By Daniel Dunaief
Most of the time, the fungus Candida albicans, which is ubiquitous on the skin, inside people’s mouths, throat, and guts, among other places, doesn’t cause problems. It can, however, be an opportunistic infection, particularly in people who are immunocompromised, leading to serious illness and even death.
Antifungal infections work best during the early stage of an infection. Once a severe infection becomes established, it responds less well to drugs, as resistance can become a problem.
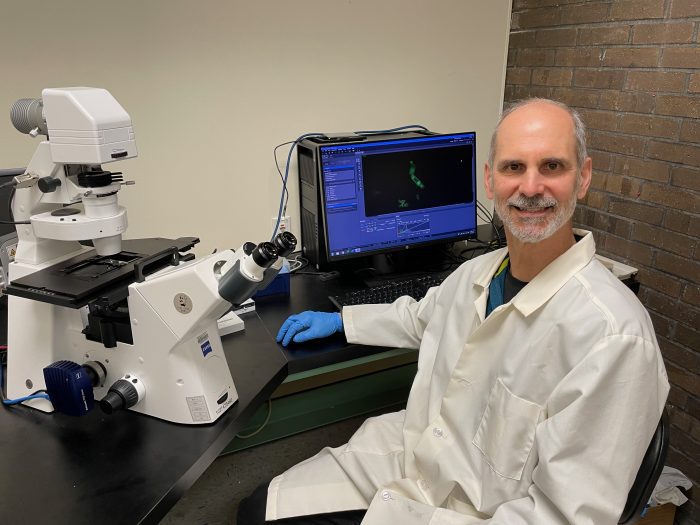
James “Jamie” Konopka, Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology in the Renaissance School of Medicine at Stony Brook University, is working to find the mechanism that enables C. albicans to resist attack by the immune system. His long term goal is to identify ways to make the fungus more vulnerable to immune defenses.
In a paper published recently in the journal mBio, which is published by the American Society of Microbiology, Konopka identified the mechanism by which hypochlorous acid, which is produced by cells in the immune system, attacks C. albicans.
He expanded this by testing forms of the fungus that lack specific genes. These mutants can be more vulnerable to attack by hypochlorous acid, which is produced by neutrophils and is also called “human bleach.” Longer term, Konopka hopes to find ways to sensitize the fungus to this acid, which would bolster the ability of the immune system to respond to an infection.
His study showed that hypochlorous acid disrupts the plasma membrane, which is a layer of lipids that surround the cell. Once this is breached, parts of the cell leak out, while more bleach can damage the fungus.
Hypochlorous acid reacts with proteins, lipids and DNA.
The activated immune system produces several chemicals known as “reactive oxygen species.” In some cells, particularly neutrophils, hydrogen peroxide is converted into hypochlorous acid to strengthen and diversify the attack.
To be sure, the discovery of the mechanism of action of hypochlorous acid won’t lead to an immediate alternative therapeutic option, as researchers need to build on this study.
Future studies will examine how some genes promote resistance, and which are likely to be the most promising targets for drug development, Konopka explained.
Increase sensitivity
Konopka suggested that increasing the sensitivity of the fungus to hypochlorous acid would likely prove more effective and less potentially toxic than increasing the amount of the acid, which could also damage surrounding tissue.
“Our idea is to sensitize fungal pathogens” to hypochlorous acid “rather than upping the dose of bleach, which could lead to negative consequences,” Konopka said. Ideally, he’d like to “take the normal level and make it more effective” in eradicating the fungus.
Other scientists funded by the National Institutes of Health created a set of about 1,000 different strains of the fungus, which provides a valuable resource for Konopka and others in the scientific community.
In a preliminary screen of plasma membrane proteins, Konopka and his team found that most of the mutants had at least a small increase in sensitivity. Some, however, had stronger effects, which will guide future experiments.
One of the challenges in working with a fungus over pathogens like bacteria or viruses is that fungi are more closely related biologically to humans. That means that an approach that might weaken a fungus could have unintended and problematic consequences for a patient.
“Although they may look very different on the outside, the inner workings of fungi and humans are remarkably similar,” Konopka explained in an email. This has made it difficult to find antifungal drugs that are not toxic to humans.
An ‘overlooked’ ally
Konopka suggested that scientists have been studying hydrogen peroxide, which is also made by immune system combatants like macrophages and neutrophils.
“It seemed to us that somehow bleach had been overlooked,” Konopka said. “It hadn’t been studied in the fungal world, so we launched” their research.
Konopka also believes the plasma membrane represents an effective place to focus his efforts on developing new drugs or for making current drugs more effective.
Hydrochlorous acid “fell into our wheel house,” he said. In initial tests, Konopka discovered that human bleach caused damage to the membrane within minutes if not sooner, allowing outside molecules to enter freely, which could kill the potentially dangerous infection.
Considering the ubiquitous presence of the fungus, immunocompromised people who might conquer an infection at any given time could still be vulnerable to a future attack, even after an effective treatment. Even people with a healthy immune system could be reinfected amid a large enough fungal load from a biofilm on a medical device or catheter.
Providing vulnerable people with a prophylactic treatment could lower the risk of infection. When and if those patients develop an ongoing and health-threatening infection, doctors could use another set of drugs, although such options don’t currently exist.
In other work, Konopka has identified proteins in C. albicans that help CoQ, or ubiquinone, protect the plasma membrane from oxidation by agents such as hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorous acid.
People can purchase ubiquinone at local stores, although Konopka urges residents to check with their doctors before taking any supplement.
Fish and beer
An organizer of a department wide Oktoberfest, Konopka was pleased that faculty, post doctoral researchers and students were able to decompress and enjoy the fall festival together for the first time since 2019.
In addition to a range of beer, attendees at the event, which occurred half way between the start of the semester and final exams, were able to partake in German food from Schnitzels in Stony Brook Village, which was a big hit.
An avid fly fisherman who catches and releases fish, Konopka said he caught some bigger striped bass this year than in previous years.
When he’s fishing, Konopka appreciates the way the natural world is interconnected. He pays attention to variables like the weather, water temperature, bait fish and the phases of the moon.
He particularly enjoys the wind and fresh air. This year, Konopka marveled at the sight of a bald eagle.
As for his work, Konopka said basic research may have an immediate effect or may contribute longer term to helping others in the scientific community build on his results, which could lead to the next breakthrough.