By Daniel Dunaief
They don’t always follow the same path with any two sufferers, but people who have migraines can and often do find themselves with symptoms including head pain, discomfort, numbness and nausea that make working, caring for family members or functioning difficult.

Among the first symptoms listed when COVID-19 became a pandemic in 2020, headaches can and have become more severe for people who become infected and then endure additional symptoms in the ensuing weeks and months.
People with migraines often suffer from a throbbing headache, nausea, sensitivity to light and loud noises that worsen with movement.
The other associated features can be “just as disabling as the pain,” said Dr. Noah Rosen, director of the Headache Program for Northwell Health. “Now that we see some of the symptoms cross over with long COVID symptoms, that becomes more salient.”
At this point, amid anecdotal evidence of migraines and long COVID, health care providers can’t say conclusively whether an infection with the current strain of the virus presents any more risk of developing migraines sometime after an infection than they were with earlier strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
“There’s no central reporting of symptoms,” said Dr. Sharon Nachman, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Stony Brook Children’s Hospital. “If you get a vaccine and you have an adverse event, you can report it. There’s no such thing for long COVID.”
Indeed, with people continuing to pass along the virus in schools, workplaces, crowded subways and other places where people gather in confined indoor spaces, the long COVID population has “overtaken any ability to track those symptoms,” Nachman said.
Nachman added that migraines could be a symptom of something else.
“It’s hard to say a true cause and effect” with regard to a particular symptom, as some immune systems may have such a strong response that they are creating autoimmune problems.
Migraines are also seen in patients with autoimmune diseases, Nachman said.
For some patients, doctors may want to do a full immune workup to make sure they are not having an autoimmune reaction.
As for long COVID symptoms, people “across the board” are developing various maladies after contracting the illness that caused the pandemic, Nachman said.
While it’s unclear at this point whether migraines or other specific symptoms increase amid the current strain of long COVID, doctors urged people who have underlying medical conditions to get tested when they develop symptoms.
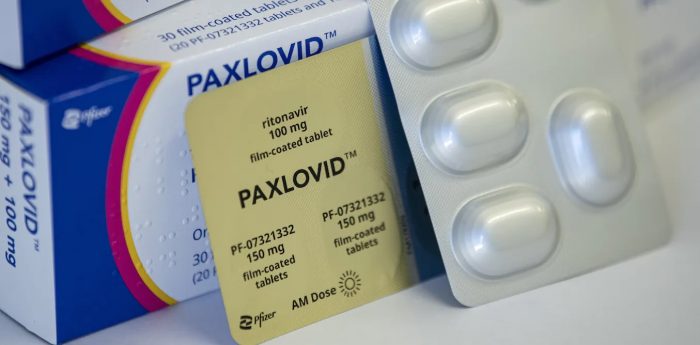
“Fewer people are actually treating the acute phase,” said Rosen. “There was some evidence that early treatment with Paxlovid can reduce the risk of long-term COVID.”
Indeed, people in high-risk groups can lower the chance of dealing with additional symptoms, called sequelae, after an initial infection.
Treatments
While numerous treatments are approved for migraines, it is unclear which might be best for people who develop these extreme and potentially debilitating headaches in the aftermath of COVID.
“Many of the new treatments haven’t been specifically looked at for post-COVID” migraines, said Rosen.
Migraines can become enough of an interruption to daily life that people alter their behaviors in between episodes, during the so-called interictal period.
Even without the pain, migraine sufferers can avoid activities because they are afraid of a trigger.
This can affect people’s social interactions or their job choices, among other decisions.
“If people are noting that they are unable to do things that they were doing before or are avoiding certain tasks, they need to step up in treatment,” said Rosen.
In terms of treating migraines, Rosen suggested that beneficial pharmacological options, such as triptans, have been around since the 1990s.
Triptans are a group of medicines that treat migraines by changing how blood circulates in the brain and how the brain processes pain signals, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Rosen said Imitrex and Maxalt are used to treat migraines during the mild phase.
“Early treatment can lead to shorter symptoms or less medicine being used and less disability,” Rosen said.
The average migraine lasts about four hours. A migraine that lasts more than 72 hours is described as “migrainosis,” which can be disabling and can require a combination of medications.
People can reduce the risk of migraines through some lifestyle modifications, such as ensuring sufficient hydration, not skipping meals, getting regular sleep, avoiding stress or engaging in behaviors that improve resilience to stress, and exercise, Rosen said.
Migraines affect about 12 percent of the population. Additionally, anyone with a migraine has about a 70 percent chance of having a first-degree relative — a parent, sibling or child — who also has migraines, according to Rosen.
Researchers have identified over 40 genes associated with migraines, which makes determining a specific genetic link complex, Rosen said.
With a link between migraines and hormones, women suffer from them at about a three-to-one ratio to men.
Other triggers
Migraine sufferers often try to identify triggers that can bring on these painful and disturbing episodes that can cause fatigue and discomfort even after the episodes end.
Many people are sensitive to environmental changes, like low barometric pressure from storms or excessive changes in temperature.
All of those are increasing amid climate change, which has had a significant effect on migraine sufferers, Rosen said.
Obesity, which is a health issue for the country, can also affect migraines.
“That places an additional burden on the health of people who suffer” from migraines, said Rosen.












 Did you have pets growing up?
Did you have pets growing up? Why did you decide to write a book about your experience?
Why did you decide to write a book about your experience? What was it like for you when the book arrived?
What was it like for you when the book arrived?