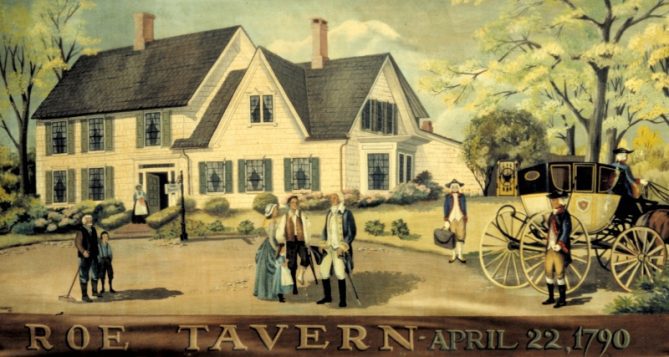By Beverly C. Tyler
We are all familiar with the lives of the famous men and women in US history. From the time we were students in school, with the images of George Washington and Abraham Lincoln staring down at us from their place of honor in the classroom, we learned of the people who made our great nation. Our coinage includes U.S. presidents as well as men and women who contributed to America and American freedoms.
We can now see movies, videos and streaming programs about these same heroes of American democracy. Students are familiar with the poem about the “Midnight Ride of Paul Revere,” but the lives of many of our local men and women, who have contributed to history, are largely unknown.
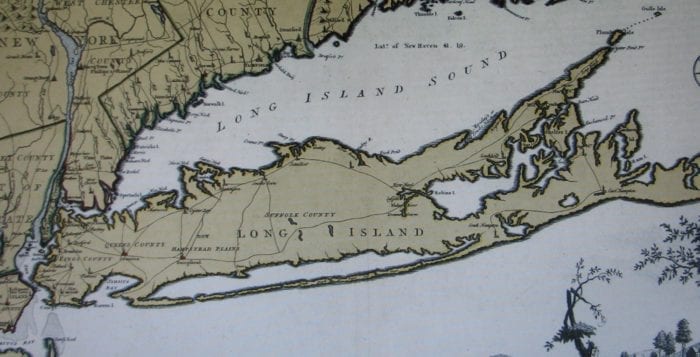
Long Island has played host to a number of these famous and well-known people from the past. In this century one of the best known was Charles Lindbergh, the Lone Eagle, who took off from Roosevelt Field on his solo flight across the Atlantic on May 20, 1927. Long Island was the scene of many other historic flights and record-setting attempts by early pioneers of flight throughout the 20th century.
Long before Lindbergh, in June, 1791, Thomas Jefferson and James Madison came to Long Island at the conclusion of a pleasure trip which included the recording of many natural science observations through New England as detailed in “Jefferson and the Rights of Man” by Dumas Malone.“ They proceeded down the Connecticut ( River), crossed Long Island Sound, followed the northern coast of Long Island to Brooklyn, and then crossed to New York. On their way they visited a nurseryman in Flushing and Jefferson left with him a large order for trees and shrubs, including all the sugar maples that were available.” Not mentioned by Malone was the Ketcham Inn in Center Moriches where Jefferson and Madison spent at least one night. During the Revolutionary War, Benjamin Havens ran the inn and provided intelligence to the Culper Spy Ring, usually through Caleb Brewster who was a frequent visitor.
George Washington also visited Long Island after the Revolutionary War. In April 1790, while he was president of the United States, Washington toured part of Long Island traveling to Setauket from Patchogue. In his personal diary for April 22, 1790, Washington wrote, “We struck across the Island for the north side, passing the east end of the brushy marsh – and Coram, 8 miles – thence to Setauket 7 miles more, to the house of Captain Roe, which is tolerably decent, with obliging people in it.” According to Selah B. Strong, in an article written in the 1920’s, “The procession was led by my great grand-father, Capt. Selah Strong. He was evidently an important man in the county, holding the offices of County Judge, supervisor and President of the Board of Trustees of Brookhaven; and County Treasurer, and afterwards State Senator. It was very appropriate that he should entertain the General at Roe’s as the house was the former residence of his grandfather, the first Strong to bear the name of Selah, who came to Setauket about 1700 and on March 23, 1703 bought the land from Thomas Clark and built the house.”
Captain Austin Roe maintained his home as a tavern and, in addition to hosting General Washington on that April evening in 1790, he is known as one of Washington’s spies during the Revolutionary War. This group of men and women, mostly from Setauket, were Patriots who, after their deeds were discovered, became famous. The Setauket Spies operated with such secrecy and modesty that their heroism and, in most instances, even their identities were not fully known until Morton Pennypacker discovered the facts, as we now know them, and published them in his book “General Washington’s Spies,” in 1939.
As detailed in the Three Village Historical Society exhibit “SPIES!”, for two years, since August 1776, when General Washington’s army was defeated by British and Hessian soldiers at the Battle of Long Island, New York City and Long Island were occupied by the enemy. Washington and the Continental Army were fighting elsewhere, in upstate New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and in the South. British headquarters was in New York City.
The only way for Washington to get information about enemy troop movements and strength was to plant reliable spies among them. But this had been tried and failed. In September 1776, Captain Nathan Hale had volunteered, crossed Long Island Sound, and gathered information on his way to and from the city, by then in British hands. Without training and support he was captured and brought to British General Howe who had him hanged the next day as a spy.
On Washington’s staff was 24-year-old Dragoon Major, Benjamin Tallmadge. Washington asked Tallmadge to create a spy ring of Patriots who could be trusted and who would support each other. Hale had been Tallmadge’s best friend at Yale. He would make sure that his spy ring would operate safely. Tallmadge was born in Setauket, a village across Long Island Sound from Fairfield, Connecticut, where Tallmadge and his Dragoons were stationed. There, Tallmadge had friends, Patriots like himself, who were determined to defeat the British. Tallmadge assured Washington that they could be trusted spies. To keep them safe, Washington did not want to know their names, so Tallmadge gave them code numbers and aliases, or spy names. General Washington called them Culper Spies, after Culpeper County in Virginia where he had his first job as a surveyor. Tallmadge gave himself an alias, too, and gave Washington and himself code numbers. Washington’s number was 711.
“SPIES!” tells the story of Washington, Tallmadge, and the Culpers. All but one was born in Setauket. Each had known Tallmadge since childhood: Abraham Woodhull, a farmer who had reason to hate the British; Anna Smith Strong, who let Woodhull know where Brewster was hiding with his whaleboats and crews: Austin Roe, a tavern keeper who rode into Manhattan as a courier for the Culper Spies; Caleb Brewster, a fearless whaleboat captain and artilleryman who crossed the Sound repeatedly to pick up and deliver spy messages, daring the British to capture him.
The one Culper spy not from Setauket was Robert Townsend. He was born in Oyster Bay. His family home was occupied by the British. Townsend owned a shop in Manhattan where Loyalists and British soldiers visited. He was in a position to gather information. He wrote messages in a code Tallmadge devised. Sometimes he wrote with invisible ink, between the lines of ordinary letters, a suggestion from George Washington himself. Roe picked up the letters and brought them back to Setauket where Woodhull gave them to Brewster, who took them back across Long Island Sound to Tallmadge in Connecticut. From there the letters were sent to General Washington. Information gathered by Long Island’s spy ring helped save the Revolution.
The homes, markers and graves of these Patriots can still be seen, many of them in the Three Village area. The location of the Roe Tavern is marked by a state plaque that locates where the house was, at the corner of Route 25A and Bayview Avenue, before it was moved. The grave and memorial for Abraham Woodhull is located directly behind the Setauket Presbyterian Church. A state plaque also marks the location of the home of Woodhull and is located on Dyke Road between Heritage and Bob’s Lane, overlooking Little Bay and Strong’s Neck. These Patriots are part of our local history and their lives can be an inspiration to us aIl.
Beverly C. Tyler is Three Village Historical Society historian and author of books available from the Three Village Historical Society, 93 North Country Rd., Setauket, NY 11733. Tel: 631-751-3730. WWW.TVHS.org