The Village of Port Jefferson is nearing a crossroads.
Residents will enter the polls this Tuesday, June 20, to decide on a successor to Mayor Margot Garant. After 14 years leading the administration, the incumbent is stepping down to head the Democratic ticket for Town of Brookhaven supervisor against Deputy Supervisor Dan Panico (R-Manorville).
Garant’s seat is being contested by Deputy Mayor Kathianne Snaden and trustee Lauren Sheprow. In an exclusive office debate spanning nearly two and a half hours, the mayoral candidates pitched their respective visions to the voters.
Introductions
Defeated by just four votes in her first bid for trustee in 2018, Snaden won election to the board the following year and has since secured several liaison posts before taking over as deputy mayor in 2021.
She said she first ran for office “to be the voice” of the people, bringing their wishes to Village Hall and putting their priorities into action.
“I am ready to run for mayor because I want to use all of that institutional knowledge, all of my experience, to do even more for the community,” she said.
Sheprow entered the board 10 months ago, unseating former trustee Bruce Miller during last year’s village election. She has since helped establish multiple advisory committees while serving as commissioner of communications, among other liaison positions.
She said she is running to take the village government in a new direction.
“I have been hearing a lot from residents and how they would like to see a fresh start for Port Jeff,” she said. “That’s what I was responding to when I decided to run.”
Petitions
This year’s mayoral contest took an unusual plot twist very recently, on May 30, when the Suffolk County Board of Elections opted to remove Sheprow’s name from the June 20 ballot over faults in her petitions.
“I take full responsibility for not putting my cover sheet on the petition submission,” Sheprow said. “But you know what? I don’t care. I’m running a write-in campaign. I would never stop fighting for the people of Port Jefferson.”
Snaden, whose campaign brought about the charges, said using the Freedom of Information Law to assess the opposition’s petitions is standard practice.
“We all have to follow the same rules,” she said. “It’s our job as candidates to know the laws and follow the laws.”
Budget
The candidates offered competing perspectives on the village’s present finances.
Snaden regarded the current fiscal health as “excellent,” noting the relatively low-interest rates the village pays when borrowing money.
She acknowledged “the budget can always use some tweaking,” adding, “there are some needs that I believe need an increase in budget.”
Chief among them are salaries, Snaden said: “Bringing those numbers up would be imperative for getting the highest quality employees we can.”
Sheprow suggested the village’s Moody’s rating, a measure that calculates an organization’s relative credit risk, “can be improved,” saying her administration would strive for a AAA bond rating [compared to the current Aa3].
The trustee proposed instituting an advisory committee of certified public accountants and other financial professionals to assist the village board in preparing its budget.
“A zero-based budget is so important,” Sheprow said. “Also, having that budget committee [will help] create a budget that is responsible to the taxpayers.”
Revenue
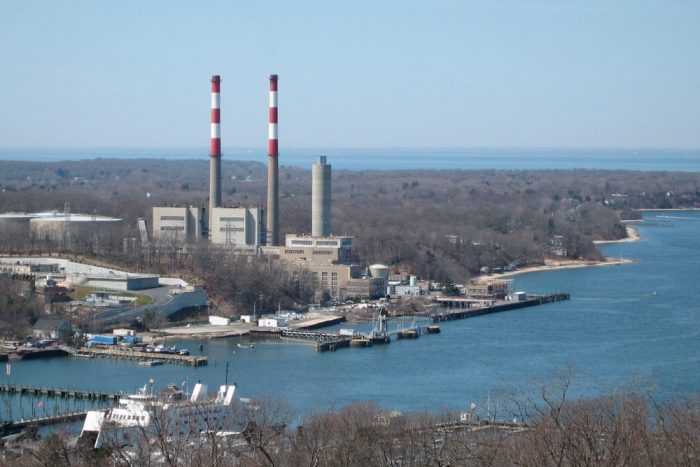
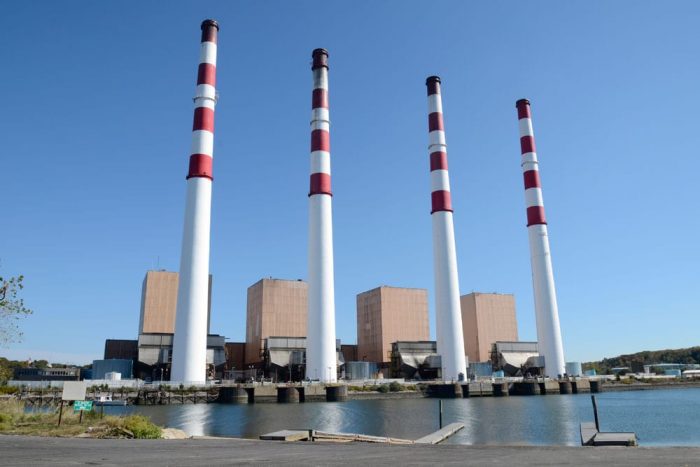
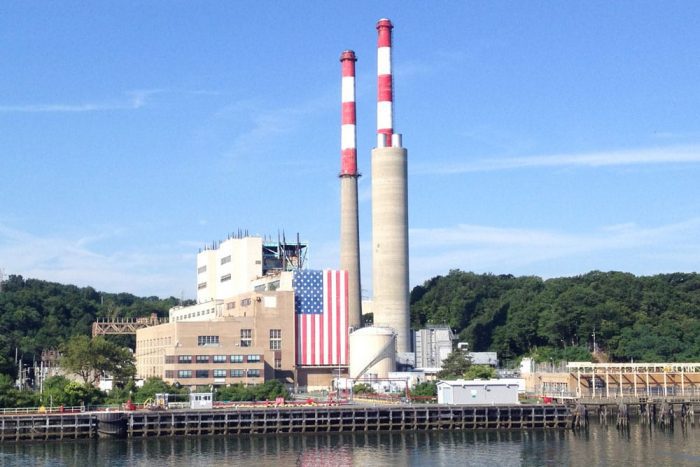
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency recently announced new regulations targeting existing power plants, placing a cloud of uncertainty over the Port Jefferson Power Station.
With questions surfacing about the possible decommissioning of the plant, the candidates were asked whether the village should begin preparing for further losses of public revenue.
Sheprow again advocated for expert consultation.
“I think we need to include the Advanced Energy Center at Stony Brook University,” she said. “Maybe we can come up with ideas about how to bring advanced energy initiatives into that location.”
Snaden said continued collaboration with wind power companies, such as Ørsted and Eversource, would remain pivotal in “bringing green energy to Long Island through the Village of Port Jefferson.”
To account for potential losses in public revenue, she also proposed “increasing our tax base through responsible development.”
Staffing
Both candidates agreed the administration is understaffed but departed on possible solutions.
Snaden emphasized hiring a planner for the building and planning department and additional personnel for the code enforcement department.
She indicated the practice of assigning multiple administrative titles to a single staff member is “absolutely not” sustainable.
“I think that’s where the budget needs to be enhanced — to hire the right people to head up these departments and divide up more of the tasks,” she said.
Sheprow maintained the hiring process should follow “a [human resources] system and policy.”
“The idea that I have, should I become mayor, is to bring in someone to take a deep dive into the organizational chart of the village,” she said. “I find there are some conflicts of interest for these positions and roles for people who wear multiple hats.”
Public meetings
To boost attendance at public meetings, Sheprow supported overhauling the village’s municipal website.
“It is not responsive,” she said. “If there’s a village board meeting coming up, it should be on the front page on the carousel of the website.”
She also favored a more dynamic social media presence on behalf of the village, with suggestion boxes and other modes of “active responsiveness” between board members and residents.
“I think we need to set up — here we go again — another committee to hear and review complaints and take [them] forward to the Board of Trustees.”
Snaden discussed the value of live streaming public meetings.
“Bringing the meetings to [residents] in their living rooms, recorded so they could watch at a later date, was key” during the COVID-19 public health emergency, Snaden said, proposing to expand and enhance these methods post pandemic.
She also touched upon the role of the Port eReport in dispersing information to the public.
In welcoming more citizens into the local decision-making process, Sheprow expressed pleasure at the reformation of the Port Jefferson Civic Association, saying, “That means the people care, that the people in the community want to get involved.”
She said the chance for more frequent communications between residents and trustees during board meetings is “a huge opportunity for us.”
Snaden said, “Regular meetings with whoever wants to have a voice,” combined with an active social media presence, would be crucial for welcoming more residents into the process.
“I also believe there’s an aspect of people going to meetings when there’s a negative issue or problem,” she added. “As a person who always looks for the positive in things, I like to believe that a portion of the people not coming to meetings are very happy with what’s going on.”
Open government
Another central administrative function is the swift distribution of time-sensitive documents, such as public minutes and agendas.
Snaden returned to hiring when asked about expediting the release of these materials.
“That rests now on the clerk’s [Barbara Sakovich] responsibility list,” she said. “She’s just overwhelmed with the amount of work,” adding, “I believe we could help by bringing in more people to divide up those duties to get [those documents] out there.”
Sheprow favored implementing a “proactive communications system,” including an internal newsletter, to bring the information to staff and the public more expeditiously.
“We need somebody who’s creating content,” she said. “The content would include a press release after every meeting [saying] here’s what happened.”
Building density
During the May 1 public hearing on possible zoning code changes for the Maryhaven Center of Hope property, several community members voiced concerns about increased villagewide building density.
Sheprow raised objections of her own.
“The proposals and the sketches that have been drawn for this space are looking like we’re bringing city life into a transitional [not entirely commercial nor residential] area of Port Jefferson,” she said. “The surrounding communities are horrified by the prospect of seeing four stories from their backyards.”
Snaden noted, “Density is already here,” referring to some existing apartment and condominium developments neighboring Maryhaven.
In moving through the building and planning stages, she said, it will be necessary to continue consulting traffic and environmental studies, which she indicated are “always done as a matter of course.”
“Residential use has been proven to be the softest use, environmentally speaking,” the deputy mayor added. “My concern is that if we don’t move ahead with … some type of a code change, then as of right, an office park could move in, causing more issues for the neighboring community.”
Parking garage
The village is also working to mediate longstanding parking issues, with both candidates detailing how a proposed parking garage could offset shortages.
“There has to be a careful balance with that — without overbuilding but creating the parking spaces that are needed,” Snaden said of the parking structure.
She also supported continued public-private partnerships for shared parking agreements.
Sheprow called for establishing a parking committee, composed primarily of business owners, to help manage the village’s municipal parking apparatus.
She referred to the proposed garage as “an idea I think residents need to hear and weigh in on.”
Flooding
During a recent climate resilience forum at Village Hall, local architect Michael Schwarting shared alarming projections of more frequent and intense flood events in Lower Port. Each candidate was asked how the village could mitigate these concerns.
“Utilizing an engineer or planner to lead that process,” coupled with a new grant writer to help underwrite new projects, could “move the village forward conceptually,” Sheprow suggested.
Snaden proposed daylighting hidden underground water bodies to offset increases in flood load. “I would like to continue building bioswales,” she added, “making gardens in conjunction with these bioswales.”
Concluding remarks
Sheprow expressed appreciation for the residents throughout the campaign process.
“I’m having a lot of fun talking to people and learning more about everyone in our community,” she said. “There’s a lot of love for this community, and I would just be grateful to represent them and have their trust put in me.”
Snaden reiterated her past experiences in positioning her for the responsibilities of mayor.
By “voting my opponent in as mayor, you lose me entirely — you lose my experience, knowledge and love for this community,” Snaden said. “However, if you vote for me, Lauren stays on as a trustee, and you have us both.”
Voting information
The public will be the ultimate arbiter of these two mayoral candidates on Tuesday, June 20. Voting will take place at Port Jefferson Village Center, where polls will be open from 6 a.m. to 9 p.m.