By John L. Turner

In a few weeks you’ll most likely be sitting down around a table with family members to enjoy an annual Thanksgiving Day meal with all the fixings: turkey, stuffing and gravy, mashed and sweet potatoes, green beans, and cranberries or cranberry sauce. The cranberries and/or sauce probably came from a commercial bog in Wisconsin, Massachusetts, Oregon, or New Jersey, the states where large commercial cranberry bogs exist today.
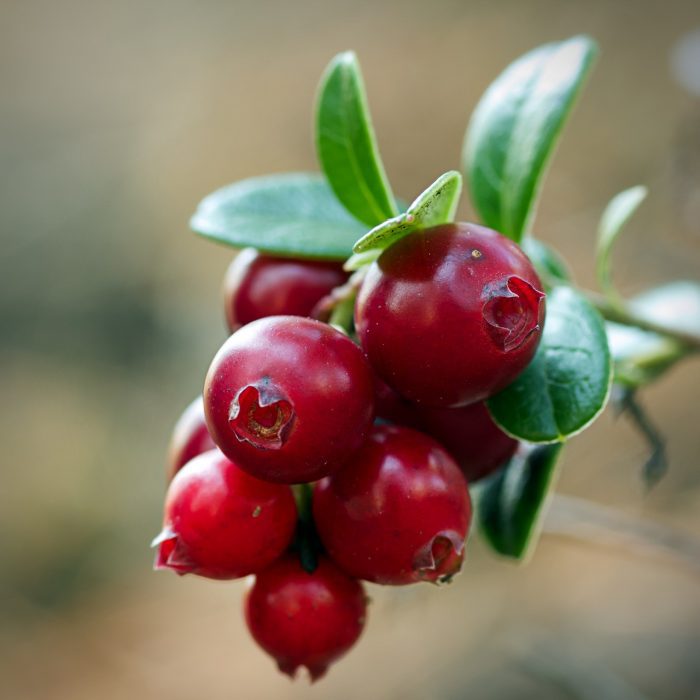
And here’s a surprise: If you had sat down to this same blessed feast about a century ago, there’s a strong likelihood the cranberries you enjoyed were harvested from a commercial bog situated somewhere on Long Island, probably from one of a dozen or so located in the Pine Barrens. Indeed, a century to a century and a half ago Long Island was the third largest supplier of cranberries to the nation.
Cranberries, being related to blueberries and other heaths, have an affinity to sandy, acid soils so the Long Island Pine Barrens, or more specifically wetlands in the Pine Barrens, provided highly suitable habitat to create bogs and cultivate cranberries.
Most of these commercial bogs were located within the large watershed of the Peconic River, flowing easterly through the Pine Barrens, including three of the river’s four tributaries — the Fox/Sandy Pond area, Swan Pond, and the Swezey’s Pond/Little River draining north from Wildwood Lake — and on the main stem of the river itself just west of where Edwards Avenue crosses over it (just north of Exit 71 of the Long Island Expressway).
Long Island’s first cranberry bog was established on the Brown’s River in Bayport around 1870; today most of it is within the 316-acre San Souci County Park and Camp Edey, a 95-acre owned by the Suffolk County Council of Girl Scouts.
The Woodhull Bog, where Cranberry Bog County Nature Preserve is situated, was perhaps the most commercially successful bog but its success was far from a sure bet when the Woodhull brothers embarked on their effort to convert low-lying swamp habitat to a cranberry bog. Here, they spent four years, beginning in 1885 years, ripping out countless trees and shrubs, damming up the Little River tributary with an earthen dike, placing a several inch blanket of sand on the organic peat of the bog, installing perimeter and internal ditches throughout the bog to ensure rapid water coverage, and, of course, planting thousands of cranberry vines. (With the adoption of the New York State Freshwater Wetlands Act, and local wetland laws, this kind of activity fortunately cannot legally happen now on Long Island).

In 1889 the first harvest was achieved with a whopping 10 bushels provided by the bog. The next year was better with 90 bushels produced and the upward trend continued in 1891 with 500 bushels. In 1892 the vines were three to four years old and had really matured and the tally for the year shows, with 21,100 bushels, going for about $2 a bushel, at market. For many years after that the bog remained profitable and productive. Other bogs like the Brown’s Bog in Calverton and the Davis Bog further west in Manorville were also productive and profitable. No wonder they called it Red Gold!
In the early years cranberries were picked by hand, the hands provided by hundreds of residents who gained supplemental income each autumn harvesting berries. Bog operators used a simple but ingenious strategy to ensure maximum crop harvest among the distracted workers busily chatting and socializing while picking. They laid down parallel rows of string like bowling alleys; each picker had an easier job of making sure all the berries within their “alley” were harvested.
The cranberry scoop was soon invented and provided a more efficient means to harvest berries. The wooden scoop, a popular item in antique stores, had tines like a fork, spaced apart a distance just slightly less than the width of a cranberry. Scoops gave way to mechanized equipment that was more efficient still and once bog owners/operators learned that ripe cranberries float they began to flood the vine-filled bogs and turned to powerful vacuum hoses to suck up the crop. You may have seen Ocean Spray commercials with harvesters up to their chests in a bright red surface of floating berries. Today, a few people can do the job that once required dozens.
Flooding the bogs, also done to prevent a seasonal frost from destroying the crop, and over the winter to protect the vines from freezing temperatures, meant a reliable water supply had to be available and this was the case for every Long Island bog.
For the Woodhull Bog this was the water from Swezey’s Pond, created by the aforementioned earthen berm. For the Davis Bog, water was supplied from Swan Pond. When an operator wished to flood the bogs to protect the berries or vines, or to facilitate autumn harvest, they would remove the wooden boards nestled in the concrete part of the dam next to the water supply source and install the boards at the outlet of the bog. A motor would kick on and spin a driveshaft attached to a large belt connected to a paddlewheel and water would quickly flood the bog. In spring the reverse would occur.

To allow for bees and other pollinators to access the cranberry flowers (the name cranberry is thought to have derived from the name “crane berry”, a reference to how the flowers look similar to the head of a crane) boards would be installed in the slots of the concrete dam next to the water supply and boards removed from the far end of the bog, thereby draining it.
By the 1920’s nearly a dozen bogs were in operation here. But about 15 years later it was down to six, according to a fine article by Tim Huss published in the New York Almanack. Long Island had several problems that made cranberry production less profitable — there were no processing facilities to make value-added products and the costs of labor and land were higher, reflected in higher property taxes, when compared with other more rural areas.
Cranberries, like most agricultural monocultures, are afflicted by pests and such was the case with Long Island’s cranberry bogs. Two notorious pests were (and still are) the cranberry fruit worm and black-headed fireworm which affects both the fruit and leaves. Cranberry producers turned to chemical means in an attempt to control the insects, with amino triazole being the pesticide of choice. This pesticide soon was in the crosshairs of the then Department of Health, Education and Welfare (HEW).
On “Cranberry Black Monday,” November 9, 1959, HEW declared amino triazole a carcinogen (cancer causing). The cranberry market was dealt a severe blow with even Mamie Eisenhower declaring she was foregoing the traditional cranberry sauce at the White House Thanksgiving Dinner in a few weeks, serving apple sauce instead. Untold cartons and cans of cranberries and sauce languished on supermarket and warehouse shelves.

The Davis Bog in Manorville was the only cranberry bog to survive this event. For years they sold their berries to the Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Company (remember A&P supermarkets around Long Island?), but the bogs south of Swan Pond were harder and harder to maintain and in 1974 this last cranberry bog ceased operation. The Long Island cranberry industry was no more.
If you want to gain some sense of the industry that was once so vital to Long Islanders both as a source of food and employment, a visit to the Suffolk County Cranberry Bog Nature Preserve south of the Suffolk County Center in Riverhead is in order. A small dirt parking lot provides parking and a wide trail leads to Swezey’s Pond which was the water supply source to the Woodhull Bog.
A picturesque trail runs around the pond (I like to walk it in counter-clockwise fashion) and by hiking the trail you’ll see where sand was excavated to make the earthen dike, the dike itself, a few of the perimeter ditches that once lined the edge of the bog, and a concrete pump house near where the stream drains from the pond into the bog. If you visit during the warmer months you should see turtles, numerous birds, dragonflies, and waterlilies. Better yet, go in the colder weather, say the day after Thanksgiving, as a way to burn off the calories from all that turkey, gravy, and cranberry sauce you ingested with relish the day before.
A resident of Setauket, author John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.




 While the main office for Long Island Repair Café (they have a Facebook page) is at 1424 Straight Path in Wyandanch, run by Starflower Experiences, an environmental educational organization, volunteers host repair cafés throughout Long Island. The main office can be reached at (516) 938-6152.
While the main office for Long Island Repair Café (they have a Facebook page) is at 1424 Straight Path in Wyandanch, run by Starflower Experiences, an environmental educational organization, volunteers host repair cafés throughout Long Island. The main office can be reached at (516) 938-6152.
 Another book that has a slightly different format but is richly informative is The Sibley Guide to Bird Life & Behavior (numerous authors). It, too, discusses the unique qualities of different bird families but before the family discussion has five chapters that delve into great detail about Flight, Form, and Function; Origins, Evolution, and Classification; Behavior; Habitats and Distributions; and Populations and Conservation. If I were able to recommend only one book for your nightstand to increase the breadth and depth of your knowledge about birds it would be this book.
Another book that has a slightly different format but is richly informative is The Sibley Guide to Bird Life & Behavior (numerous authors). It, too, discusses the unique qualities of different bird families but before the family discussion has five chapters that delve into great detail about Flight, Form, and Function; Origins, Evolution, and Classification; Behavior; Habitats and Distributions; and Populations and Conservation. If I were able to recommend only one book for your nightstand to increase the breadth and depth of your knowledge about birds it would be this book. 







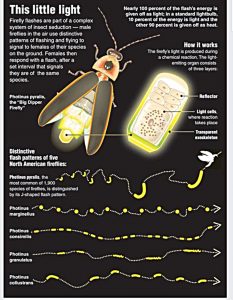 As for rare firefly species that may occur on Long Island, Katie indicates “The only documented IUCN Red List species that has occurred on Long Island is Photuris pensylvanica (Dot-dash Firefly) ranked as Vulnerable. … I suspect at least two other IUCN species that may occur on Long Island. It could be a long shot, but there is potential for Pyractomena ecostata (Keel-necked Firefly) ranked as Endangered and possibly Photuris bethaniensis (Bethany Beach Firefly) ranked as Critically Endangered by IUCN and petitioned to be federally listed as Endangered.”
As for rare firefly species that may occur on Long Island, Katie indicates “The only documented IUCN Red List species that has occurred on Long Island is Photuris pensylvanica (Dot-dash Firefly) ranked as Vulnerable. … I suspect at least two other IUCN species that may occur on Long Island. It could be a long shot, but there is potential for Pyractomena ecostata (Keel-necked Firefly) ranked as Endangered and possibly Photuris bethaniensis (Bethany Beach Firefly) ranked as Critically Endangered by IUCN and petitioned to be federally listed as Endangered.”  A resident of Setauket, author John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.
A resident of Setauket, author John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.

