By Daniel Dunaief
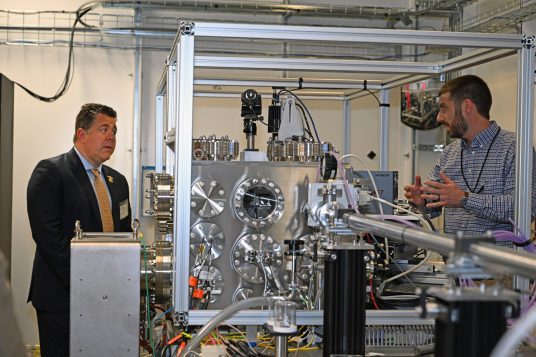
With support from state political leaders and the federal government, Brookhaven National Laboratory is continuing to move forward with its ambitious plans to build the Electron-Ion Collider.
Designed to study strong forces inside the atom, the EIC is set to receive $97.9 million from the federal government as a part of a budget that passed last month.
In addition, the Department of Energy Under Secretary for Science and Innovation approved Critical Decision 3A, which gives the project the formal approval to purchase long-lead procurements such as equipment, services, and materials.
“Passing this milestone and getting these procurements underway will help us achieve our ultimate goal of efficiently delivering a unique high-energy, high-luminosity polarized beam electron-ion collider that will be one of the most challenging and exciting accelerator complexes every built,” EIC Project Director Jim Yeck said in a statement.
Buying materials and equipment for the accelerator, detector, and infrastructure before construction will help the team that includes a partnership with Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility in Virginia adjust for any supply chain issues and work out technical details and challenges.
The government approval will allow for the purchase of about $90 million in superconducting wires and materials for making magnets, cryogenic equipment for superconducting accelerator devices, substations, new power supply and other specialized parts.
The funding for these purchases will come, in part, from the Inflation Reduction Act money awarded to the EIC in 2022 to stimulate economic development and through annual appropriations funding from the DOE Office of Science.
Applications
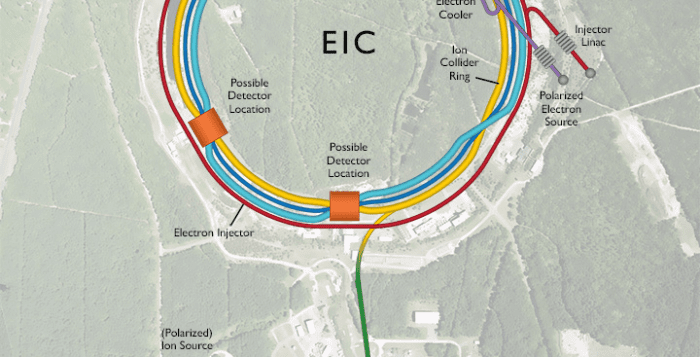
Scientists expect the work at the accelerator, which will include a first of its kind 2.4 mile circumference particle collider, to have applications in a wide range of fields, from nuclear physics, to medicine, to energy and national defense.
The work could also help with the study of simulated space radiation that could protect future astronauts. The completion of the EIC could dovetail with upcoming National Aeronautics and Space Administration efforts to send astronauts to Mars in the 2030s.
The collider and the work that leads up to its construction, which is expected to cost between $1.7 billion and $2.8 billion and be completed in the next decade, will provide educational and workforce development opportunities to train experts in a range of fields.
Political support
In addition to government approval to purchase services and equipment from the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, BNL also received funds earmarked for the EIC from the recent federal budget.
With bi-partisan support of politicians including Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D) and U.S. Rep. Nick LaLota (R-NY1), the recent budget includes $97.9 million for the collider, $95 million of which will support construction and $2.9 million for other projected costs.
“We appreciate the continued support of Congressman LaLota, Senator Schumer and the entire New York delegation for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science and Brookhaven National Laboratory,” Lab Director JoAnne Hewett explained in an email. “These funds will support staff working on the EIC project design and developing a baseline schedule and funding profile, allowing us to better plan the future transition of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and its workforce to this new, world-class facility.”
In building the EIC, BNL staff will use infrastructure from RHIC. The majority of EIC accelerator components are designed to fit within the existing RHIC tunnel, and will reuse key infrastructure.
“It’s important that members of Congress use their positions to advocate for important projects and spending in their districts,” LaLota said in an interview. Though he’s a freshman Congressman who was elected in 2022, taking over the seat previously held by Lee Zeldin (R-NY1), LaLota appreciates the support Republican leadership provided during appropriations.
LaLota said procuring the funding “wasn’t easy” given the competitive nature of government spending.
LaLota, who plans to visit BNL every four or five months to receive updates, urges sustained federal government investment in the collider and infrastructure.
BNL provides a “vital role in high quality employment” for Long Islanders, he added.
Long Island will benefit from the EIC in the short term through construction jobs, infrastructure employment and the various applications of research on site to areas including military and commercial applications, the congressman added.
Through taxpayer funding, BNL helps ensure a “stronger military and economy,” LaLota said.
During his visits to the DOE lab, LaLota spoke with Hewett, whom he describes as a “steady hand” who serves as a “real conduit between the lab and Congress” advocating for the lab’s needs.
Solar cells
BNL conducts research in a range of fields, including Energy & Photon Sciences, Environment, Biology, Nuclear Science & Nonproliferation, Computational Sciences, Nuclear & Particle Science and Advanced Technology Research.
LaLota describes himself as an “all-of-the-above energy Republican,” who supports alternative resources, such as the ones BNL scientists are developing and enhancing.
Homeownership problem
Apart from BNL, LaLota addressed broader questions, including the challenge of homeownership for New York residents.
New York has the “dubious distinction of having the highest effective tax rate” when combining property, sales and income taxes, which has led to the highest out of state migration, LaLota said.
Without a better tax policy, New York will continue to hemorrhage people to places like the Carolinas and Florida, he predicted.
“Most of that starts in Albany,” LaLota said. “I would encourage my friends in Albany to figure that out and make life more affordable” by increasing state and local tax deductions.
As for the ability of Speaker of the House Mike Johnson (R-LA) to continue in a role some Republicans are prepared to challenge, LaLota suggested the speaker should play “every game like it’s his last.”
LaLota added that Johnson should “smartly move forward funding the government, as he has,” and “smartly move forward on funding of military aid overseas.”