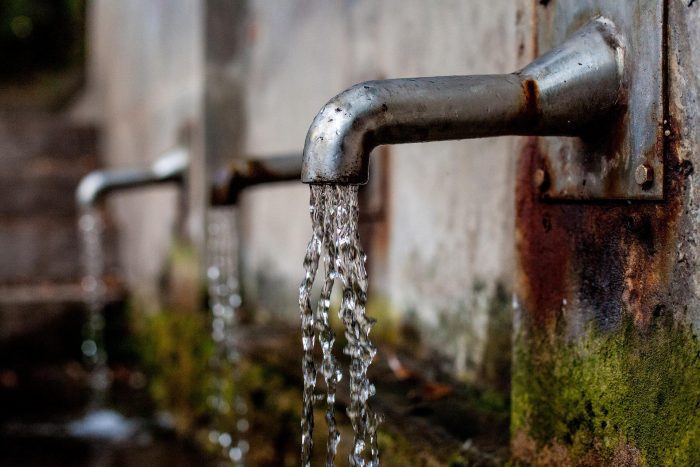
In late July, amid some of the hottest weeks of the year, the Suffolk County Water Authority put out a statement urging residents to conserve water.
“With continued hot and dry weather leading to excessive early morning water use that is pushing water infrastructure to its limits, the Suffolk County Water Authority is urging residents to immediately take steps to conserve water,” the statement read. “Though it is always important to conserve water, during hot and dry periods it is imperative to do so, as residents tend to overwater lawns and set their irrigation timers to the same period of time in the early morning hours.”
SCWA’s deputy chief executive officer for operations, Joe Pokorny, outlined the issues surrounding high temperatures. While the underground aquifer is not at risk of going dry any time soon, he said high water consumption is placing a greater strain on the water authority’s infrastructure.‘We’re asking people to shift their watering patterns to the nonpeak periods.’ — Joe Pokorny
“There is only so much water that we can pump at any given time,” he said. “The aquifers are full of water, but we have limited wells and pumps in the aquifer to deliver water to the customer.”
Strain on the pumps is a problem of supply and demand, according to Pokorny. Higher temperatures increase the demand for water, thereby limiting the supply of water. Pokorny asks that customers be mindful that simultaneous water use can overwhelm their pumps, which could lead to diminished water pressure, possibly harmful to communities.
“We just can’t keep up with demand, so we ask people to curtail [water consumption] because our pumps can’t keep up,” he said. “If that happens for long enough, then we start to see a decline in water pressure and then we get concerned about having enough water available to fight fires and general pressure for people to have in their homes.”
To alleviate the challenges associated with high heat, Suffolk County customers are asked to modify their water habits slightly. By cutting back on water during the peak hours of the highest heat, residents can ease pressure on the pumps.
“We’re asking people to shift their watering patterns to the nonpeak periods,” Pokorny said. “That gives our infrastructure a break. People will still get the water they want, they just get that water at a different time.”
‘Literally, the height of groundwater in the aquifer is declining by many feet during the summer period.’
— Christopher Gobler
The conversation around water conservation prompted a broader discussion around the Long Island water supply. Christopher Gobler, endowed chair of Coastal Ecology and Conservation and a professor at the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences at Stony Brook University, discussed the unique relationship that Long Islanders share with their drinking water.“We have a sole-source aquifer, which means that all of our drinking water comes from underneath our feet,” Gobler said. “When water hits the land, almost all of it seeps into the groundwater and, as it does, it carries with it what’s on the land. And once it’s in our aquifer, that’s our drinking water source.”
For those who tap into the public water supply, the water that they drink typically comes from within just a few miles of their own homes. For these reasons, community members and local governments have a certain obligation to be mindful of their activities on land.
Open space, according to Gobler, is generally most beneficial for promoting water quality within the underground aquifer. These spaces generally act as filters, flushing out contaminants as they work their way through the groundwater and into the aquifer.
“Different land-use practices have different impacts on the way that the water that is falling on land affects our drinking water,” Gobler said. “For example, pristine forests or undisturbed vegetation tend to be really good at, say, taking out nitrogen as water strikes land or falls from the atmosphere.” He added, “Without that, you have just impermeable surfaces and the water may run directly into the groundwater without any benefits of vegetative treatment.”
As summers continue to become longer and hotter due to climate change, the question of the long-term prospects for water supply is likely to arise. Gobler explained that the aquifer is drained and then replenished based on the seasons.
“On average in any given year, about half of the rainfall that falls on Long Island … is what’s called ‘recharged’ into the aquifer,” he said. “The other half that is not recharged undergoes a process called evapotranspiration, which essentially means it either evaporates or is taken up by plants.”
In the warmer months, little to no water gets recharged into the aquifer as it evaporates. Gobler said the window of time during which no recharge is taking place is likely expanding because of climate change.
“I think there’s an old paper from the ‘80s and it said that Sept. 15 is around when the aquifer starts recharging,” he said. “Well, that’s probably not the case anymore. Our falls are getting warmer, and particularly after a really hot and dry summer, the ground is going to be really dry.”
Gobler said SCWA is experiencing two dilemmas at once. During the summer months, the water authority must accommodate both zero recharge to the aquifer and maximal extraction of its water. “Literally, the height of groundwater in the aquifer is declining by many feet during the summer period,” he said.
On the whole, the aquifer is being recharged at a greater rate than it is being extracted from. Long Islanders are not at risk of having their aquifer drained dry. However, climate change is altering the balance, which could create issues decades down the road.
“In broad-brush strokes, we’re fine,” Gobler said, adding, “We’re not in the Southwest of the United States where they’re relying on the Colorado River for their water supply. But we are at a time when the balance of water-in and water-out is getting closer to even.”
Moving forward, residents of Suffolk County should remain aware of the impact that they have on both the quantity and quality of their water supply. “Everybody needs to recognize that there is not only a quantity issue but also a quality issue,” Gobler said. “Everyone impacts both, as do all of the activities that are happening on land.”