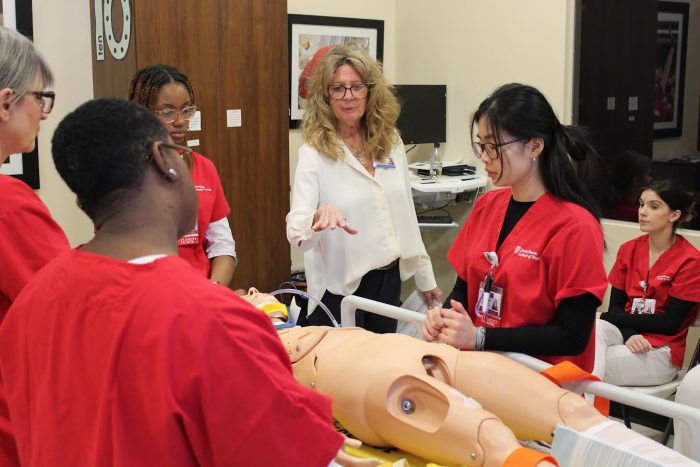
Initiative will enhance and broaden nursing education with funds totaling $20.5 million
The Stony Brook University School of Nursing has been selected as a State University of New York (SUNY) Regional Nursing Simulation Center, one of only three in New York State. Governor Kathy Hochul announced the news this month about the selected centers, which will involve an overall $62 million investment to bolster nursing training at many levels throughout the state.
Stony Brook will receive $10 million from SUNY, with matching funds of $10.5 million from Stony Brook University. The total of $20.5 million will be used to create a new simulation center at Stony Brook that includes the latest simulation technologies to help train more nursing students and enhance the overall experience of nursing education.
The selected campuses include the University of Buffalo, named the SUNY System-Wide Nursing Simulation Center of Excellence, and SUNY Canton and Stony Brook as the regional centers. Each center will provide high-quality, hands-on training for some of the most needed clinical practice areas in health care, such as labor and delivery, high acuity cases, and community health.
According to the Governor’s office, with their investments, each campus has committed to significant prelicensure nursing program enrollment growth, leveraging the legislation Governor Hochul signed in May of 2023 permitting nursing students to complete up to one-third of their clinical training through high-quality simulation experiences.
“By investing in nurses of the future, we’re investing in the talent of aspiring professionals across our state and in the health care workforce we all rely on,” says Governor Hochul.
“As Suffolk County’s only academic medical center, Stony Brook University is proud to be at the forefront of healthcare education and workforce development,” says Dr. William A. Wertheim, Executive Vice President for Stony Brook Medicine. “This designation as a SUNY Regional Nursing Simulation Center reflects our long-standing commitment to preparing the next generation of nurses. Through this important partnership with SUNY, we will expand access to high-quality, hands-on clinical training – helping to address the critical nursing shortage, grow the healthcare workforce and ensure our communities have skilled professionals they need to thrive.”
The new regional nursing simulation center at Stony Brook will support a 19 percent increase in prelicensure (baccalaureate) nursing enrollment in the first-year post-project completion. There is a projected 27 percent increase over the next five years.
“We are grateful to Governor Hochul, SUNY, and Stony Brook University for this opportunity to expand and enhance nursing education through simulation-based learning,” says Dr. Patricia Bruckenthal, Dean of the Stony Brook School of Nursing. “Our NEXUS Innovation Center epitomizes our commitment to advancing nursing education through innovation and collaboration. By integrating cutting-edge simulation technologies, we are not only enhancing the clinical competencies of our students and students across the region but also fostering an environment where interdisciplinary teams can engage in transformative learning experiences. This center stands as a testament to our dedication to preparing nurse leaders who will shape the future of healthcare delivery.”
According to the plan as a regional center, Stony Brook will significantly expand its simulation space footprint to enhance in-person nursing education. Additionally, the center will leverage advanced simulcast software technology to provide remote learning opportunities across Long Island.
Currently, simulation baccalaureate nursing curriculum is integrated into every clinical course in the School of Nursing. Due to space constraints, students are rotated through the Learning Resource Center in small groups, which enables hands-on experiences in the simulation lab under the supervision of the lab director and clinical faculty. The expansion of simulation training and a new dedicated center will streamline this workflow.
The announcement of the three nursing simulation centers across the state also builds on previous efforts by SUNY to expand and enhance nursing education through simulation-based learning. Last October, SUNY Chancellor John B. King Jr. announced the inaugural class of the SUNY Nursing Simulation Fellowship, which includes Dr. Debra Giugliano from Stony Brook Nursing; and SUNY has invested $3.7 million through its High Needs Nursing Fund to further advance simulation-based education across 40 of SUNY’s nursing programs.