Phase 1 of the East Beach Bluff Stabilization was the first part of a $10 million initiative aimed at arresting bluff erosion and preventing the Village of Port Jefferson-owned country club from sliding down the slope.
This first phase of the project was completed in June 2023. By any official accounts of the time, Phase 1 was a success. But within months of completion a series of storms in late 2023 and early 2024 damaged the site, undoing costly work, setting back progress and hampering the goals of the project.
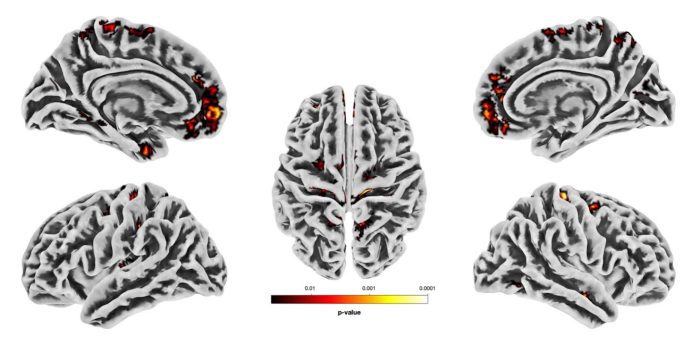
According to the May 2024 Bluff Monitoring Report covering the period from September 2023 to February 2024, conducted by GEI Consultants of Huntington Station (the engineering firm that designed Phase 1), the village had not implemented recommended repairs, increasing the risk of more complicated and expensive upkeep and repair in the future.
The report stated that “no maintenance or repairs to date were undertaken by the village following the storms,” further suggesting that the village implements “necessary repair to the project as soon as possible.”
The report’s findings have raised questions among residents and officials about the long-term viability of the stabilization efforts and financial resources needed for continued upkeep and repairs.
TBR News Media reviewed GEI’s 2024 Bluff Monitoring Report — required under the Department of Environmental Conservation permit for Phase 1 — and spoke to experts, village officials and residents, exploring the report’s recommendations and the obstacles confronting the village in completing its requirements.
Costs of phases 1 and 2
At the completion of Phase 1, a 358-foot wall of steel and cement was constructed at the base of a steep bluff, about 100-feet-tall, situated on East Beach, facing north toward the Long Island Sound.
As part of the project, the severely eroded bluff face — scoured and denuded by years of storms — underwent restoration. Native vegetation was planted and secured with eight rows of timber terraces, and coir logs (interwoven coconut fibers) at the lower section and, toward the crest, with burlap netting.
The total cost of the Phase 1 project according to village treasurer, Stephen Gaffga, is “$6,024,443 million, of which $677,791 is related to design/engineering/permitting/ surveying, and $5,346,652 was spent on construction.”
At the crest of the bluff, approximately 30 feet beyond the precipice, sits the country club. Phase 2 involves the installation of a 545-foot long, 47-foot-deep steel barrier driven into the bluff’s crest, just a few feet seaward of the country club. The barrier is designed to stabilize the area landward of the bluff and prevent erosion, further reducing the risk of the building collapsing.
The cost of Phase 2 will be partially funded by federal taxpayer dollars as a $3.75 million FEMA grant, the final approval recently completed this past week, allowing for the village to receive bids for the work in the coming months for the construction of the upper wall. Local taxpayer dollars will fund the remaining Phase 2 expenses.
According to Gaffga, the Phase 2 “complete expenses are yet to be determined,” he explained in an email. The total cost will be better understood once the village receives bids for constructing the upper wall
The stabilization project, since its inception in 2017 has been presented by village officials as an urgent necessity. With this imperative in mind, the trustees approved a $10 million bond resolution, without a community referendum, in 2021 to fund the project’s two phases.
In a January 2023 statement by former Mayor Garant, after permitting and plans had been finalized, she warned, “If immediate measures to combat and stop the erosion are not implemented, the building foundation will get exposed, will lose structural support, and slowly but surely will fail — causing significant structural damage first, followed by complete collapse of the [country club] building.”
2024 GEI report findings
Heavy rainstorms swept across Long Island in the early fall of 2023, beginning with Hurricane Lee on Sept. 12 followed by another severe storm on Sept. 23.
According to the GEI report, these storms caused “post-storm stress” to the new vegetation leading to plant die off, shifting sands and forming a small ravine — also referred to as a gully — past the western edge of the wall at the base of the bluff.
To prevent further damage, GEI recommended that the village “replant beachgrass in stressed areas of the bluff face and protect the western edge of the wall by adding a filter fabric and stone.”
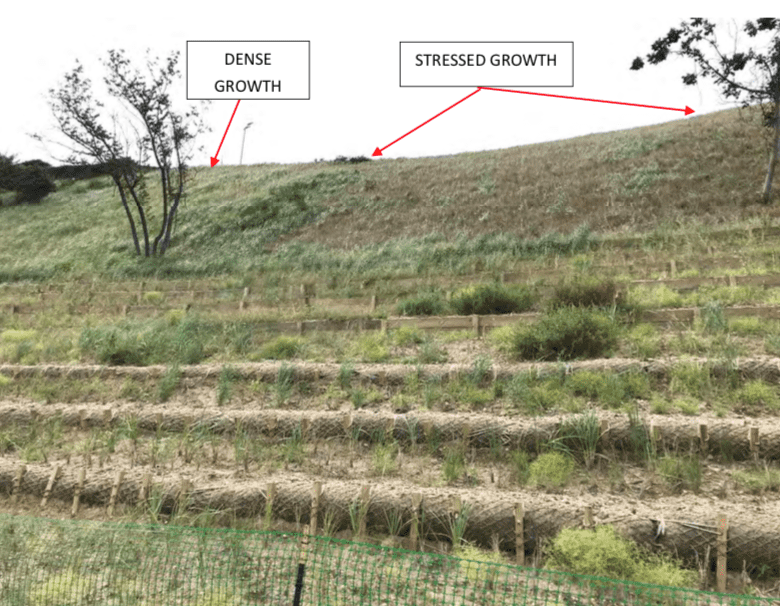

However, two additional major storms in December 2023 and February 2024 brought strong winds and heavy rainfall expanding the damage started in September. A GEI post-storm inspection in the days following the storms found that a large ravine had formed on the eastern edge of the bluff face, further damaging the vegetation, matting and terracing within the ravine.

In total, the May 2024 report outlined detailed recommendations involving improved drainage, repairs to terracing, laying down of erosion control fabric and replacement of beachgrass. The report’s recommendations concluded with concerns about utilizing honeycomb grids by Coastal Technologies Corp. under consideration by village officials, namely: “GEI has expressed concern that such an installation may not be effective at East Beach due to the types of soils present and the steepness of the East Beach Bluff.”
Despite these concerns, the Board of Trustees at the Oct. 23 public meeting approved a resolution to use American Rescue Plan Act funds at the total cost of $33,920 to pilot test Coastal Technologies stabilizing devices, pending a revised permit from the DEC.
In response to GEI concerns, George Thatos, Coastal Technologies co-founder and head of design, said, “Our Cliff Stabilizer system stabilizes near-vertical slopes with vegetation, unlike terracing which requires major regrading and cliff-top land loss.” He added, “Our solution naturally reforests bluffs.”
According to DEC representative, Jeff Wernick, if a permit holder “cannot follow a report recommendations due to environmental conditions, DEC works with them to modify the permit to correct the issues. If the recommendations are not followed due to negligence, it could result in a violation of the permit and enforcement action.”
Port Jeff Citizens Commission on Erosion
This reporter attended a recent meeting of the Port Jefferson Citizens Commission on Erosion. Their mission, in summary, is to act as a volunteer resident advisory group to the village on matters of erosion confronting the village. So far, much of the group’s focus, chaired by village resident David Knauf, has been on the East Beach Bluff Stabilization project.
On Jan. 20, the committee submitted detailed written questions to Mayor Lauren Sheprow expressing concerns about the overall status of the stabilization project. It questioned plans to proceed with Phase 2 before implementing drainage recommendations and before updating the land survey of the upper bluff that is about three years old. The commission urged these steps be completed before soliciting bids for the construction of Phase 2.
”There was damage that occurred since the Phase 1 was completed that hasn’t been addressed, meaning that it keeps getting more pronounced. There were ongoing reports that were done during the past year,” Knauf said at the Jan. 23 commission meeting.
He added that repairs “should have been done up to now so that whatever was occurring [with Phase 1] didn’t get worse.”
The commission, to date, has not received a comprehensive update on maintenance done on the bluff/wall as recommended in the May 2024 report, according to Knauf.
According to village trustee Robert Juliano, any maintenance and repair done during the time frame of the 2024 report “was minor, such as grooming the beach by village employees.”
Other concerns brought up at the meeting included a request to review a retreat plan allegedly completed under former Mayor Garant and actively participating in vetting of contract bids.
Sheprow, present at the meeting, told TBR News Media her responses to the written questions from the commission, reviewed at the Jan. 23 meeting, would be posted on the village website.
“The village will look to enlist the Citizens Commission on Erosion to help facilitate an open forum where GEI will present the Phase 2 project design and a path forward for Phase 1 remediation and restoration,” the mayor said in an email to TBR News Media.
The 2023 Annual Post-Construction Bluff Monitoring Report dated May 2024 and related items can be viewed at the Port Jefferson Village website at: www.portjeff.com/ 206/East-Beach-Bluff.
For earlier reporting by TBR News Media, visit tbrnewsmedia.com and key in “East Beach Bluff Stabilization project.”