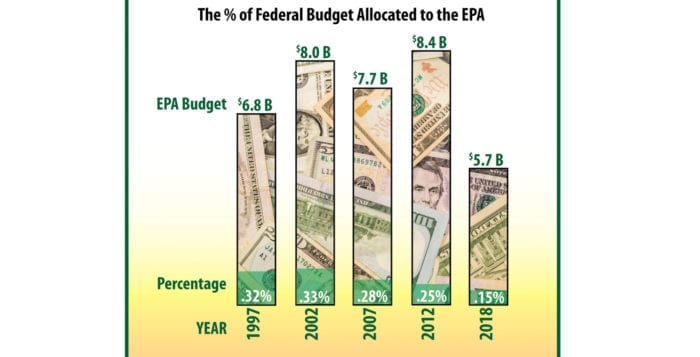
Sills Gully Beach, Shoreham:
Sills Gully Beach in Shoreham is a prime example of erosion due to storm events, according to Brookhaven Councilwoman Jane Bonner (C-Rocky Point). “When you harden the shoreline by constructing hundreds of linear feet of vertical retaining walls or bulkheads, you create a condition where the energy stored in the waves caused by tidal surge and storm events hits up against the hardening structure and reflects back to the Sound,” Bonner said. “These reflected waves cause scour at the base of the bulkhead and a loss of sand from the beach. To minimize this impact, both the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation and the town require armor stone, big rocks, in front of any bulkhead to dissipate the reflected wave surge, reducing the impact that bulkheads have on the beaches.” According to the councilwoman, bulkheads that were constructed in the past “increased the rate of erosion but also separated the beach from its natural sand source.” The practice led to either a narrow or non-existing beach during high tide. With recent changes of bulkheads being moved landward or reducing their elevations, plus the installation of armor stones, erosive impacts have been reduced, and “the beaches tend to be wider and more resilient to storm events.”

Port Jefferson Village:
Port Jefferson was originally known as Drowned Meadow because the area that now comprises most of the commercial district was a marsh that flooded every high tide, according to the book “Images of America: Port Jefferson,” written by Port Jefferson library staffers Robert Maggio and Earlene O’Hare. They wrote, “That flooding, and the steep hills and deep ravines that surrounded the marsh, made farming difficult, and the village grew slowly. In fact, by 1800, there were only a handful of houses.”

Setauket Harbor:
In the last decade, Shore Road along Setauket Harbor has flooded approximately a half a dozen times a year, which is more than in the past due to astronomical tides. “All coastal communities will be increasingly impacted by rising sea level, and sea level rise goes hand in hand with climate change,” George Hoffman of the Setauket Harbor Task Force said. “One way to identify the areas that will be impacted is to look at the areas that are now impacted by storms and astronomical tides. All the low-level shore areas in the Three Village community are the most vulnerable. And, they tend to be the areas that we like to go down to, along the shore, such as beaches and docks and harbor areas. It is projected that in the next hundred years as sea level continues to rise that we will see portions of Route 25A flooding during storm events that we haven’t seen before.”

Nissequogue River, Smithtown:
According to Jan Porinchak, educator and naturalist, the Nissequogue River watershed would be threatened by rising sea levels due to climate change. The river consists of two main branches that start near the southern boundaries of the town in Hauppauge, and then the water flows into the Sound. “Rising sea levels will drown out the native marsh grasses which dissipate wave action and anchor the sediments comprising the shoreline,” Porinchak said. “With the marsh grasses such as Spartina removed, areas further inland would be threatened with shoreline loss from erosion.” Erosion can also have a negative impact on marine species. “With rising sea levels compromising marsh land vegetation, salt water can reach the roots of non-salt-tolerant woody plants further inland, which kills those plant species,” he said. “This creates a domino effect, resulting in yet more erosion when the roots of those plants are eliminated. Increased sediment from these eroded areas will wash into the Nissequogue and similar ecosystems. This sediment can negatively impact shellfish and other marine species, and fuel algae blooms to the widespread detriment of the marine food web.”

Long Beach, Smithtown:
Visitors to Smithtown’s Long Beach, a narrow land spit, will find an artificial berm to keep stormwater out during the winter. Many of the private roads slightly east of the town beach experience flooding when it’s high tide. Larry Swanson, interim dean of the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences at Stony Brook University, said the cause of the problem is the disruption of sediment due to a combination of rising sea levels and homeowners building sea walls to protect their property. “Long Beach is a spit that needs sediment supplied from the erosion of the bluffs of Nissequogue,” he said. “There are places where the supply is somewhat diminished to maintain sufficient elevation, perhaps where currents are stronger than elsewhere water can overflow.”

Asharoken, Huntington:
The incorporated village of Asharoken in the Town of Huntington provides the only essential land access way contacting the Eaton’s Neck peninsula to Northport, with its Asharoken Avenue. Due to hurricanes and nor’easters, the Long Island Sound side of the peninsula has experienced moderate to severe beach erosion. In 2015 the Asharoken village board took into consideration a U.S. Army Corps of Engineers-backed proposal to replenish the community’s eroding beaches. The plan consisted of creating a berm and dune system with groins on the northwestern end of the project area. The area includes properties on the Long Island Sound side of Asharoken Avenue. However, in January Asharoken officials voted to bring an end to the restoration project after many residents rejected part of the plan that included creating public access points at certain private properties, which would leave residents liable for any injuries or mishaps that happened when the public was on the shoreline of the property.