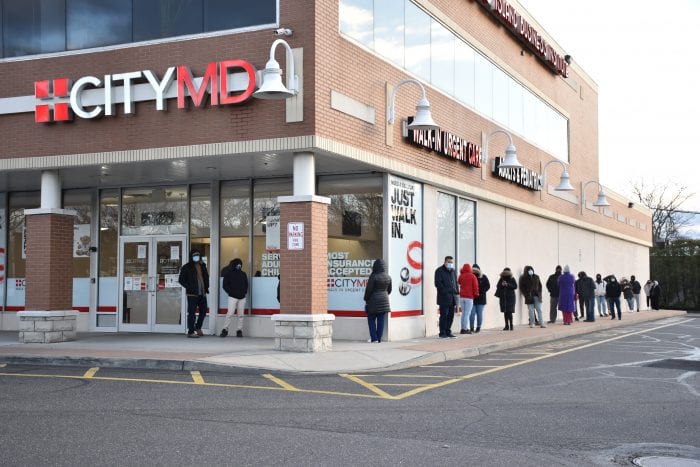
Around this time of year, parking lots are often full.
That’s true of the mall parking lot, as people go out to shop for holiday gifts for their friends and family, but it’s also true, especially this year, for hospitals and urgent care centers.
With the so-called “tridemic,” which is a combination of viruses that typically affect the lungs, including COVID-19, the flu and respiratory syncytial virus (or RSV), infecting people of all ages, the need for health care and medical attention has been high in the weeks leading up to the holidays.
When Dr. Sharon Nachman, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Stony Brook Children’s Hospital, arrives at work at 7 a.m., she drives past urgent center parking lots that are “full for a reason. It’s because people are sick” and need medical attention at the start of the day.
Indeed, the combination of the three viruses, as well as other viruses and bacteria in the community such as adenovirus and enterovirus, has made it difficult for some children to attend schools and for adults to go to work.
For the week ending Dec. 10, which is the most recent period for which data is available, Suffolk County reported 3,936 cases of the flu, which is up 35% just from the prior week. The week ending Dec. 10 alone represents more than half of all flu cases for the entire 2019-2020 season, according to data from the New York State Department of Health.
At the same time, COVID and RSV numbers have climbed.
“We almost doubled our COVID census over the last three to four weeks,” Dr. Michael Khlat, chief medical officer at St. Catherine of Siena Hospital in Smithtown, explained in an email. St. Catherine currently has almost 60 COVID-positive patients. Nearly a third of those patients are admitted for COVID and are receiving intravenous remdesivir, while the others are incidental findings in the context of other medical needs.
“What is special about this surge is that it is inclusive of COVID, influenza, rhinovirus as well as RSV,” Khlat wrote. “The symptoms are very similar, and treatments are all supportive at this time.”
Family gatherings at Thanksgiving contributed to the increase, adding “extra turbocharging to the current respiratory viruses,” Nachman said.
The most vulnerable patients are the immunocompromised, patients with diabetes, chronic lung and cardiac disease, obese residents and patients with chronic liver and kidney disease, Khlat added.
Demand for beds
The influx of patients has meant that St. Catherine has had to increase its capacity of staffing using nursing agencies to meet the needs of the community for “seamless, high-quality care,” Khlat explained.
St. Catherine has also added more providers on the medical wards to care for patients and has load balanced patients with their Catholic services partner St. Charles Hospital and other Catholic Health facilities.
Nachman urged residents to see their primary care doctor if they have routine viral symptoms. Coming directly to the emergency room slows the process of delivering urgent care.
To be sure, Nachman urged anyone with chest pains or stroke-like symptoms should head directly to the emergency room.
Nachman said Stony Brook Children’s Hospital is transitioning to a model in which they triage patients who walk into the ER to assess the need for services.
As people prepare for family gatherings, Nachman suggested that they evaluate the risks of interacting with others.
People with an immune deficiency might want to wear masks or speak outside with others, particularly if someone in the group had one of the respiratory viruses.
Viruses like RSV are generally contagious for about three to eight days, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
RSV spreads through close contact, which means that passing someone in a supermarket won’t likely spread the virus, while sitting and doing homework or eating a meal next to someone could.
As for COVID, Nachman continued to urge people to get the bivalent booster shot.
Every study, she said, shows that the booster drastically reduces the risk of being hospitalized with COVID.