By Daniel Dunaief
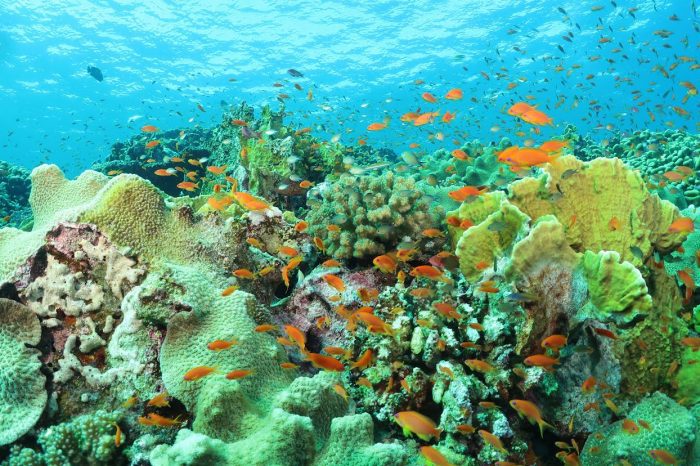
While global warming threatens most of the warm water reefs of the world, the reefs off the coast of Egypt and nearby countries are capable of surviving, and even thriving, in warmer waters.
That, however, does not mean these reefs, which live in the Northern Red Sea and the Gulf of Aqaba and are along the coastline of Egypt, Israel, Jordan and Saudi Arabia, are safe.

Indeed, several factors including unsustainable tourism, sewage discharge, coastal development, and desalination discharge threaten the survival of reefs that bring in more money than the Great Pyramids.
Recently, Karine Kleinhaus, Associate Professor at the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences at Stony Brook University, published a letter in the prestigious journal Science that suggested it’s time to conserve the Egyptian reefs, which constitute about 2 percent of the country’s gross domestic product.
Along with co-author Ellen Pikitch, Endowed Professor of Ocean Conservation Science at SOMAS, whe urged an expanded and fortified marine protected network. As of now, the MPAs only protect about 4 percent of Egypts’s waters.
Kleinhaus, who is President of the Red Sea Reef Foundation which supports scientific research on the reefs, also urged more effective fisheries management and enforcement and an investment in sustainable tourism practices and infrastructure that mitigates land-based pollution, such as waste-water treatment infrastructure and garbage disposal mechanisms.
Science published the letter just days before the 27th Conference of the Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP27), which was held in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt.
During the COP27 conference, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) committed up to $15 million to scale reef-positive blue economic growth and conservation finance in the Red Sea in partnership with the Global Fund for Coral Reefs.
Kleinhaus called the investment a “great start” in protecting a “valuable global treasure. It’s great that the US recognizes the value of this place and that the US is working to contribute to preserve it.”
Other work ahead
Kleinhaus added that considerable works lies ahead to protect one of the few reefs capable of surviving climate change. “We can’t turn the clock back right this minute on warming the oceans, [but] we can stop the conditions that are happening along the Red Sea reef,” she said.
Kleinhaus suggested that all the threats to the reefs are significant. Tourists who are not educated about the fragility of the nature they’ve come to see have damaged the reef. Scuba divers, meanwhile, smash into the reefs with their tanks or drag their regulators and other gauges over the reefs, killing or injuring them.

During Covid travel restrictions, Kleinhaus heard that some parts of the reef, which would have otherwise been damaged by visitors, recovered. Raw sewage and general pollution reaching the reefs also threatens marine life, as is over fishing.
Other reefs, such as the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, have sustained damage from global warming. Kleinhaus described those reefs as a “warning that things are going to change.”
Transplanting parts of the Red Sea reef into other parts of the world to enhance temperature resilience is unlikely to work, Kleinhaus said. These reefs include a diverse ecosystem that supports it, including algae, bacteria, invertebrates and fish.
“We don’t have the scientific knowhow to transplant entire ecosystems at this time,” said Kleinhaus
Evolution of resistance
Kleinhaus explained that heat resistance in the Red Sea reefs developed through natural selection of the coral animals.
During the last Ice Age, the Red Sea got cut off from the Indian Ocean, which meant the temperature climbed and the sea didn’t have any rivers emptying into it. When the Ice Age ended, waters rose into the Red Sea that carried coral from the Indian ocean. The coral that survived had to be tolerant of heat and salt.
“That is the working hypothesis as to why the corals in the northern Red Sea are resilient,” Kleinhaus explained in an email. “They were selected to tolerate hotter water than where they live now.” She called this resilience a “lucky break” for the reefs.
Unusual path
Kleinhaus, who grew up in Westchester, New York, followed an unusual path into marine research.
After attended medical school in Israel at Tel Aviv Medical School, she practiced briefly as an obstetrician in New York. From there, she was the divisional vice president for North America for an Israeli biotechnology company.

Kleinhaus was reading about the effect of heatwaves and global warming on coral reefs. Upset that they were dying, she decided to make a career change and earned her master’s degree in Marine Conservation and Policy at Stony Brook’s School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences.
The common thread in her career is that she was working on cell therapy using cells from the placenta, which is an extension of her obstetrics career. Nowadays, she studies reproduction in corals.
Like humans, corals have the hormones estrogen, progesterone and testosterone. Unlike humans, reefs are hermaphrodites and can switch back and forth between genders. Kleinhaus is exploring the relationship between hormones and the stages of reproduction in coral.
Numerous species of coral spawn once a year within 20 minutes of each other. Their reproduction is tied to the moon cycle. Kleinhaus has collected over two and a half years of data and plans to publish those results in a scientific journal.
She started diving in 1993 and said she enjoys seeing the colors, the shapes, the fish, turtle, octopuses, dolphin and barracuda. Invertebrates and sponges also contribute to the “overwhelming and glorious” experience of visiting reefs.
Down the road, she’d like to collect information from the COP27 conference and write a follow-up piece that would include more deep research about policies and conditions of the reef.
The point of the letter was to “highlight that this has to be protected and it’s a serious interest to everybody in Egypt.”