By John L. Turner
With a 65th birthday looming on the horizon for later this summer, I recently found myself, not surprisingly, thinking about “Bucket Lists” — lists comprising places to visit or things to do before “kicking the bucket.” It’s a concept made popular from the movie “The Bucket List,” starring Morgan Freeman and Jack Nicholson as two terminally ill older men living out their last desires, and the impending birth date — signaling a lifetime spanning two-thirds of a century — motivated me to develop “bucket list” priorities for the time I have left.
So I began to think about different types of bucket lists. Travel destinations with my family; bird trips; visits to major league baseball stadiums (been to about half of them) and, of course, the ultimate global nature bucket list — snorkeling with Whale Sharks in the coastal waters off Belize, witnessing the Wildebeest migration in the African Serengeti, sitting quietly near any one of our closest relatives — Chimpanzees, Gorillas, Bonobos, or Orangutans in the tropical forests of African and Asian countries — or walking in reverence amidst tens of millions of Monarch Butterflies at their winter roost in the highland fir forests of Mexico.
But there will be no exotic far-flung places for this article; this bucket list is more modest in scope, relating to natural phenomena that I long to see on Long Island. For a few of these, I’ve witnessed them many years ago but for others I await the first experience.
Here goes:
Seeing a Smooth Green Snake
Of the nearly dozen native snake species found on Long Island, undoubtedly the most beautiful is the Smooth Green Snake. It is a tropical lime green color on top and lemon yellow on its belly with a golden-colored eye. They are a bit wider than a pencil with adults reaching about two feet in length. You’d think such a brightly colored snake would stand out but laying motionless in grass they can disappear. I have never seen one on Long Island or anywhere else and would love to!
While on the subject of snakes I’d also love to see a Hognose Snake again and especially one performing its famous ‘death feign’ act. I’ve seen this behavior twice in my life, once on Long Island, but both experiences were decades ago. If disturbed the snake often but not always feigns its death by writhing spasmodically and rolling onto its back and abruptly “dies”. Adding to the convincing nature of the act the Hognose can even spill blood from its mouth by rupturing capillaries that line it. Of course, it’s all a ruse to stop a potential predator from attacking.
Finding an Ovenbird nest
In larger woodlands the Ovenbird sings out with its ringing teacher! teacher! song filling the spaces between and under the trees. With a little bit of luck you might find this songbird perched on a branch in the sub-canopy as it sings, its little warbler body shaking as song spills forth loudly. Despite years of searching on many a forest floor I’ve never found their “Dutch oven”-shaped nest which gives the bird its name.
Twice in the Pine Barrens, once in Shoreham, the other in Riverhead, I’ve made a concerted effort to look for their nests, after observing nearby adults with food in their mouths. On my knees I very slowly and carefully inspected the forest floor starting where I thought, based on the bird’s behavior, the nest might be. Methodically, I spiraled outward in my search but, alas, despite half an hour of on-my-knees-searching came up empty.
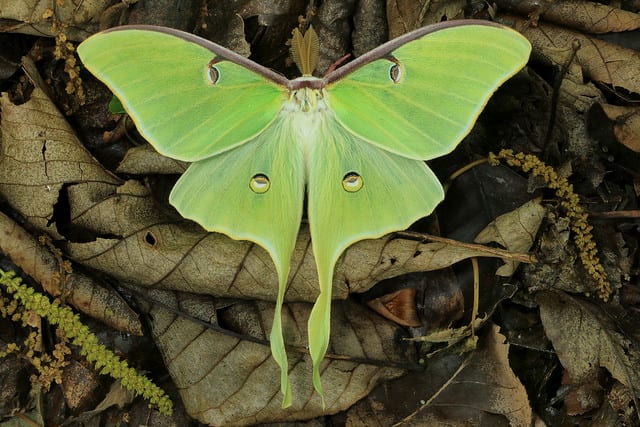
Spotting a Giant Silk Moth

If you want to familiarize yourself with a remarkable, stunning, spectacular (fill in your own adjective here once you’ve seen what they look like) group of insects native to Long Island, check out photos of the following moth species: Luna, Cecropia, Polyphemus, Promethea, and Buck Moths. These are among the largest flying insects we have with wingspans as large as six inches.
At one time they were common but no more. The host trees they depend upon as caterpillars are still relatively common to abundant on Long Island so its not a loss of food that explains their decline; widespread spraying of poisonous pesticides is the suspected cause for their significant drop.
The last of three live Luna Moths I’ve seen on Long Island was a decade ago. I’ve never seen a live Promethea or Cecropia and the last Polyphemus was six years ago — a ragged individual so beat up from bird strikes it was weakly fluttering along the asphalt in a shopping center parking lot. I scooped it out of harm’s way but it died later that day.
Fortunately, the beautiful black, orange, and white Buck Moth, one of the iconic species of the Pine Barrens, is still common. Spared from spraying in its vast Pine Barrens forests, the Buck Moth can be observed during the day flying around the dwarf pines of Westhampton in the autumn as male moths seek out females to create the next generation.
Seeing a River Otter
One of the bits of good news relating to Long Island wildlife is the sustained natural reintroduction of river otters, presumably from wandering individuals emigrating from Westchester and western Connecticut and island hopping to the North Fork via the island archipelago of Plum, Little Gull, Great Gull, and Fisher’s Islands. However the prospecting animals did it, they’re here now. And while I’ve seen wild otters in locations off Long Island and seen otter signs on Long Island, in the form of otter runs and scat (fishy poop) as close by as Frank Melville Memorial Park in Setauket, I’ve not seen one of these charismatic creatures here.
Observing a Mola mola
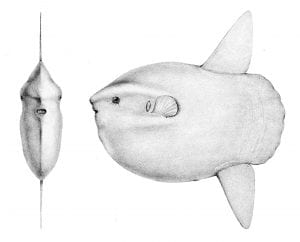
This strange looking enormous fish (in fact it really doesn’t look like a fish) is often seen by fisherman and whale watchers afloat in the Atlantic Ocean in the summer. Also known as the ocean sunfish, they are world’s largest bony fish weighing in at more than one thousand pounds. They can dive deeply and after returning from cold ocean depth, they warm up by turning on their side to bask in the sun, showing off a flattened profile, a view that many (except me!) have enjoyed.
Do you have a nature-themed bucket list?
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.






