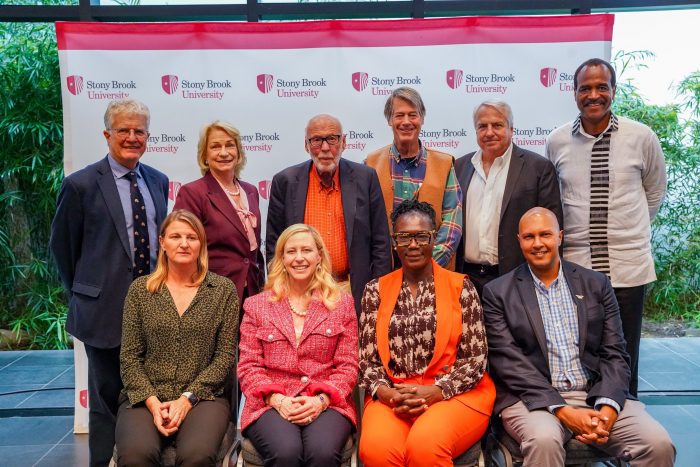
Stony Brook University announces that noted Kenyan entomologist and evolutionary biologist Dr. Dino J. Martins will begin serving as the director of the world-renowned Turkana Basin Institute beginning on September 1, 2024.
Martins has served as the CEO of TBI (Kenya) Ltd. since August 1, 2022, and has been affiliated with TBI since 2011. In this transition from CEO for TBI’s Kenya operations to serving as director across the entire TBI operation, Martins will lead vision and strategy to build upon the institute’s legacy as a critical site of research and discovery around some of the biggest questions of our time concerning our origins, our current role and responsibilities and, most critically, our future on a changing planet. Martins will oversee all Institute activities including recruitment, hiring and evaluation of faculty and postdoctoral researchers; development of facilities and fundraising.
Martins will succeed Dr. Lawrence Martin, who has served as the director of TBI since 2007 and will be named TBI director emeritus, taking on a new role to support TBI’s fundraising efforts by organizing and leading donor visits to Kenya as well as working on several other projects for the university.
“As Lawrence and Dino have worked hand-in-hand over the last several years, this will be a seamless transition in the leadership of TBI. I am grateful to Lawrence for his outstanding leadership of TBI, and I look forward to working with Dino to build upon the incredible foundation that has been established and to elevate TBI to even greater heights,” said Carl Lejuez, Provost of Stony Brook University.
Martins earned his PhD in Organismic and Evolutionary Biology from Harvard University in 2011 before joining TBI as a postdoctoral fellow at Stony Brook University. Martins had previously graduated with a B.A. in Anthropology from Indiana University and with a M.SC. in Botany from the University of KwaZulu Natal. Martins taught in the TBI Origins field school every semester it has been offered since spring of 2011, when the field school began.
Upon completion of his postdoc, Martins took on the position of resident academic director of the TBI Origins Field School and served for three years before accepting the position of executive director of the Mpala Research Center in Laikipia, Kenya, which is overseen by Princeton University, the Smithsonian Institution, the Kenyan Wildlife Service, and the National Museums of Kenya. During his seven years as director, Dino worked to improve the operations and finances of Mpala and expanded the number of institutions conducting research there.
Martins’ research in the Turkana Basin has included the description of new species of bees, including some of the most ancient lineages of bees known and the discovery of genera previously not recorded from Africa. Martins is also a Co-PI of the Turkana Genome Project, which is bringing together dozens of international scientists to look at the complex interactions among human genes, the environment and adaptation. Dino is actively building links and collaborations globally to expand the scientific frontiers of research at TBI. This includes building on the excellent fundamental research around human origins and evolution, to other disciplines that intersect with the fields of evolution and ecology, climate change and the future of sustainable human existence and development.
About TBI
The Turkana Basin Institute (TBI), a Stony Brook University Institute was established by the late celebrated paleoanthropologist, conservationist and Stony Brook University faculty member Richard Leakey. TBI’s mission is to facilitate the logistics of field research in the Turkana Basin, a remote region of sub-Saharan Africa, by providing permanent research support infrastructure. Fundraising to implement the project began in 2005 and funds have been raised every year since for the construction and running costs of two field campuses.
TBI today houses a sophisticated environment to support the research of scientists and students at its two field campuses, TBI-Turkwel and TBI-Ileret, as well as through an administrative support center in Nairobi. Each of the field campuses comprises 15 to 20 major buildings providing accommodation and dining facilities for up to 60 scientists and students as well as the permanent staff of about 40. In addition, there are multiple laboratories, classrooms for field schools, and conference facilities. TBI has purchased and maintains a Cessna 208 Grand Caravan airplane, which operates as Air Turkana, providing reduced cost flying for education and research that is subsidized by revenue from commercial charters.