When local teams bring in superstars, the typical sports fan salivates at the prospect of winning a national championship. At the player level, success often breeds success, as other stars and talented players are eager to join teams where they believe in the philosophy of management and the talent of their teammates.
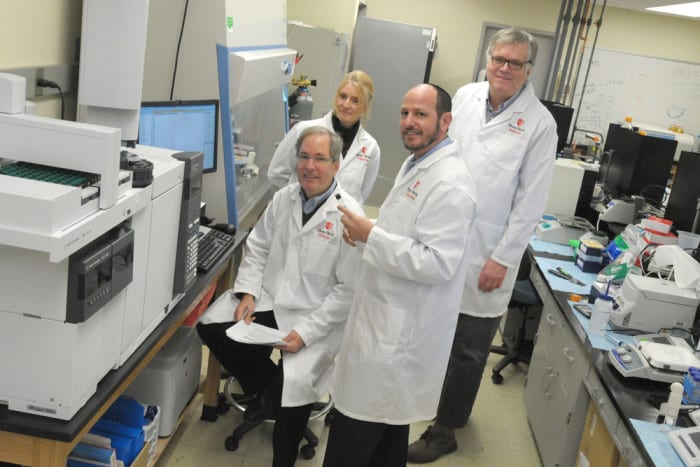
With considerably less fanfare to the typical Suffolk County resident, Stony Brook University has lured some promising researchers from around the country to its growing pathology department. What’s more, the newest members of the team not only have big plans for themselves and their department — they want to help Long Islanders who are battling cancer.
Their research aims to give doctors tools to make a more informed cancer diagnosis, create jobs by developing start-up companies and contribute to the Cancer Center’s goal of receiving a National Cancer Institute designation, which would allow Stony Brook to bid on multimillion dollar grants.
“We are looking for new ways to advance the practice of pathology that will improve the quality of health care nationwide and worldwide,” said Ken Shroyer, the head of the pathology department.
When Shroyer arrived in 2007, he said his first goal was to bring together the talent that was already working at the university. Like siblings who grow apart after they leave home, the clinical research and basic research efforts were working in parallel, rather than together.
After finding common ground for those groups, Shroyer added staff on the clinical side. His next priority, he said, was to boost the research department, which had only one externally funded investigator. That number now stands at 12, with four of the new staff coming in the last 18 months.
The newest researchers joined the pathology department and became leaders in the Cancer Center. “Each of these four individuals has a national reputation and special expertise in a particular area of cancer research,” Shroyer explained, saying he combed the research landscape to find the right experts in their field.
For their part, the new staff share an enthusiasm for the department and a vision for where it’s heading. An expert in finding biomarkers that help identify patients at risk of cancer recurrence, Patricia Thompson plans to encourage basic scientists to make discoveries that affect patient care.
Geoffrey Girnun, meanwhile, continues to study how cancer’s metabolism works, hoping to find differences between cancer cells and normal cells that can become targets for intervention and therapy.
After two decades searching for therapeutic targets for cancer, Scott Powers shifted gears and is now looking for ways to detect cancer earlier.
John Haley is concentrating on exploring how cancer cells escape detection from the immune system and become metastatic.
The director of the Cancer Center, Yusuf Hannun said the partnership with the pathology department is “key to bridging basic research discoveries to cancer specific research and then to human applications,” which could include biomarker discoveries, new therapeutics and individualized and personalized genomic cancer research.
Hannun believes the Cancer Center will continue to push the envelope in diagnosis, treatment and prevention. “We want to bring more special and unique abilities in the war against cancer,” Hannun said. “The inroads in cancer are happening.”
Stony Brook could become involved in prevention, where doctors and scientists work with patients before they develop any signs of the disease. “That domain is clearly within the scope of the Cancer Center,” Hannun said. “We are working on novel biomarkers that could detect very early cancer.”
Hannun described Shroyer as his “alter ego” in the Cancer Center. “He is a very capable leader and does very exciting cutting edge research with a steeped history in early diagnostics.”
Shroyer focuses his work on the discovery of biomarkers that can be used to improve diagnostic accuracy, provide prognostic information and identify more effective treatments for cancer, he said.
Five years from now, the success of the effort will be reflected by the extent to which the group can enhance the national standing of Stony Brook Medicine and the Cancer Center as leading institutions in basic and translational cancer research, Shroyer said.