Three local waterways score in top five for Long Island Sound water chemistry
By Mallie Jane Kim
The water chemistry in Port Jefferson Harbor rates as some of the best among bays in Long Island Sound, according to a new report by bistate environmental organization Save the Sound.
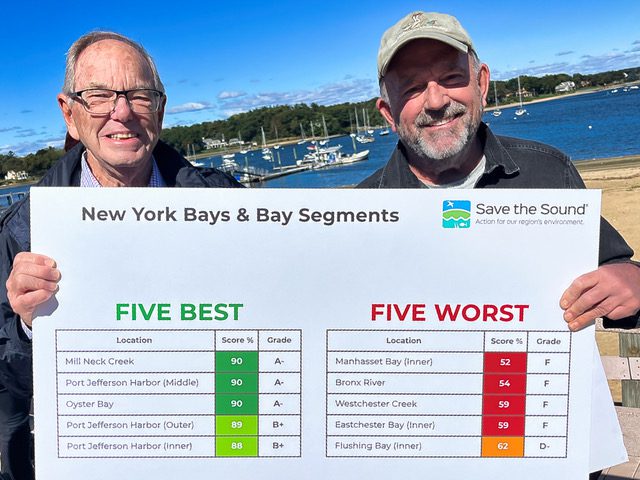
The biannual report card released Oct. 10 was based on data collected in 2023 and showed middle Port Jefferson Harbor, the area near Strong’s Neck and Old Field, tied for top marks with Oyster Bay and Mill Neck Creek, which is also in Oyster Bay. Those three areas earned an “A-” in water chemistry quality.
Inner Port Jefferson Harbor, also known as Setauket Harbor, and outer Port Jefferson Harbor, adjacent to Port Jefferson Village, both received a “B+” to round out the top five. The inner port score is up from a “C” in the report card released in 2022, and the outer harbor is down from “A-.”
“We’re pretty happy about it,” said George Hoffman of the Setauket Harbor Task Force, which has been taking water chemistry measurements at set locations within Port Jefferson Harbor twice a month from May through October since 2018. “We’re seeing small evidence of the improvement that we have advocated for.”
According to Hoffman, the harbors have seen a 50% reduction in nitrogen in the harbor over the last 30 years due to structural improvements in stormwater catchment systems and tightened regulations on nitrogen levels in treated sewage that is piped out into area bays.
The task force was part of securing a grant that paid for a storm water collection system on 25A near Setauket Pond Park, and they regularly educate boaters about a free pump-out service to prevent them from dumping human waste into the harbors.
“We’re like guardians of the harbor,” Hoffman said.
The task force is one of 27 harbor groups in Connecticut and on Long Island that participate in the Save the Sound program. Citizen scientists wake up at early hours to bring scientific equipment to specific locations and take measurements at predetermined depths, together monitoring 57 bay segments in the Sound. They measure things like dissolved oxygen, water clarity, chlorophyll, salinity and temperature. They also look at seaweed accumulation.
To note, area counties are responsible for testing for bacteria and other direct water-quality markers, but the water chemistry factors are also indicative of water health. For example, high chlorophyll levels tend to predict algae blooms.
More than 98% of Long Island’s open waters earned a grade “B” or higher, though several areas close to New York City, in the “Western Narrows,” earned an “F.”
“It’s clear that past investment in nitrogen pollution reduction from wastewater infrastructure is linked to improving the open waters of Long Island Sound,” said Save the Sound’s vice president for water protection, David Ansel, at the report card release “Now, our challenge is to find the political will to extend and expand this investment.”






