By Daniel Dunaief
Jim and Marilyn Simons put their money where their mind is.
The power Stony Brook University couple, who were already legends around campus for their intellectual and financial gifts to the university, outdid themselves and everyone else this year with their academic generosity — not to mention their busy travel schedule.
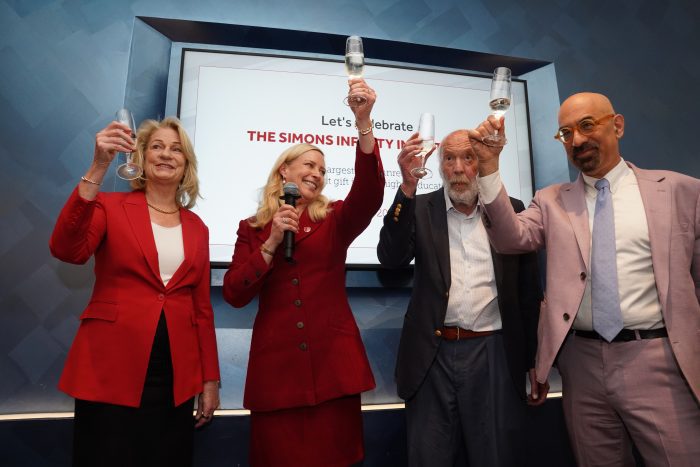
Through the Simons Foundation, the power couple contributed $500 million over seven years to Stony Brook University’s endowment, the largest unrestricted endowment gift to a higher education institution in American history.
The gift, announced in June, followed just a month after the Simons Foundation announced a $100 million contribution to Stony Brook University’s successful bid to develop Governors Island into a climate solutions center.
When the Simons Foundation announced the endowment gift, Lawrence Martin, professor in the Department of Anthropology and director of the Turkana Basin Institute, used a word echoed by many around campus to describe its impact: “transformative.”
For philanthropy that not only makes it possible for academic dreams — particularly among those who are first-generation college students — to become reality, but also that inspires meaningful contributions from other donors, TBR News Media is pleased to recognize the Simonses as 2023 People of the Year.
A significant victory
While the $500 million gift set records and offered financial fuel for an encouraging academic future, the victory in the competition to run a climate center on Governors Island positions Stony Brook to make meaningful contributions to the future of the planet.
Competing against other established universities with a depth of talent and breadth of ideas, including Northeastern University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a group co-led by CUNY and the New School, Stony Brook emerged as the winner for a climate exchange designed to advance research, innovation, sustainability, climate justice and outreach.
The $100 million in support from the Simons Foundation, coupled with $50 million from Bloomberg Philanthropies, “demonstrated the seriousness of Stony Brook’s proposal,” said Kevin Reed, associate provost for climate and sustainability programming and professor at the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences. The partnership “helped us get over the finish line” and was a “game changer for us.”
The initial support from the Simons Center is “opening doors as we continue to fundraise to build the center,” said Reed.
In its history, Stony Brook has helped address and solve challenges in New York as a public institution, Reed suggested. Becoming a flagship university for the state and with the support of the Simons Foundation, Stony Brook has opportunities to demonstrate leadership nationally and internationally, Reed added.
In addition to the climate exchange, Stony Brook will provide students with opportunities for internships that tap into public health, engineering and other interdisciplinary areas, which “came through in our proposal,” Reed added.
Multiplier effect
As for the $500 million donation, Jim and Marilyn Simons have not only stepped in to ensure the current and future academic strength and range of opportunities for faculty, students and the community, but they have also encouraged and inspired other donors.
With support from a program championed by Gov. Kathy Hochul (D) and the Simons gift, donors can triple the effect of their contributions.
Long-term contributors to the university have stepped up this year.
The Simons donation, which has eclipsed what others have done, “encourages the rest of us to keep giving,” said Cary Staller, member of the Board of Trustees of the Stony Brook Foundation and of the SUNY Board of Trustees. “We can see the difference that Jim and Marilyn’s philanthropy has brought about at Stony Brook. It changed the culture.”
Staller has contributed $500,000 this year to the Staller Center Endowment. Staller, whose father donated $1.8 million in 1988 and whose family has contributed over $16 million, said he is talking to other family members about adding to their contributions.
Among the earlier and more noteworthy contributors to the university, the Staller family helped establish a pattern of supporting the Long Island institution.
“When we first gave money to Stony Brook to endow the Staller Center, it really raised a lot of eyebrows among folks,” said Staller. When they made their donation, the Stallers felt “Stony Brook was a preeminent institution that was worthy of support.”
The effect of the Simonses’ support has “eclipsed not only what we’ve done, but really what all of Stony Brook supporters have done,” said Staller.
Staller suggested previous contributions from the Simonses also made it possible to put together the Governors Island proposal.
Jim and Marilyn Simons helped create a Presidential Innovation and Excellence Fund, for which they pledged $25 million. They planned to match another $25 million for that fund, with donor matches that brought the total to $75 million.
“It’s incredible what that money has done,” said Staller, which includes supporting the Governors Island bid. “Those sorts of things cost real money, which is hard to find in a state system,” Staller added. “This allows Stony Brook to really achieve excellence.”
The givers that keep on giving
Stony Brook’s Advancement team recognizes that the couple represents an unusual gift that has kept on giving — to the tune of over $1.2 billion and counting.
“When I talk to my colleagues around the country in similar roles, they are frankly blown away by a philanthropist that has given a gift for the future institution” without any requirements about how the university or future presidents use the funds, said Justin Fincher, vice president for advancement and executive director of the Stony Brook Foundation. The contribution is “something that builds over time” that supports future leadership and demonstrates trust in the institution.
The contribution has “instantaneously raised our profile across the country,” said Fincher. The gift has “made a huge splash” with an instant boost to the school’s reputation.
Jed Shivers, senior vice president for finance and administration, suggested that “a lot of cylinders are starting to fire in synchrony right now.”
Shivers described the $500 million donation as a “seminal” moment for the university, reflecting the confidence the couple has in SBU President Maurie McInnis and the current administration.
This excitement has built throughout the university, with potential high-level recruits showing enthusiasm for a college system on the rise.
In a conversation with Kathleen McGary, the Thomas Muench endowed chair for economics, Shivers said McGary, who joined the university in June, was “extremely excited to come here. At a faculty level, the university has been very successful at recruiting high-quality deans, chairs and faculty.”
Carl Lejuez, provost at SBU, said the university hired seven deans last year, with most of them coming from the Association of American University, or AAU, top public flagship universities.
“Leaders who have strong vision want to come here,” Lejuez said.
These new recruits have helped build the sense of the university providing strong value, with many students who are in the bottom 20% in income when they enter rising to the top 20 percent in the years after graduating.
Hungry minds
Jim and Marilyn Simons do so much more than cutting checks, boosting the profile of the university and supporting its application for marquee projects. The couple is a visible presence wherever the Stony Brook University flag flies.
This year, Jim and Marilyn Simons attended a memorial conference on campus for the late famed paleoanthropologist Richard Leakey. Arriving early and chatting with McInnis and National Geographic Society CEO Jill Tiefenthaler, Jim and Marilyn Simons listened to several lectures, including a well-attended presentation by Louise Leakey, Richard’s daughter and director of public education and outreach for the Turkana Basin Institute and a research professor in the Department of Anthropology at Stony Brook University.
The Simonses “cannot get enough of learning about new things,” said Martin.
Martin highlighted their commitment to learning with an anecdote about a trip Jim and Marilyn made to Kenya earlier this year to honor Leakey.
While they were traveling in the Suguta Valley, which is one of the hottest places on Earth, one of the helicopters needed a spare part. Left in an area with no shade and that can reach over 130 degrees Fahrenheit, Jim and Marilyn Simons “decided to climb a hill to get a better view,” Martin recalled.
Later, while they were waiting for the rest of the group, they had a chance to rest. They had no interest in sitting and waiting, taking a walk with a geologist, where they learned about the geology of the Turkana Basin.
Lejuez suggested that the contributions from the Simons family will “likely have an impact for years to come,” helping to make Stony Brook a first choice university for prospective students.
Stony Brook hopes to reach the same echelon as successful and well-known public universities, such as the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the University of Michigan, and several of the public universities in California, such as UCLA.
Shivers added that the contributions from Jim and Marilyn Simons speak volumes to other donors and investors.
“What better endorsement than to have one of the world’s greatest investors invest in Stony Brook University,” said Shivers.