By John L. Turner
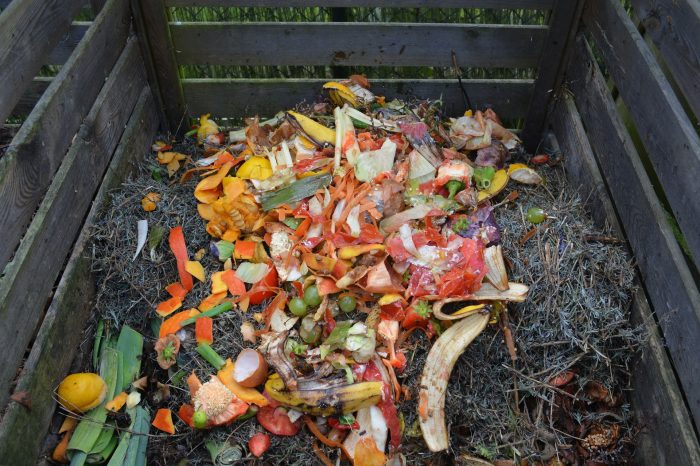
Pretend for a minute that you’ve just bought five spiffy new shirts and, pleased with your purchase, proudly place the shirts on the closet shelf. Three days later you visit the closet, pull two of the never-worn shirts off the shelf, walk outside and throw them into the garbage can. Sounds odd, strange, and disturbing, no? Well, welcome to the world of food waste, a huge, yet little recognized environmental problem.
To put numbers around the problem, the average American family throws away roughly 240 pounds of food annually, between one-third and two-fifths of the food they buy, costing them about $1,800. That’s 50% of the seafood they bought, about 40% of the fruits and vegetables, 25% of the meat and 20% of the milk, and one-third of the grain. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, enough food is wasted nationally to annually fill 450,000 Statue of Libertys!
Why should we care about food waste? Because food production, consumption, and associated waste has relevance and is connected to so many important and interrelated issues: environmental degradation, hunger and food insecurity, economic inequality, and ethical use of animals, to name just a few.
Let’s take environmental degradation as one example. The environmental impacts resulting from the foods we eat (and waste) are nothing short of enormous: water depletion and water quality impacts, methane (a potent greenhouse gas) production from landfilled food items, loss of habitat (including wetlands) due to lands being converted to agriculture, widespread use of energy intensive fertilizers and agricultural poisons from pesticides, and a decline in abundance of marine life are several of the many results stemming from food production.
If we reduce the amount of food we waste we proportionately reduce these impacts because we would not need to produce as much food as we do. That could mean more parks, forests, wetlands, grasslands and prairies and more food for the 57 million Americans who are food insecure.
Food waste constitutes a large fraction of garbage (about 24% of the garbage in a landfill is food). As it decomposes in landfills, food wastes generate methane, a potent greenhouse gas (according to the Environmental Protection Agency methane has 80 times the warming power of carbon dioxide during its first several decades of circulating in the atmosphere). Rotting food in landfills is estimated to generate about 8% of the annual greenhouse gases released into the global atmosphere.
Water use stands out as another significant environmental impact made worse by food waste: fifty-six million acres of crops are irrigated in the United States, making agricultural water use the single largest consumer of water with eight out of every ten gallons of water used in the United States directed to agriculture for growing food — a total of more than 27 trillion gallons of water used annually. Unfortunately, pumping this amount of water to irrigate crops is depleting groundwater aquifers and drying reservoirs, rivers and streams.
And we could, of course talk about the amount of chemicals in the form of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides — and their impact to human and wildlife health — applied to our centralized food production system, but you get the picture.
Food waste occurs throughout the food production process from the point of harvest to consumption by consumers, from “farm to fork,” as the saying goes. For example, crops are often left unharvested due to changing market conditions, weather events, etc. This result was brought to bear with the COVID pandemic as millions of tons of various produce rotted on farms due to changes in the national food chain.
More food is wasted at the retail level, a fact made clear to me on a recent trip to a local Setauket supermarket. I was walking along the frozen/refrigerated food aisle and watched as an employee took packages out of the cabinets, gently tossing them into a shopping cart. Curious, I asked what he was doing. “I’m tossing them,” he said, “They’re past the expiration date.” While there’s no evidence that a food item a few days past the “expiration date” is not safe, I suspect the employee was simply following company direction.
Food waste is, of late, being addressed as lawmakers nationwide have started to grapple with the significance of the problem. New York State has already responded with the adoption of a law which becomes effective in January of 2022: the New York State Food Donation and Food Scraps Recycling Law. This law requires large producers of food waste (averaging more than two tons of food weekly) to donate edible food and to compost food that has perished. These efforts can have a very positive result. For example, in the United Kingdom food waste has dropped by about 21% due to a similar coordinated public-private effort.
And now to the stage where most food is wasted — at the family or consumer level caused by throwing out leftovers or unused foods that are past their “sell-by or best-used-by” dates. If you’ve read this far in the article you’re probably thinking of ways you might be able to reduce the amount of food waste you and family members throw in the garbage. There are many ideas to reduce the amount of food waste and to be part of the solution. Here are five to get started:
Love your leftovers — Save uneaten food and once in a while, consciously and specifically, plan your dinner by “loving your leftovers.” For dinner target various leftover dishes that are patiently biding their time on your refrigerator’s shelves.
Your nose knows — As one website notes: “Expiration dates are misleading and nonstandardized, leading many to toss out perfectly good food.” Foods generally don’t go bad instantly and you have a very sensitive and accurate tool to determine if food is still edible and its conveniently located in the middle of your face. Your nose is quite adept at picking up scents or whiffs of food that’s gone or going bad- don’t hesitate to use it. Trust your sense of smell!
Buy “ugly” fruits and vegetables —Consumers want the perfect apple with no spots or blemishes, yet that imperfect, slightly-spotted apple is perfectly fine to eat. Purchasing imperfect but healthy and safe produce is a sure way to prevent food from being deep-sixed in the supermarket’s garbage dumpster.
Say no to the garbage can, yes to the compost bin — If food has gone bad, compost that spoiled salad lettuce rather than disposing of it in the trash. This same lettuce, which in the landfill generates dangerous methane, makes wonderful garden soil if composted.
Buy a smaller turkey at Thanksgiving — one-third of turkey meat (that’s 204 million pounds) is thrown away each year, created by a mismatch between the size of the store-bought turkey and peoples’ appetites for it. The solution is simple: buy a smaller turkey.
Food waste is a significant problem. The good news is that each of us can play a role in solving it.
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.







 A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.
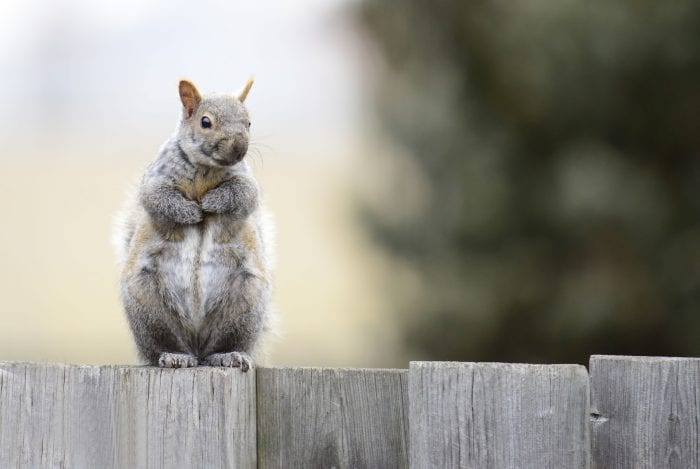














 My interest in squirrels and their nests came about from a book I had looked at in the junior high school library; I think it was entitled “Animal Homes”— although this factoid I don’t remember quite so clearly! But what I do remember in the book was the account which explained that grey squirrels make two types of nests — those in tree cavities, often used in winter, and the one I was going to inspect consisting of a globe-shaped leafy ball, known as a “drey,” wedged amidst branches, also used in winter but more often during the warmer months. The account mentioned that most dreys consisted of a single chamber although occasionally they make two chambers — the equivalent of a foyer leading into the living room.
My interest in squirrels and their nests came about from a book I had looked at in the junior high school library; I think it was entitled “Animal Homes”— although this factoid I don’t remember quite so clearly! But what I do remember in the book was the account which explained that grey squirrels make two types of nests — those in tree cavities, often used in winter, and the one I was going to inspect consisting of a globe-shaped leafy ball, known as a “drey,” wedged amidst branches, also used in winter but more often during the warmer months. The account mentioned that most dreys consisted of a single chamber although occasionally they make two chambers — the equivalent of a foyer leading into the living room. Many years ago I worked in a nature preserve and one day went to look at some white baneberry growing along a trail I knew was developing fruits (also known as doll’s eyes due to the resemblance of the fruits to the eyes once used in old fashioned porcelain dolls, white baneberry is in the buttercup family). As I neared the plants I noticed, at the base of a large chestnut oak on the other side of the trail, a small brownish object. Inspecting it I realized it was a freshly dead flying squirrel. I sadly wondered if the squirrel had misjudged the location of the tree or got carried by the wind and collided with the tree with such force that it caused its demise.
Many years ago I worked in a nature preserve and one day went to look at some white baneberry growing along a trail I knew was developing fruits (also known as doll’s eyes due to the resemblance of the fruits to the eyes once used in old fashioned porcelain dolls, white baneberry is in the buttercup family). As I neared the plants I noticed, at the base of a large chestnut oak on the other side of the trail, a small brownish object. Inspecting it I realized it was a freshly dead flying squirrel. I sadly wondered if the squirrel had misjudged the location of the tree or got carried by the wind and collided with the tree with such force that it caused its demise.






