By Rich Acritelli
It was 156 years ago this month, that after four long years of war, the confederacy was on the brink of destruction. For most of this time, Gen. Robert E. Lee’s Army of Northern Virginia operated with far less men and materials to oppose the Union.
Through decisive leadership, he stymied the union at every turn, invaded Maryland in 1862, Pennsylvania in 1863, and his cavalry operated extremely close to Washington, D.C., in the summer of 1864 — where they were within sight of the capitol building. The Confederates kept fighting, with the outside hope of securing a peace that would not end slavery or curb their state’s rights.
At the helm of the union leadership was President Abraham Lincoln (R) who continually agonized over the ferocity of the fighting and the extreme losses of all-American soldiers. He desperately wanted to end this carnage, but not until the south was defeated, the northern soldiers continued to fight to preserve the union and end slavery.
Right up until the election of 1864, Lincoln and his closest allies were concerned that this president was vulnerable to losing to democratic opponent General George B. McClellan, who was also the former commanding general of all northern armies.
Union citizens were not sure of McClellan’s plan if he won this election, in the type of peace that would be accepted with the south and the fate of slavery.
But the end was near when Lincoln promoted Ulysses S. Grant to the rank of Lieutenant General and the overall commander of all union forces within March of 1864.
Grant was the most successful fighting figure within the entire nation, and he was the first person since George Washington to be permanently given this rank. Up until Petersburg and Richmond fell in early April 1865, Grant waged an unrelenting war against the confederacy.
Grant never wanted to hold territory; his armies were expected to constantly pursue the confederate forces that operated against the Union. From 1864 to 1865, Grant’s strategy of “Total War” brought the confederacy to an end. Although he had taken heavy losses and was called a “Butcher,” Grant’s plans paid heavy dividends against an enemy that was completely unable to match the union strength in men, resources, and money that also caused them to be exhausted from the fighting.
By the spring of 1865, the confederates were reeling from the warfare in the wilderness and were forced to guard the heavy fortifications that were in front of Petersburg and Richmond. Gen. William T. Sherman took over Atlanta in the summer of 1864, by that Christmas, he took Savannah, and moved up the coastline.
His men destroyed everything that was in their path and brought the war to the people of South Carolina that widely supported the firing against Fort Sumter in 1861. At no point were the con-federates able to stop the determination of Sherman that squeezed the southern soldiers through the Carolinas, where he planned to reinforce Grant in Virginia. Both generals and their massive armies expected to fight and defeat Lee.
 Grant promoted Gen. “Little Phil” Sheridan to run the Army of Shenandoah Valley. For too long, the massive resources of this part of Virginia were used to feed Lee’s forces. Through the tenacity of Sheridan and his men, he carried out the will of Grant who stated that he did not want a “Crow” to fly over these productive lands. Sheridan vehemently fought Confederate Gen. Jubal Early that wreaked havoc on the Union homes and resources that were near Washington, D.C. and Maryland.
Grant promoted Gen. “Little Phil” Sheridan to run the Army of Shenandoah Valley. For too long, the massive resources of this part of Virginia were used to feed Lee’s forces. Through the tenacity of Sheridan and his men, he carried out the will of Grant who stated that he did not want a “Crow” to fly over these productive lands. Sheridan vehemently fought Confederate Gen. Jubal Early that wreaked havoc on the Union homes and resources that were near Washington, D.C. and Maryland.
That December, Virginian Gen. George Thomas who remained loyal to the Union was always seen as a slow figure, but when he finally moved, he hit like a “Sledgehammer.” His command was almost fired by Grant who believed that Thomas waited too long to oppose the confederacy under Lt. Gen. John Bell Hood that threatened the Tennessee city of Nashville.
Lincoln was concerned about this state being overrun by the confederates and Grant worried that if Thomas did not halt this movement, Hood would push his men toward the Ohio River. Over two days on Dec. 15 and 16, Thomas smashed this southern army that retreated back into Mississippi. As a result of this battle, Thomas demonstrated his decisiveness as a fighting general through his re-solve in soundly defeating Hood.
By the early spring of 1865, it was Grant’s turn to change the tide of the fighting in Virginia. It was a painfully slow process for Grant to overrun the positions that were well fortified and held by Lee. At this final stage in the war, Grant completely extended his lines in front of Richmond and Petersburg. Lee’s men were still willing to fight, but they were unable to fill in their lines with fresh soldiers, as many men were starving and deserting in large numbers.
Many of these men understood that the confederacy was on the brink of defeat through the successes of Sherman, Sheridan, and Thomas. With scarce food for the residents of Petersburg and Richmond and Lee unable to secure enough feed for his horses that were to weak to pull artillery pieces, Grant was confident that the end of this conflict was imminent.
At this stage in the war, Grant invited the president to leave the politics of the capitol, and to visit the union headquartered at City Point, VA. Lincoln spoke to soldiers, visited the wounded, rode horses with Grant and told stories around nightly fires. Although both men barely personally knew each other, Lincoln’s trust in Grant far surpassed any other general in the union.
They had a good deal in common, where Grant and Lincoln both lived difficult lives that saw failure, were from the mid-west, and they wanted the quickest way to win this war. Lincoln appreciated the honesty of Grant, his tenacity to fight Lee, and the battlefield success that Grant achieved that helped the president win his re-election against McClellan.
After four years of setbacks, Lincoln was on the cusp of victory by one of the strongest armies in American history that the nation ever mobilized.
After the union victory at Five Forks, Virginia, Grant ordered Sheridan to assault the right flank of Lee, and to operate within the rear of Confederate forces to end this 292-day military siege to take Petersburg. By April 2, 1865, Grant ordered assaults across the entire southern lines that penetrated the defenses of the confederates and made progress towards Petersburg and Richmond.
 In a matter of days, Lee lost 10,000 soldiers that were killed, wounded and captured. As the union moved forward, the valuable railroads from Petersburg were cut off from Richmond. In a matter of moments, the trenches that were firmly held by the confederates, were empty, and in full retreat. As these two notable southern cities were about to be captured, Lee warned Confederate President Jefferson Davis that Richmond would only be held for a couple of hours and that the government had to flee, or it would be taken by Grant.
In a matter of days, Lee lost 10,000 soldiers that were killed, wounded and captured. As the union moved forward, the valuable railroads from Petersburg were cut off from Richmond. In a matter of moments, the trenches that were firmly held by the confederates, were empty, and in full retreat. As these two notable southern cities were about to be captured, Lee warned Confederate President Jefferson Davis that Richmond would only be held for a couple of hours and that the government had to flee, or it would be taken by Grant.
It was only four years before Richmond fell to Grant that he was a private citizen in Galena, Illinois. Since he left the army under the threat of a court martial due to heavy drinking on duty in 1854, Grant struggled to earn a living for his family.
Once the war began, he quietly stated that any person that opposed the union was treasonous against the government. While Grant is perhaps the finest general to lead American armies, when the war started, he was refused a commission back into the regular army under McClellan. Illinois Governor Richard Yates presented Grant with the last of four colonel positions to lead a volunteer regiment.
Quickly, Grant understood that the only way to win this war was to insensately fight the confederates. He captured enemy armies at Fort Donelson in February 1862, Vicksburg in July 1863, and narrowly missed the destruction of General Braxton Bragg at Chattanooga at Thanksgiving of 1863.
As Lee was a respected general, he never captured any union armies. But Grant captured three confederate armies, the last being at Appomattox Courthouse on April 9, 1865.
This unassuming American, that was a farmer, a storekeeper, a seller of firewood, and a veteran of the United States-Mexico War was the most important weapon that Lincoln had at his disposal to preserve the Union and end slavery.
It was at this moment many years ago that Lincoln received word that Petersburg and Richmond fell and that the Union would be preserved due to the support of Grant and his armies.
Rocky Point students Sean Hamilton and Zachary Gentile helped contributed to
this story.
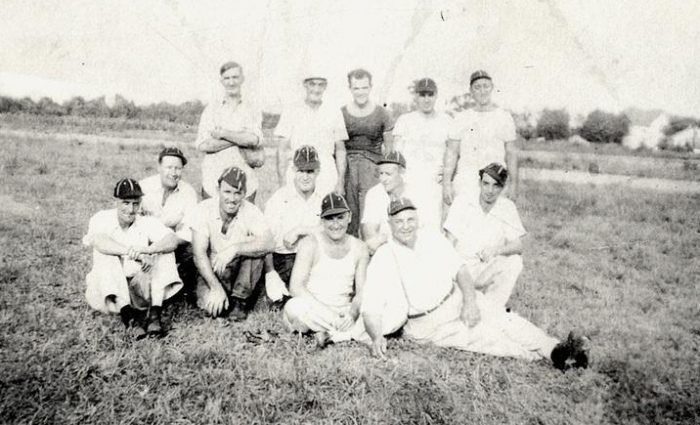



 If you can identify any of these players, please reach out to the local history team at Middle Country Public Library at
If you can identify any of these players, please reach out to the local history team at Middle Country Public Library at 
 Grant promoted Gen. “Little Phil” Sheridan to run the Army of Shenandoah Valley. For too long, the massive resources of this part of Virginia were used to feed Lee’s forces. Through the tenacity of Sheridan and his men, he carried out the will of Grant who stated that he did not want a “Crow” to fly over these productive lands. Sheridan vehemently fought Confederate Gen. Jubal Early that wreaked havoc on the Union homes and resources that were near Washington, D.C. and Maryland.
Grant promoted Gen. “Little Phil” Sheridan to run the Army of Shenandoah Valley. For too long, the massive resources of this part of Virginia were used to feed Lee’s forces. Through the tenacity of Sheridan and his men, he carried out the will of Grant who stated that he did not want a “Crow” to fly over these productive lands. Sheridan vehemently fought Confederate Gen. Jubal Early that wreaked havoc on the Union homes and resources that were near Washington, D.C. and Maryland. In a matter of days, Lee lost 10,000 soldiers that were killed, wounded and captured. As the union moved forward, the valuable railroads from Petersburg were cut off from Richmond. In a matter of moments, the trenches that were firmly held by the confederates, were empty, and in full retreat. As these two notable southern cities were about to be captured, Lee warned Confederate President Jefferson Davis that Richmond would only be held for a couple of hours and that the government had to flee, or it would be taken by Grant.
In a matter of days, Lee lost 10,000 soldiers that were killed, wounded and captured. As the union moved forward, the valuable railroads from Petersburg were cut off from Richmond. In a matter of moments, the trenches that were firmly held by the confederates, were empty, and in full retreat. As these two notable southern cities were about to be captured, Lee warned Confederate President Jefferson Davis that Richmond would only be held for a couple of hours and that the government had to flee, or it would be taken by Grant.
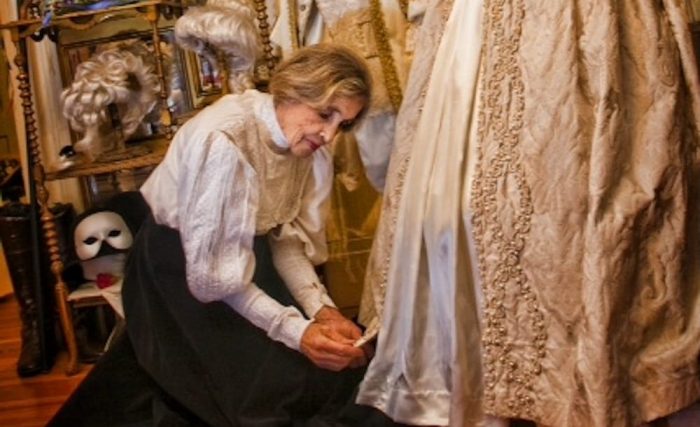


 Nan left an incredible impact on so many, but to me, she was an unlikely friend and unforgettable mentor and confidant. Despite an age difference of some 60 years, our lives were wonderfully intertwined. We first met when she costumed me at just 10 years old as a Dickensian pickpocket for the Village of Port Jefferson’s annual Charles Dickens Festival. By chance, her son and his family had bought my childhood home which brought both of us great joy.
Nan left an incredible impact on so many, but to me, she was an unlikely friend and unforgettable mentor and confidant. Despite an age difference of some 60 years, our lives were wonderfully intertwined. We first met when she costumed me at just 10 years old as a Dickensian pickpocket for the Village of Port Jefferson’s annual Charles Dickens Festival. By chance, her son and his family had bought my childhood home which brought both of us great joy.