By Daniel Dunaief
When cancer spreads, it becomes especially dangerous. Indeed, metastatic cancer accounts for 90 percent of deaths from this disease.
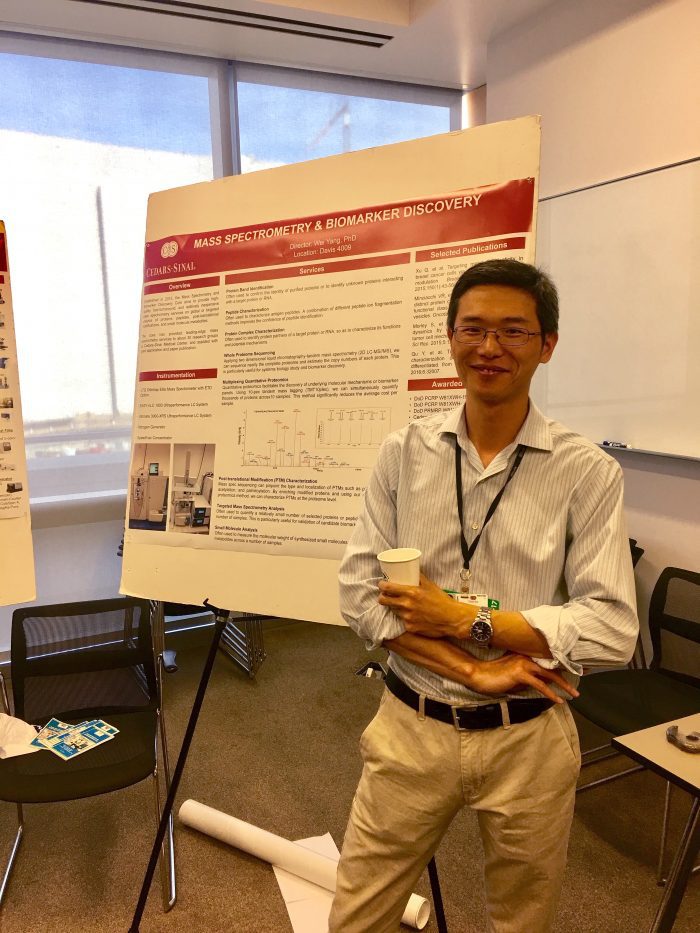
Stony Brook University Associate Professor Wei Yang, who joined the Pathology Department on August 1st, hopes to reduce metastatic mortality.
Yang is looking both upstream for the kind of molecular biological signals that might make cancer more likely to spread and downstream, for processes that overcome the body’s natural defenses and that lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
As he described, the goal is to prevent micrometastases, which are metastatic tumors that are too small for a radiographic scan, from growing into clinically relevant macrometastases that can be detected through imaging such as X-ray scans.
Micrometasases can form at an early stage, sometimes even before the detection of primary tumors. They are typically asymptomatic and are rarely lethal, as many cancer survivors die with, but not of, these micrometastases.
In work he conducted in California at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Yang focused on the protein kinase RIPK2, which is over expressed in prostate cancer.
By inhibiting RIPK2 kinase in cell culture and animal models, Yang reduced prostate cancer metastasis by over 90 percent after four weeks of treatment. Inhibiting this protein made cancer progression over 10 times slower.
Innate immune cells and epithelial cells express RIPK2 at various levels. RIPK2 is over expressed in about 18 cancer types and the high expression is generally associated with worse patient outcomes.
RIPK2 is localized in the cytoplasm, which is inside the cell, rather than on the cell surface, which makes it difficult to train the immune system to destroy it. Small molecule compounds, however, can penetrate into the cytoplasm of tumor cells.
Developing oral drugs to shut off RIPK2 is a promising approach to disrupting this protein.
Repurposing an existing drug
The Food and Drug Administration has already approved a multi-kinase inhibitor called Ponatinib, which can inhibit the pro-metastatic RIPK2 signaling pathway in prostate cancer.
Yang believes it is “very promising” to repurpose this drug to treat prostate cancer patients who don’t respond to hormone therapies.
His animal experiments showed that RIPK2-higher tumor cells can grow into macromestases in multiple organs, such as bones, liver and adrenal glands. RIPK2 was also detected in cancers such as kidney and breast. Its expression levels are typically higher than in normal tissues.
Yang is the first to demonstrate that targeting RIPK2 reduces cancer metastasis.
He has been working on prostate cancer since he conducted his postdoctoral research at Harvard University/ Boston Children’s Hospital in 2006.
He started by analyzing three comprehensive and publicly available clinical databases. Using stringent criteria, he identified seven promising drug targets in prostate cancer metastasis. Among the seven, RIPK2 was the most significantly overexpressed and its expression increased along with prostate cancer progression from benign to lethal cancer.
Most patients diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer die within two to three years. About 31 percent live five years or longer.
For Yang, who earned his PhD from Peking University, the goal is to understand and prevent the lethal process of metastatic progression. He aims to develop clinically actionable drug targets and biomarkers.
Upstream and downstream
Yang is searching for genes and proteins that regulate the expression of this protein kinase, to find out what increases the expression of RIPK2 in tumor cells.
He has identified three transcription factors that are important for the expression of RIPK2 mRNA in prostate cancer cells. Previous studies showed that these factors are key drivers of prostate cancer aggressiveness.
He explained that it’s promising that patients with the overexpression of these transcription factors may benefit from targeting RIPK2 to reduce cancer aggressiveness. He is also identifying a gene signature associated with RIPK2 signaling activity. This will allow him to identify additional patients who may benefit from inhibiting this protein.
Seeking collaborators
Yang said he came to Stony Brook University for a host of reasons, including to have more lab space where he can employ two post doctoral researchers, two or three graduate students, one research support specialist and two undergraduates.
He is in the second year of a five year National Cancer Institute grant and is also in the second year of a three-year Department of Defense grant.
Yang would like to find collaborators at Stony Brook who can bring specific levels of expertise in areas such as lipid signaling.
In addition to RIPK2, Yang also focuses on palmitoylation signaling in cancer metastasis. Palmitoylation is a type of lipid modification on proteins and is a reversible post-translational modification whose deregulation contributes to diseases including cancer.
Stony Brook has a “world class lipid signaling research center,” he explained in an email, and he would like to find collaborators in this arena.
Hobbies
Married with a 14-year old son, Yang enjoys traveling with his family to cities and national parks and reading history and science fiction books. One of his favorite authors is Yuval Noah Harari.
As a child, Yang was particularly interested in science. Cancer affected his family, as his grandfather had liver cancer that was diagnosed early enough to receive treatment and his aunt is living with lung cancer.
While he has a sense of urgency to study metastatic cancer, Yang said the field does not receive as much funding and attention as other areas of cancer research. He estimates that about 10 percent of the cancer budget supports investigations into metastatic cancer.
His approach, he said, will remain focused on actionable plans and on efforts that have “high translational potential,” he explained.