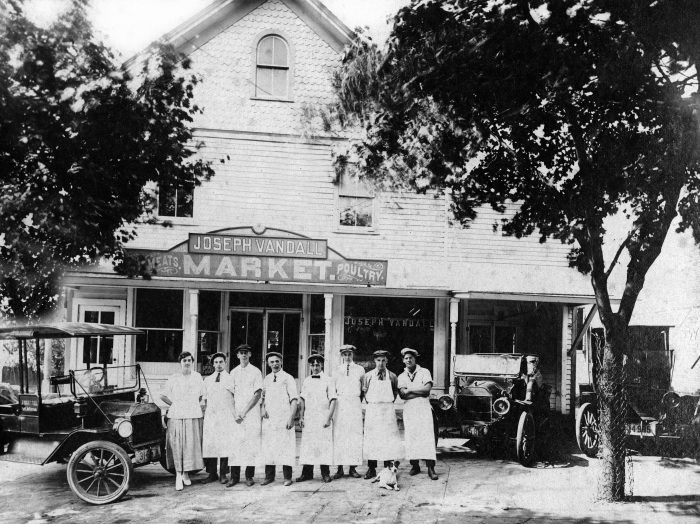
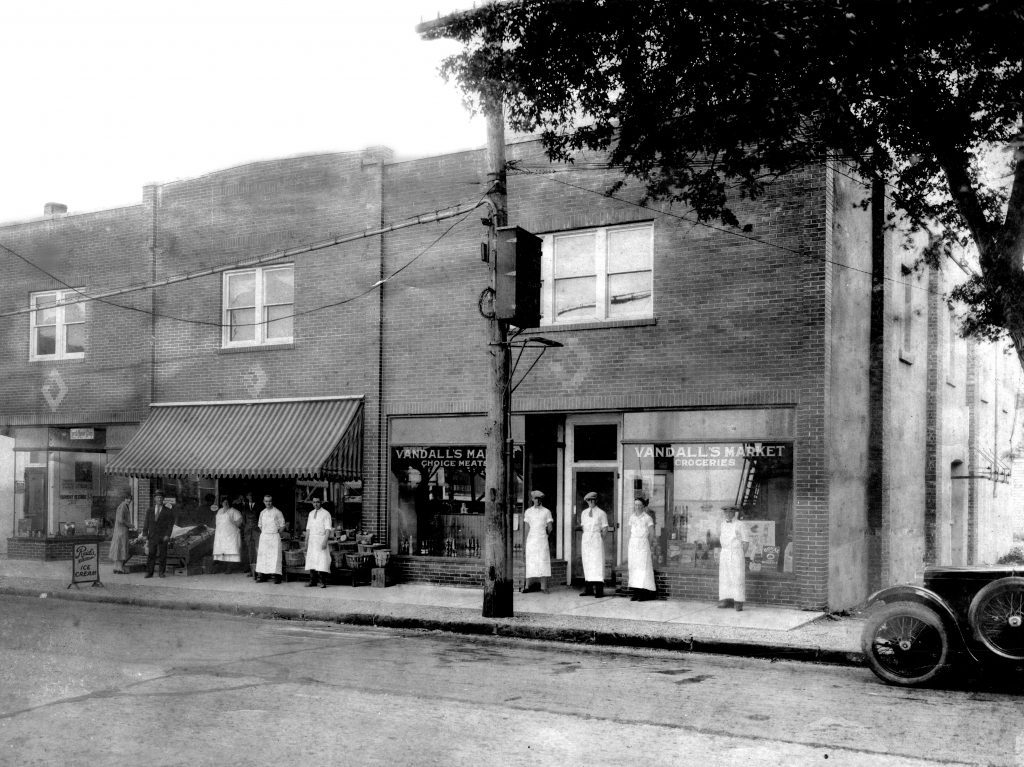
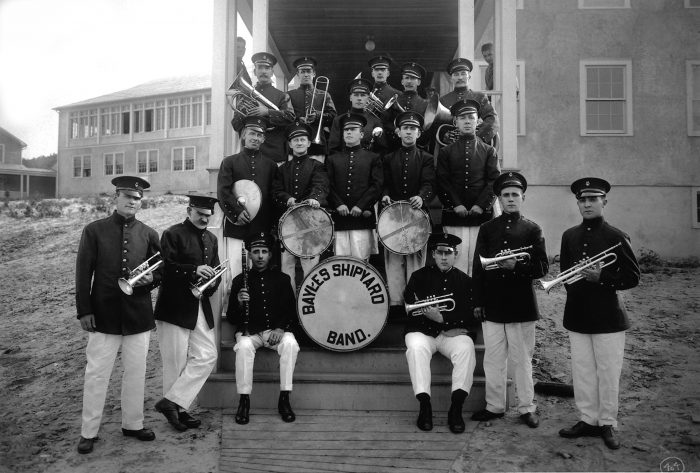
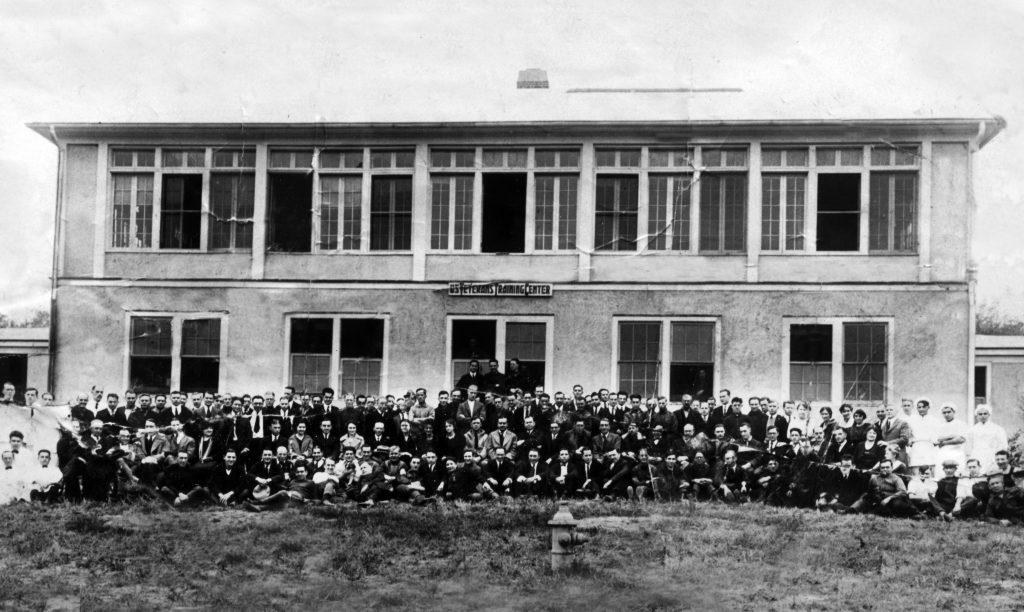
After Port Jefferson incorporated in 1963, the village Board of Trustees established a temporary village hall in leased facilities on the west side of Main Street.
Since the easily forgotten storefront location was hardly impressive and the small space soon proved inadequate, a plan for a permanent village hall was advanced in 1964 by Port Jefferson’s first mayor, Robert L. Robertson.
He proposed the construction of an elegant and capacious million-dollar village center that would house both government offices and recreational facilities, including a community swimming pool.
The multipurpose complex would be built on West Broadway, facing Port Jefferson Harbor, on land acquired by the village and once occupied by Loper Brothers Lumber Yard.
While The Port Jefferson Record applauded Robertson’s “visionary” proposal, the Board of Trustees decided not to proceed with the project, pending the completion of a village master plan by consultants Raymond & May.
The master plan, released in July 1965 during the administration of Port Jefferson’s second mayor, Clifton H. Lee, provided a guide for the future development of the village and recommended that the West Broadway tract be used exclusively for Port Jefferson’s seat of government.

Milton S. Osborne, who had directed the Penn State School of Architecture, also conferred on the project, and supported using the West Broadway site strictly for village hall while building public parks and recreation areas at other locations throughout Port Jefferson.
With a clear goal in mind, the Board of Trustees formed the Architectural Selection Committee which reviewed sketches and interviewed architects before recommending Anthony J. Lorio (1928-2013) as their choice to design village hall.
Lorio proposed the construction of a 7,000-square-foot, two-story, Georgian-style brick building, on a raised podium. Preliminary renderings were displayed throughout Port Jefferson, and residents were invited to offer their opinions.
While most reviews were positive, there were some who called for softening the village hall’s facade. After making minor modifications in his design, and with the trustees’ support, Lorio began preparing working plans for the building.
In April 1966, construction of village hall went out to bid, but all 19 proposals were rejected as too expensive. The Board of Trustees, which had wanted to keep total costs under $200,000, went out to bid a second time in winter 1967 but was frustrated again with the high numbers.

After considerable discussion, the trustees agreed that construction costs were likely to increase because of the Vietnam War’s inflationary impact and it was best to accept a $264,000 bid before prices rose even more.
Port Jefferson broke ground for village hall in April 1967, but nationwide strikes in various industries so delayed progress locally that the building was not ready for business until May 1968.
Over the years, village hall has become more than just a municipal building and is now a seaside landmark, evoking that sense of place that makes Port Jefferson so special.
Kenneth Brady has served as the Port Jefferson village historian and president of the Port Jefferson Conservancy, as well as on the boards of the Suffolk County Historical Society, Greater Port Jefferson Arts Council and Port Jefferson Historical Society. He is a longtime resident of the village.