By Daniel Dunaief
When Jacqueline Olsen learned the day before her birthday last November that she needed surgery for lung cancer, she felt anxious about a procedure she knew could be painful and could involve a lengthy recovery.
“It’s not only my birthday, it’s Thanksgiving,” said Olsen, who is a resident of St. James and is an agent for personal insurance such as home, auto and umbrella insurance. “Everybody was real tense. It was not a pleasant holiday.”
Olsen’s father, William Leonard, and father-in-law, James Olsen, had died of lung cancer after having open chest surgeries. The pain of what her father went through 48 years ago and father-in-law over 20 years ago was fresh in her mind as she readied herself for her own procedure.

Speaking with doctors at Stony Brook University Hospital, Olsen heard about newer, better options.
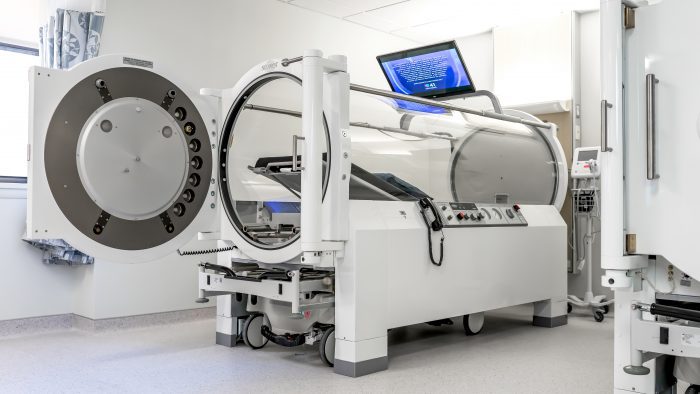
Dr. Ankit Dhamija, Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Director of Thoracic Robotic Surgery at Stony Brook Medicine, suggested to Olsen that she was a candidate for a robot-assist surgery called the da Vinci Surgical System.
Olsen and her family gathered considerable information about the procedure.
“I did some research on it and it said it would be a faster recovery and I would be up and back to my normal self pretty soon afterward,” said Olsen. “It seemed like a less invasive surgery.”
The robotic surgery does not involve turning over the procedure to a machine, Dr. Dhamija explained.
Instead, the process involves making considerably smaller incisions and guiding the robot through the body to remove the cancerous tissue.
“The robot is a machine that is an extension of our hands,” said Dr. Dhamija, who has performed about 500 such procedures with the help of a robot, including around 70 since he arrived at Stony Brook.
The robotic system allows surgeons like Dr. Dhamija and Dr. Henry Tannous, Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Chief of the Cardiothoracic Surgery Division at Stony Brook Medicine, among others, to sit in the operating room with the patient while the robot enters through an incision. The robot provides a three dimensional view of the inside of the body, magnifying cells by ten times.
The robot assist can also improve the ability of surgeons to perform fine operations.
The system “does have a machine algorithm associated with it that actually is known to reduce tremors in surgeons that have tremors,” said Dr. Dhamija. “Someone that may not be able to do a certain portion of the operation due to their technical limitations can subsequently do it with the robot.”

In the procedure, the surgeon can see and maneuver through the body effectively, searching for the specific cells to remove.
An interventional radiologist can inject a dye which under CT guidance allows the surgeon to “see where the lesion is and to verify that you have adequate margins” or the border between cancerous and non-cancerous cells, Dr. Dhamija said. “Having the dye in there to identify [the cancer] is helpful,” he added.
By using the robot instead of creating a large incision, doctors can reduce the time patients spend in a hospital down to as little as one to three days from the four to eight days after an open chest lobectomy.
“There’s so much to be said about someone [recovering] in their own home,” said Dr. Dhamija. They “get to sleep properly, their bowel habits are more normal, and they get to reengage in their daily life functions sooner. I’m a big proponent of a patient taking charge of their own postoperative care.”
Indeed, Stony Brook doctors have become so confident and comfortable with the robot assist that it has become the main platform for thoracic oncology patients at Stony Brook Medicine, explained Dr. Tannous. Tannous estimates that 90 percent of the lobectomies will be performed robotically in 2022, up from 10 to 20 percent in 2021.
In an email, Dr. Tannous wrote that other specialties that have adopted the robotic platform include gynecology, urology, colorectal, bariatrics, and general surgery.
Stony Brook is also expanding robotic surgery to include cardiac procedures in 2023.
Dr. Tannous said robotic procedures that cut down on recovery time means less risk of hospital-acquired infections, lower extremities blood clots, and numerous other benefits.
Some day, theoretically, the robot may enable remote procedures, with surgeons operating the robot with the help of an on-site local medical team. That could be helpful for astronauts who develop a medical problem far from home where they need emergency surgery.
An important caveat with that, Dr. Dhamija said, is that the staff on site would need to be able to complete a procedure if an open chest surgery became necessary.
Olsen, who was out of the hospital less than 24 hours after she had surgery in late May, has become a fan of the technology and of the team at Stony Brook.
Olsen, who has three scars on her back and two on her side, felt pain for about a week. As she recovered, she never felt the need to fill a prescription for a stronger painkiller, choosing to treat the pain with Motrin. She plans to continue to take blood tests every three months and to get CAT scans every six months.
Olsen was thrilled with the quality of care she received and is pleased she can look forward to sharing quality summer time during the family’s annual beach trip. “It’s heaven to me,” she said, where she can “spoil my grandchildren.
As for a perspective on her surgery, she said the difference between 20 years ago and now is “unbelievable. It was such an awful experience” for her father and father in law. “This was a million times better.”