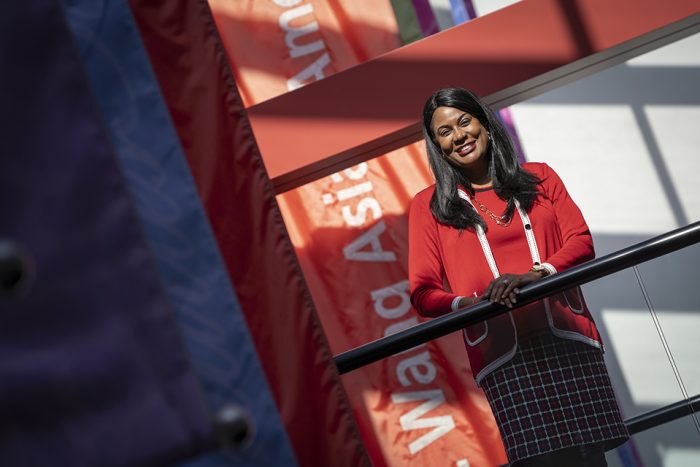
Judith Brown Clarke, a silver medal winner in the 400 meter hurdles at the 1984 Olympics, is taking a prominent role at the National Fitness Foundation.
Clarke, who is vice president for Equity & Inclusion and chief diversity officer at Stony Brook University, will become the chair from 2022 to 2024 of the only non-profit organization established by Congress to support youth sport, health and fitness initiatives. She will serve on the board until 2028.
The White House held a Conference on Hunger, Nutrition and Health on Sept. 28. Clarke said her goal after that conference as chair is to “take that call to action, look at what our role is in lifting some or those things off the page, and improving nutrition and physical activity, food insecurity and ending hunger.”
Tackling a number of challenges, such as the obesity epidemic, access and affordability of healthier foods, the lower rate of participation in youth sports among girls, and a need to increase physical activity will involve working with numerous partners and taking a multi dimensional approach.
“Some of the things that complement what happens at home” such as the expectations in gym class and the overall approach to health and nutrition “need to be strengthened,” Clarke said.
Lower levels of activity among some children stem from concerns about safety. Children may not play in the park, ride a bike, jump rope or go outside because areas where they might engage in these activities could involve some risk.
The foundation will partner with parents, teachers and corporations.
“How often do you find within the ingredients [of popular foods and condiments] where there’s sugar and salt?” she asked rhetorically. Numerous foods have supplemental ingredients that may be for taste, but that are above the daily allowance. People start to crave foods with high levels of salt and sugar.
Working with companies that manufacture food products, the foundation hopes to encourage the kind of decision making that helps their customers and their workers.
“Unhealthy people” who have eating habits that include high levels of carbohydrates, sugar and salt have “higher levels of absenteeism” within a corporation, Clarke said. “It actually is a financial model for organizations and corporations to lean into this. There’s a return on investment as it relates to their organization’s enterprise model.”
Conference pillars
The foundation plans to use the five White House Conference Pillars to guide their efforts and assessment of their effectiveness.
The White House conference is focused on improving food access and affordability. This includes expanding eligibility for an increase participation in food assistance programs and improving transportation to places where food is available.
Another pillar is to integrate nutrition and health. By prioritizing the role of nutrition and food security in overall health, the conference hopes to address the nutrition needs of all people.
The third pillar is to empower consumers to make and have access to healthy choices.
Fourth, officials would like to support physical activity for people, in part by ensuring that people have access to safe places to be active. The conference also hopes to increase the awareness of the benefits of physical activity.
Fifth, the conference plans to improve nutrition metrics, data collection and research to inform nutrition and food security policy, particularly regarding issues of equity, access and disparities.
Xavier Becerra, Health and Human Services secretary, expressed confidence in the ability of the board to reach their goals. “This experienced group of advisors will enable the National Fitness Foundation to take the next steps in advancing the health of our nation through fitness and nutrition,” Becerra said in a statement.
In addition to serving as a role model through her success as an athlete, during which Clarke was a four-time national collegiate champion and 1987 Sports Illustrated Woman of the Year, she also hopes to encourage girls and their families to learn about the benefit of ongoing participation in athletics.
According to the National Fitness Foundation website, 30% of girls aged six to 12 participate in sports, compared with 39% of their male peers.
The foundation supports organizations committed to providing equal opportunity for girls to play sports.
In addition to leading healthy lives, women who participate in sports are often successful in the workplace, taking their disciplined approach to training, their ability to work together, and their recognition for how to handle fluid situations into a wide range of professional settings, Clarke said.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of some of these efforts may depend on the ability of people in communities to access these programs.