Architects identify problem spots in PJ flooding

If Port Jefferson experiences another “100 year flood” sooner than a century, then at least it knows where the water is coming from.
Professionals from Port Jefferson-based Campani and Schwarting Architects attended the Aug. 19 village meeting showing map after map of where the problem areas for Port Jeff flooding are, and offered suggestions, some big and some small, of how to combat the issue of flooding.
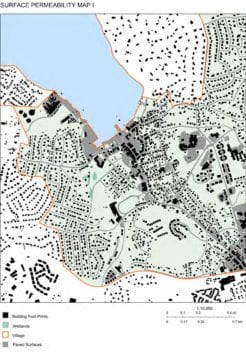
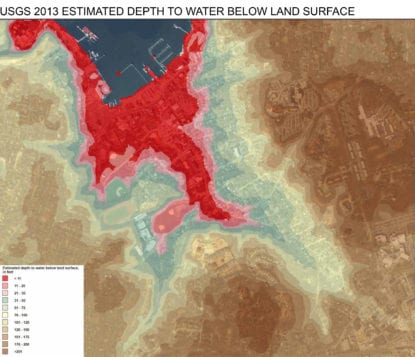
Michael Schwarting said many of the issues are due to an excess of hardscape, both building roofs and roads, and a significant lack of permeable spaces, especially in areas where the depth of the water table is less than 11 feet below ground. Forty percent of village property is non-water-permeable.
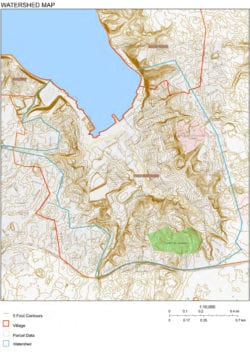
“There’s a fair density of buildings that contribute to the groundwater conditions,” he said. “That contributes in bringing water from the watershed to the lowest point.”
In the three-square-mile village, with a population of just over 8,000, the vast majority of land sits within the Port Jefferson watershed area.
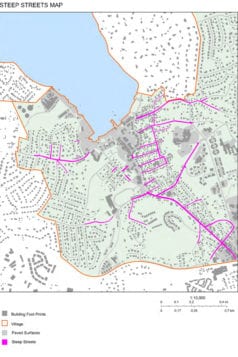
The village tapped the PJ-based architectural firm back in February to construct a water management and storm surge study. While the study still needs to be finalized, with map after map, the architect discussed numerous issues contributing to flooding. One such map described how there were numerous roads that sloped down toward Port Jefferson Harbor. Some roads house catch basins to collect the water before it reaches trouble points, some streets have too few or no catch basins while others had more than is likely necessary.
Last September, Port Jefferson was bowled over with water, with nearly 4 inches of rain collected in a short span of time. Buildings like the Port Jefferson firehouse and the venerable Theatre Three were drowned in 3 to 4 feet of water, causing thousands of dollars in damages in the case of the theater.
The architect said what is likely a major cause of this is due to piping systems that draw a lot of water to the end of Barnum Avenue and the driveway to the Port Jefferson high school. Schwarting added there are stories of when that pipe was being built, children used to walk to school along it, meaning the system sits close to the surface.
“All of these pipes, some coming from North Country Road to Main Street with a lot of catch basins are contributing to this one point at Barnum and high school,” he said.
Mayor Margot Garant said they have received a report from Bohemia-based engineering firm P.W. Grosser Consulting about the pipe running from that culvert to the outfall pipe behind village hall. That report said there was sediment buildup at a low point in the pipe, also showing the pipe had “a pinch and a jog” that leads down toward the harbor.
In June, Port Jefferson Village presented its Waterfront Revitalization Plan to the Long Island Regional Economic Development Council, describing its intention to perform immediately needed maintenance of the storm drainage system and provide emergency equipment to deploy in a rain event to protect properties in the village in catastrophic flooding.
At its July 15 meeting, the village voted unanimously to apply for grant funds not to exceed $1 million from the state Division of Planning’s Local Waterfront Revitalization Program, Empire State Development and any other applicable state agencies.
The architects point out numerous small projects that can be done around the village to aid in flood mitigation, mostly in increasing permeable surfaces around the village. This would include rain gardens and bioswales, a landscape element designed to concentrate or remove debris and pollution out of surface runoff water, permeable paving systems, tree trenches and bioretention planters, acting as plant bed medians with grooves cut in the curb allowing water to drain in and flow into local outlets.
Though the architectural firm also endorsed several major projects, such as “daylighting” Mill Creek and the firm’s own plan proposal, given to the village in 2013, to completely remake the Brookhaven Town parking lot and boat ramp, adding significantly more greenery and passive recreational space in what is now hardscape.