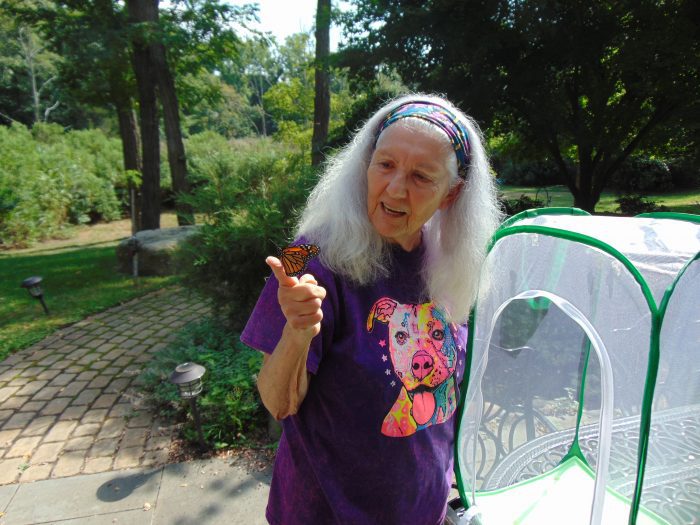
A Stony Brook resident is doing her part to help the ecosystem, one monarch butterfly at a time.

Theresa Germaine knew she had to keep busy when the pandemic shut down practically everything in 2020. Pre-COVID-19, the now 83-year-old traveled frequently, and when she wasn’t making trips, Germaine split her time between New York City and Stony Brook, where she shares a house with her sister.
When everything shut down, the retired educator decided Long Island was the best place to be. Shortly after, she decided to grow milkweed, a flowering perennial plant, in her garden and encourage the growth of the monarch butterfly population. Not only did she attract the butterflies with the milkweed — the only place they will lay their eggs on — she also took their eggs and nurtured them.
“There are so many negative things going on in the world that you have to find some way to make yourself feel good about something,” Germaine said.
The butterflies, distinguished by their orange and black coloring with white spots, have recently been added to The International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species. The environmental network considers the monarchs an endangered species, even though the U.S. itself has not yet added the pollinators to its endangered-species list.

When the pandemic shutdowns struck, Germaine read about the monarch butterflies and how to attract and raise them. This year marked the third year of her garden and, once again, she has been busy looking for the tiny eggs, about the size of a pin, under the milkweed leaves where the butterflies lay them. She then brings them inside her home where she puts the eggs and leaves in a container.
After the eggs hatch, they emerge as caterpillars and are very small. Germaine puts them in mesh butterfly tents bought online along with pieces of milkweed from her garden in tubes to feed them. She has a few of the enclosures to handle each stage, from the caterpillar — larva stage — to pupa, where they form a chrysalis around themselves, and then the emergence of the butterfly.
Germaine said once the monarch butterfly appears, it climbs up the side of the cage and needs time for its wings to dry. Once the monarch begins fluttering around the enclosure, she knows it’s time to release them outside. She brings the enclosure outside and allows the creatures to leave at their will.
“I’ve always kind of been a Girl Scout type of person,” Germaine said. “I was a Girl Scout when I was young, and I always had an interest in nature.”

While she nurtured a dozen of the pollinators in 2020, last year she released 41 and this year so far, 45. She said she estimates that approximately 10 more butterflies will emerge before the summer ends.
Over the last couple of years, Germaine has purchased more milkweed plants, and the perennials have become more robust over time.
A native of the Bronx, she taught in Manhattan for nearly 30 years, and was an assistant principal for two years in the borough. She retired in 1995, and she said she never chose to get married or have children. Germaine said while many her age may be busy with grandchildren; she was keeping herself busy with her travels and entertainment. The raising of the monarchs has been a welcomed activity.
“As you get older, it’s very important that you have a purpose in life,” she said.
Her hope is that everyone will grow a little milkweed in their garden to help the monarchs. She said while it’s not the most attractive plant, even a small garden with the flower in a corner of one’s property can make a difference. While the eggs have a better chance of surviving inside — more than 80% — just having milkweed can increase the monarch butterfly anywhere between 3% to 10%, Germaine said based on her research.
“If everybody did their part, we would see more butterflies,” she said. “And who does not love to see a butterfly?”