By John L. Turner
In March of 1995 wildlife officials began a fascinating ecological experiment in Yellowstone National Park, one that is still playing out today twenty-five years later. For in that month they released fourteen grey wolves in the park. Wolves were, as recently as 75 years before, a key ecological component of the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem but hatred and prejudice toward predators at the time resulted in their extermination.
With wolves eliminated from the park, elk populations flourished. Their abundance wasn’t such a good thing for the park’s vegetation though, especially in the richer, low-lying areas along rivers, creeks, and other wetlands where they overgrazed the vegetation, destroying habitat and creating erosion problems. The situation quickly changed with the reintroduction of the wolf and for the past two and a half decades wolves have fundamentally reshaped the park’s ecosystem, causing a series of expected, and a few unexpected, changes.
Elk became both less abundant due to predation and more dispersed in an effort to avoid wolves, allowing riverside forests of cottonwood and aspen to become reestablished. The return of these forests set the stage for beavers to increase. It also meant the growth of more berry producing plants which grizzly bears favored. Coyotes decreased as a direct result of wolf predation and less coyotes meant more foxes which, in turn, affected the abundance of birds, rabbits and other small mammals.
Changes in these species affected other plants due to changes in their grazing and eating intensity of leaves, fruits, and seeds. All of these ripple effects, created by restoring wolves to their rightful place in the Yellowstone ecosystem, underscores the brilliance in John Muir’s famous quote:
“When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to
everything else in the universe.”
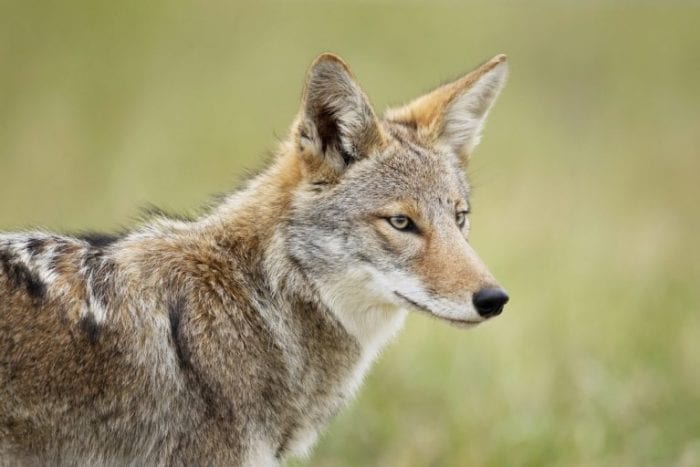
Well, let’s fast forward to the present and focus locally for we have a similar ecological experiment involving the appearance of an apex predator unfolding before us — but its not Grey wolves and a western National Park but the Eastern coyote and the land mass we call Long Island, the last place in the continental United States the coyote was absent from.
The first evidence of coyotes appearing on Long Island happened on June 24, 2013, in Bridgehampton on the South Fork. A potato farmer, working in one of his fields, spotted an animal that looked like a German Shepherd but it wasn’t any breed of domestic dog, nor was it a red or gray fox. He was able to snap a photograph and a review by experts confirmed it as an Eastern coyote, the first that had ever been sighted on Long Island.
Since then there have been several other conclusive sightings of coyotes in a few places and then, most notably, a breeding pair (and subsequent family) set up a territory near LaGuardia Airport. Unfortunately, people began to feed them. Adapting to human presence because of the feeding they became more visible and some neighbors began to view them as a safety threat. They were able to convince staff from the federal Department of Agriculture’s “Wildlife Services” Program (an agency that despite its innocuous sounding name kills wildlife as its main mission) to exterminate the family (save one fortunate individual that escaped).
This was a setback but through subsequent colonization attempts the wily coyote has established itself in northwestern Long Island where several breeding pairs now exist. These occurrences, and past efforts, suggest that it’s but a matter of time before coyotes extend their hold here and fully colonize Long Island. As they do, their presence will likely have far reaching impacts to both human and natural communities, as coyotes are likely to cause ecological effects that will ripple through the natural communities on Long Island and the wildlife species that make them up, not unlike what wolves caused at Yellowstone, although obviously involving different species.
Though generally shy and retiring and typically avoiding direct contact with humans, coyotes will, nevertheless, establish territories adjacent to, and within, suburban developments. This fact suggests Long Islanders should change some behavioral habits to minimize adverse interactions.
For example, coyotes are known to prey on pet and feral cats and small dogs in urban and suburban communities, so it is imperative that pet owners remain diligent and aware. Releasing a pet cat outside to “do its business” (a bad idea because of the ecological damage cats cause by preying on birds and small mammals) in areas where coyotes occur can put the cat’s life in peril. Letting small dogs out into the backyard unattended for the same reason may result in the same outcome.
There are a few strategies that can be employed to reduce the likelihood of coyotes visiting your yard in the first place. These include keeping pet dishes empty outside and securing household garbage.
Another potential source of conflict between humans and coyotes involves livestock and other domestic animals, although this is not likely to become a major issue here given the relatively few sheep, goats, and pigs. In view of the popularity of chickens though, predation might become an issue, so those who have free ranging chickens might want to consider another strategy like indoor enclosures, within which the birds can safely spend the night.
Coyotes have a highly varied diet and some of these diet items can be viewed favorably from a human perspective. For example, in addition to preying on feral cats (and pet cats as mentioned before) that have a devastating impact on backyard birds and small mammals, coyotes eat roadkill thereby helping to clean up roadsides. They also prey on white-tailed deer fawns which may help to reduce their current unhealthy population levels or at least slow down the growth in deer populations.
The current density of deer is having an adverse impact to Long Island forests by eating native plants to such an extent that many forest trees are unable to replace themselves, causing forests to lose their understory and overall diversity. One specific example is the loss of our native orchids such as pink ladies slippers which have become increasingly rare due to deer browsing.
Coyotes also prey on rabbits, opossums, reptile and bird eggs (including the eggs of the ubiquitous Canada Goose), and a variety of berries. Notably, they eat numerous rodents, the reduction of which may be positive in reducing the number of white-footed mice that play a fundamental role in the transmission of the Lyme’s disease spirochete.
Some studies have documented that coyotes often displace fox in shared habitat so one of the ecological effects scientists will look out for is the long-term impact of coyotes on fox populations. There will be interest in assessing their impact on other mammals, such as prey like woodchucks and mammalian competitors like raccoon and fox.
We’re not sure of these ecological outcomes and how precisely these ecological effects will unfold; such is the unpredictability and complexity of the natural world. Perhaps coyotes will have no impact in reducing deer numbers, no role in assisting in the recovery of Long Island’s forests, displacing foxes, or play no part in affecting Lyme’s disease. But like the wolves of Yellowstone National Park, coyotes by their mere presence, as part of the Long Island environment, WILL have an ecological impact and, likely, a broad and significant one at that.
The coyotes have begun the experiment and naturalists and ecologists look forward to seeing how it plays out both for their sake and for the two and four-legged occupants who live here.
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.










 live grey fox, the most recent experience in the autumn two years ago. Spying him before he saw me as I fortuitously was hidden behind a bushy, young Pitch Pine tree, this beautiful grizzled looking animal was patrolling along a sandy trail in the Dwarf Pine Plains of the Long Island Pine Barrens.
live grey fox, the most recent experience in the autumn two years ago. Spying him before he saw me as I fortuitously was hidden behind a bushy, young Pitch Pine tree, this beautiful grizzled looking animal was patrolling along a sandy trail in the Dwarf Pine Plains of the Long Island Pine Barrens.
 A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.






 A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.
A resident of Setauket, John Turner is conservation chair of the Four Harbors Audubon Society, author of “Exploring the Other Island: A Seasonal Nature Guide to Long Island” and president of Alula Birding & Natural History Tours.


