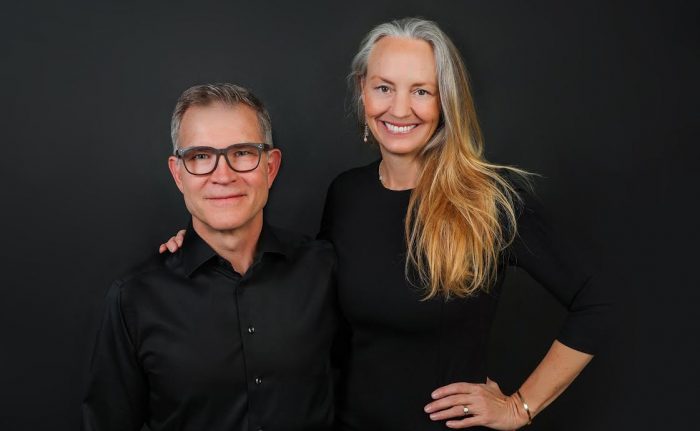
Stony Brook University has announced a philanthropic gift to develop Neuroblox, a software platform developed by biomedical engineer and neuroscientist Lilianne Mujica-Parodi that will model brain circuits to treat brain disorders. The gift was made possible by David Baszucki, founder and chief executive officer of Roblox, and his wife, bestselling author Jan Ellison Baszucki.
Mujica-Parodi took inspiration from Roblox in conceiving Neuroblox as a cutting-edge platform that will open up a world of modeling possibilities for neuroscientists without training in computational sciences. The platform will allow researchers to explore the complexities of brain-based disorders by providing a blueprint for individualized care.
Roblox is an interactive platform that allows users to create their own immersive experiences and release them with one click to smartphones, tablets, desktops, consoles and virtual reality devices. Anyone can use the platform, even those without programming experience.
“Right now, there is a disconnect between the aims of clinical research and the computational tools we have to exploit that research,” said Mujica-Parodi. “Neuroblox is doing something fundamentally different. It’s trying to bridge that gap.”
Brain disorders like bipolar disorder, dementia and schizophrenia impact millions of families who have long struggled to find answers, including the Baszucki family. Jan and David Baszucki reached out to Mujica-Parodi after learning about her first-of-its-kind study exploring the role of ketosis on brain functioning. This was an area of particular significance for the Baszuckis, as it was a ketogenic diet that put their own son’s bipolar disorder into remission.
Fueled by enthusiasm for the potential of this project, Mujica-Parodi quickly assembled a team of the brightest minds in computing, neuroscience, biomedical engineering and beyond to bring the Neuroblox vision to life.
“Here was a neuroscientist unveiling the mechanism by which ketones work to stabilize brain networks,” Jan Ellison Baszucki said. “This explained why a ketogenic diet gave our son his mind and his life back. We had to wonder if building on this knowledge by investing in metabolic neuroscience could be the first step toward helping others suffering from mental illnesses.”
The $6.2 million investment from the Baszucki family includes $3.2 million to help build and launch Neuroblox and $3 million to create the Baszucki Endowed Chair for Metabolic Neuroscience at Stony Brook University. Mujica-Parodi will be the inaugural holder of this chair, which recognizes an exceptional researcher in metabolic neuroscience.
“Lily is building a software platform where neuroscience researchers worldwide can refine, test and share models to help us understand how the brain regulates energy — a critical driver of mental health,” said David Baszucki. “Our family believes Neuroblox’s impact on understanding and treating brain-based disorders, including mental illness, will be transformative.”
The gifts will be enhanced by an additional $550,000 from Stony Brook’s Presidential Innovation and Excellence Fund. This fund is designed specifically to accelerate the university’s highest ambitions.
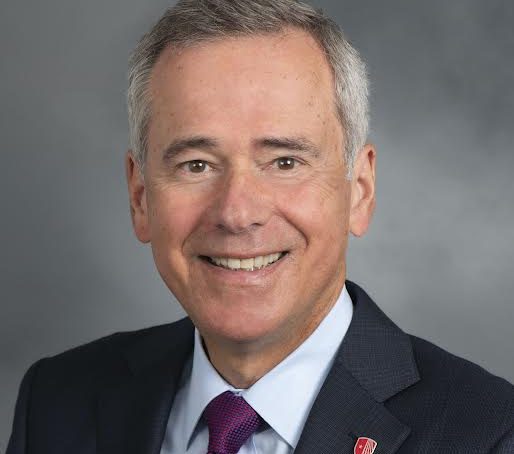
“Lily’s innovative approach to one of our most pressing societal issues — our mental health and well-being — is inspiring. It underscores our commitment as an institution to advance knowledge that will have a long-term, significant impact on the world,” said President Maurie McInnis. “We could not be prouder of these efforts, and we are thrilled that the Baszuckis have chosen to invest in Lily’s trailblazing work in a way that will undoubtedly change lives.”