SBU News: Biochemist Benjamin Martin receives MIRA Award
Benjamin Martin, PhD, Associate Professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology at Stony Brook University, and member of the Stony Brook University Cancer Center, has received a $2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) to conduct research to understand the molecular and cell biology of neuromesodermal progenitors. The grant term, effective June 1, 2023, is five years.
The Martin Lab uses zebrafish embryos as a model system. The grant enables Martin and colleagues to carry out research designed to more clearly define and observe neuromesodermal progenitors, stem cells that contribute to spinal cord or skeletal muscle development. The overall goal of the lab is to advance an understanding of the vertebrate body plan via the zebrafish embryos and provide insights to understand stem cell biology and mechanisms of cancer metastasis.
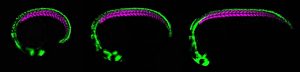
Martin and colleagues observe zebrafish to demonstrate how differentiated neurons and muscle expand as embryos grow. Neuromesodermal progenitors exist in all vertebrate embryos, so zebrafish are used as a common model to these cells’ development to better define how the embryonic body plan is formed and how spinal cord and skeletal muscle are induced from this population.
Martin’s NIGMS grant is called the Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award (MIRA), under the category of supporting established scientific investigators. This distinction recognizes the importance of the lab’s research, and reinforces their efforts to reach a breakthrough in this area of cell biology.
NIGMS supports fundamental studies that shed light on biological processes and catalyze advancements in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases. It also leads efforts to train the next generation of scientists, promote diversity in the workforce, and expand research capacity nationwide.







