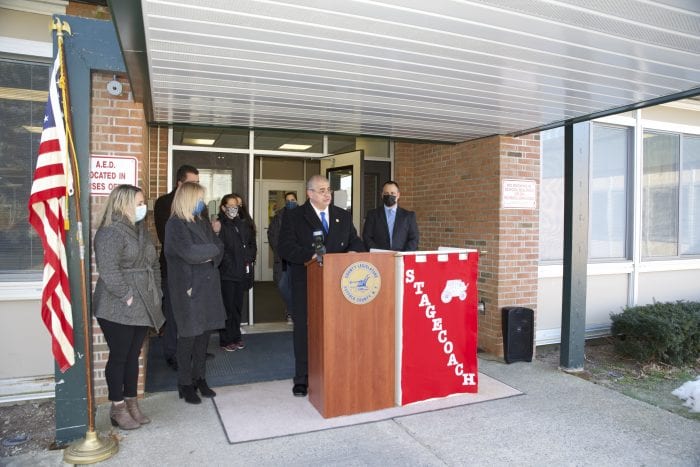
Dozens of community activists from across Long Island rallied outside Suffolk County Executive Steve Bellone’s (D) office in Hauppauge this week, asking lawmakers to adopt “The People’s Plan.”
Earlier this month, police reform advocates created their own plan to hold law enforcement accountable and calling on them to be transparent within the community.
“We’re gathering here today nearly a year after the George Floyd uprisings because our communities took to the street and said enough is enough,” said Elmer Flores with Long Island United to Transform Policing and Community Safety. “We are yearning for change. And for far too long our elected officials have not met our demands with the gravitas that it demands.”
Some of the plan includes civilian oversight of police misconduct, creating unarmed traffic enforcement and ending pretextual stops when someone is pulled over.
“Mistrust is pervasive between the police and the communities they are supposed to represent,” he added. “And part of that is that we need to get to the root causes of why crime happens and how we can address it and prevent it from happening. But to do that, it requires leadership. It requires bold and effective action that’s going to change the way policing happens on Long Island.”
This plan is separate from the reform Bellone submitted to lawmakers last week, and these local activists demand the reforms be included in the plan due to the state April 1.
Jackie Burbridge, co-founder of the Long Island Black Alliance, said to the crowd that for years the Suffolk County Police Department has been actively turning a blind eye to crime being committed in this county in order to continue harassing people who are not white. She said the recommendations that the county task force came up with don’t go far enough in preventing or mitigating discriminatory policing.
“The plan that was released by Suffolk County in response to Governor Cuomo’s [D] executive order falls short of the transformative changes to the way we conceive of public safety that this moment in our community members are demanding,” she said. “Black and brown communities across Long Island are overpoliced, resulting in outsized opportunities for interactions between vulnerable community members and police officers. … It’s not that people are being brutalized because cops see threats. They don’t see threats in our community, they see prey. And what we need is police reform that’s actually going to address that.”
The collective groups have spent months crafting the 12, research-backed proposals for structural reform that make up the 310-page “The People’s Plan” to address numerous structural components of transforming and reimagining policing and public safety on Long Island.
Suffolk’s police reform proposal directs the county’s Human Rights Commission to review complaints of police misconduct.
However, the police department would still have the power to investigate and discipline police misconduct. Activists say they are asking for lawmakers to consider other measures, like mental health counselors for certain situations, and create a community council to review and hold police accountable for misconduct.
Members from local groups headed to Hauppauge, too, including Myrna Gordon of the North Country Peace Group, to show their support and signs.
“How can we not be here?” she asked. “It’s what we need to do to keep fighting for peace and justice. We need to see that Steve Bellone is on board with ‘The People’s Plan,’ and every peace and justice group in Suffolk County and the Three Village area needs to be on board.”
Peggy Fort, a member of the United For Justice in Policing Long Island and Building Bridges in Brookhaven groups, said ‘The People’s Plan’ addresses not just the community, but could benefit police officers, acknowledging the stresses police officers face.
“We’re not trying in ‘The People’s Plan’ to micromanage the police department,” she said. “What we’re trying to do is really address the problems and the racial bias that exists.”