By Daniel Dunaief
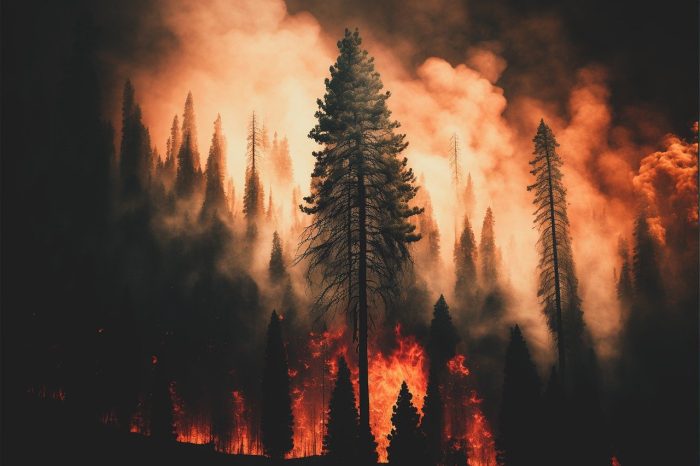
Small particles from the raging wildfires in Los Angeles that have killed residents, destroyed homes and businesses and have caused massive evacuations have crossed the country, reaching Long Island.

“Our instruments are picking up evidence detecting California wildfires already,” said Arthur Sedlacek, III, Aerosol Processes Group leader in the Environmental & Climate Sciences Department at Brookhaven National Laboratory. “What’s happening 3,000 miles away can impact us” just like the fires in Quebec did.
The amount and concentration of particles on Long Island from these particles doesn’t present a health risk to many people in the population.
“For those who are sensitive to inhalation irritation, it opens up the possibility” of developing breathing difficulties or adding particles that could irritate their lungs, Sedlacek continued.
To be sure, the majority of people on Long Island and the east coast may not react to levels of particulates that are considerably lower than for residents of Los Angeles and the surrounding areas.
Local doctors suggested that these particles can trigger a range of health problems for those who are closer to the flames and smoke.
“The general rule is the larger the exposure, the greater the effect,” said Dr. Norman Edelman, a pulmonologist at Stony Brook Medicine.
Researchers have shown that the exposure doesn’t have to be especially high to affect health.
‘We more we look, the more we see that lower and lower doses will have negative effects,” said Edelman.
If and when particulates build in the air where patients with lung challenges live, pulmonologists urge residents to take several steps to protect themselves.
First, they can adjust their medication to respond to a greater health threat.
In addition, they can wear a particle mask, which is not an ordinary surgical mask.
Over time, continued exposure to particulates through pollution, wildfires or other emissions may have a cumulative health effect.

In the South Bronx, about 40 percent of children have asthma, compared with closer to 10 percent for the rest of the country. While genetics may contribute to that level, “we believe it’s because they are exposed to intense, continuous air pollution from motor vehicle traffic,” said Edelman, as cars and trucks on the Cross Bronx Expressway pollute the air in nearby neighborhoods.
The cumulative effect on people with existing disease is more pronounced.
Even when exposure and a lung reaction end, people “don’t quite come back to where [they] started,” said Edelman. “They lose a little bit of lung function.”
Particulates not only can cause damage for people who have chronic lung issues, like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but can also cause problems for people who have other medical challenges.
“We do know that this kind of pollution generates heart attacks in people with heart disease,” said Edelman. “That’s relatively new knowledge.”
A heating cycle
The ongoing fires, which started on Jan. 7 and were exacerbated by the Santa Ana winds of 70 miles per hour, have been consuming everything in their path, throwing a range of particles into the air.
These can include organic particles, black particles, which is akin to something that comes out of the tailpipe of a school bus and all sorts of particles in between, Sedlacek said.
These particles can form condensation nuclei for clouds and water droplets and they can absorb solar radiation and light.
Heating the upper troposphere with particles that absorb radiation alters the typical convention dynamic, in which hot air usually rises and cool air sinks
These changes in convection, which can occur with each of these major wildfires, can affect local air currents and even, in the longer term, broader air circulation patterns.
Sedlacek suggested that some areas in California and in the west may have reduced the use of controlled burns, in part because of the potential for those fires to blaze out of control.
“With the absence of range management and controlled burns to clear out the understory, you don’t have those natural fire breaks that would otherwise exist,” said Sedlacek. “In my opinion, you have to do controlled burns.”
Wildfires, Sedlacek added, are a “natural part of the ecosystem,” returning nutrients that might otherwise be inaccessible to the soil.
Without wildfires or controlled burns, areas can have a build up of understory that grows over the course of decades and that are potentially more dangerous amid a warming planet caused by climate change.
Indeed, recent reports from the Copernicus Climate Change Service indicate that 2024 was the hottest year on record, with temperatures reaching 1.6 degrees Celsius above the average in pre-industrial revolution levels. The Paris Climate Accord aimed to keep the increase from the late 19th century to well below 2 degrees, with an emphasis on a 1.5 degree limit.
The fires themselves have become a part of the climate change cycle, contributing particulates and greenhouse gases to processes that have made each of these events that much worse.
“These fires generate greenhouse gases and aerosol particles in the atmosphere that can then further increase or contribute to a warming of the globe,” said Sedlacek. “We have this positive feedback loop.”
In the climate change community, researchers discuss feedback, which can be positive, pushing an event or trend further in the same direction, or negative, which alters a process.
Sedlacek likens this to driving in a car that’s heading to the right towards the shoulder. In negative feedback, a driver steers the car in the other direction while positive feedback pushes the car further from the road.
Wildfires, which contribute and exacerbate global warming, can push the car towards a ditch, Sedlacek said.
Some scientists have urged efforts to engage in geoengineering, in which researchers propose blocking the sun, which would cause negative feedback.
“That might be a great idea on paper, but I don’t know if you want to play chemistry on a global scale,” said Sedlacek. Considering efforts to reduce solar radiation has merit, he suggested, but requires a closer analysis under controlled circumstances to understand it.
“I sincerely hope that the powers that be will appreciate the importance of what we do to understand” these processes, Sedlacek said. Understanding the models researchers have created can inform decisions.