Between You and Me: Trying acupuncture to manage knee pain
By Leah S. Dunaief

For the first time, I am trying acupuncture. I hope it will help my sore knee, which suffers from osteoarthritis. A fair number of people have suggested I try this ancient Chinese medical technique for relieving pain, some with great enthusiasm from their own experience. Now I know this won’t cure my problem, which is the result of my having used up the cartilage that separates the bones, and in fact, I have been diagnosed as having bone-on-bone in my knee. That feels just as unpleasant as it sounds. In short, when I walk, it hurts.
So if I can’t fix the ailment, perhaps I can fix the pain.
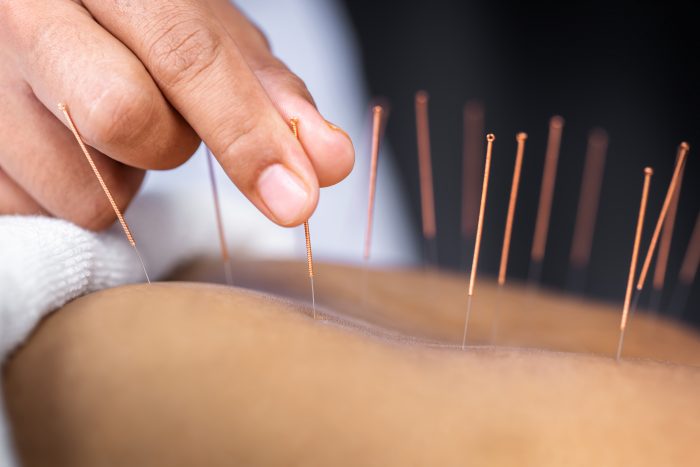
I wore a shirt and shorts, so he could get to my knee easily and went to a local acupuncturist, who was highly recommended, and was directed to one of several small rooms in his office. In the room was an examining table covered by a white cloth and pillow, and as I lay down, he asked after my general health. Finding nothing of particular interest, he proceeded to take out a series of short metal needles, each individually wrapped like a toothpick and explained that he was going to insert them around the knee.
I had done some research and read that acupuncture was devised in China around 2500 BC and can even act as an anesthetic during surgery. Needles no thicker than a human hair are pressed into the skin and underlying tissues, usually for 0.1 to 0.4 inches at precise points. They may have a slight arrowhead or an extremely fine tip, and they may be twisted to cause a tiny wound and thus stimulate the body’s natural healing abilities. While there is little to no discomfort as the needles are applied, especially in areas of thicker skin and muscle, the insertion causes enough damage to make the cells release pain-killing chemicals that are picked up by adenosine receptors on nearby nerves, which in turn react by damping down pain.
The doctor probably applied 15 needles in and around the knee, then left me to doze on the table for 20 minutes or so. When he returned, he carefully removed each needle. One, on my shin, caused a bit of bleeding, to which he applied pressure and then an ointment. He next energetically massaged the knee for about ten minutes, making the area feel wonderful. I had read that massage after acupuncture enhances the effectiveness of each and results in a more complete treatment.
I also read that acupuncture can be used to relieve discomfort from chemotherapy, dental pain, fibromyalgia, headaches (tension and migraine), labor, lower back, neck and … osteoarthritis. BINGO!
It seems effective in reducing inflammation, which happens when chemicals from the body’s protective army of white cells enter the blood or tissue. This raises the blood flow to areas of injury or infection, causing redness and warmth. Fluid leaking into the tissues causes swelling, which I have.
The effects from an acupuncture session generally last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. I was advised by the doctor to come twice a week for the first 2-4 weeks, then once a week, then once every other week, followed by once a month and then as often as needed.
When he finished, and as he was leaving the room, the doctor cautioned that I should get up slowly and take my time coming out. I did feel a bit lightheaded but was cheered that my knee felt, if not pain free, at least numb as I walked. He also advised that I avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise. There could be side effects, like bleeding, nausea, skin rash, infections or allergic reactions, I had read. Fortunately, I experienced none of those except the momentary bit of blood at the end.
What I especially like about this therapy is that it urges the body to cure itself. That’s far different than turning to surgery. If it works. So far, it’s too soon to tell.