By Tara Mae
Serving in one of the 19th century’s most profitable and perilous industries, Black mariners risked their lives, livelihoods, and liberty in the pursuit of a meager but available wage. The Whaling Museum of Cold Spring Harbor’s new two year special exhibition, From Sea to Shining Sea: Whalers of the African Diaspora, examines the too-frequently ignored Black heritage and contributions to the whaling industry.
Guest curated by Dr. Georgette Grier-Key, Executive Director of Eastville Community Historical Society in Southampton, the exhibit opened on Feb. 15 and will run through 2024.
“This exhibit is focused on expanding and expounding on stories of Black mariners in maritime history and sharing the untold/under-told stories of whalers of African descent and whalers of color in our whaling history,” said Gina Van Bell, Assistant Director of the Whaling Museum.

The exhibit casts the African American whalers for what they were: main characters in their own lives, who took up whaling as a means of survival and, in many cases, transformed it into a stepping stone for other successes.
“We want people to understand the vastness of their lives, which is sometimes missed,” Dr. Grier-Key said. “We really wanted to focus on that, just going a little bit deeper and not stopping at the surface of BIPOC whalers and their lives, probing what they were able to do and what it meant in the context of the times. We want to offer more of a world view, a holistic look at whalers and their lives.”
Like a ship’s crew comprised of many individual roles, this exhibit consists of items from the museum’s own archives as well as items on loan from 10 different historical organizations. It honors the artistic pull the sea has had on creators throughout the centuries by incorporating art inspired by the water and maritime culture.
Awash with primary source documents, artifacts, and artwork, the interactive display explores what life was like at sea and ashore for non-white mariners while contextualizing the greater experience of people of color who in lived in coastal areas during the 1800s.
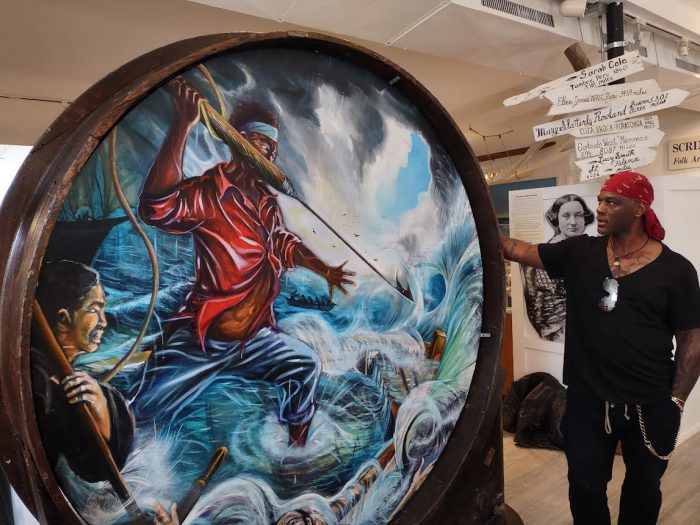
The story of one such Black man, Pyrrhus Concer, inspired local artist and Southampton gallery owner Hulbert Waldroup, whose oil on canvas painting The Life and Legend of Pyrrhus Concer (2022), is included in the show. This circular painting, reminiscent of the shape of a porthole, depicts in vibrant colors the nautical scope of Concer’s life, framed in repurposed boat wood rescued from a salvage yard.
A formerly enslaved Southampton man of African descent, Concer became a sailor after he was freed in 1832 (slavery in New York formerly ended in 1827.) He sailed aboard the whaling ship Manhattan, the first American ship to visit Tokyo, Japan, where he was greeted with wonder, being the first Black man many of the Japanese had ever seen.
“It was painted purely out of love and respect for Concer,” Waldroup said. Drawn to the stories of Black cowboys and whalers, who have traditionally been erased from popular lore, Waldroup was intrigued by Concer, whose career as a whaler enabled him to establish himself as a businessman and philanthropist on the shore.
Whaling and other maritime endeavors were often precursors for the precarious promise of more stable lives away from the water, but such pursuits were fraught.

“The first Black Americans who were treated as ‘citizens,’ in a way, were sailors. During the nineteenth century, working as a merchant seaman or whaler was one of the few occupations which offered free Black people a relative level of independence and self-sufficiency, along with the opportunity to travel the world with a Seaman’s Protection Certificate,” said Executive Director of the Whaling Museum Nomi Dayan.
From circa 1796-1940, American mariners carried this document as proof as citizenship. It was particularly vital to Black sailors, as they were not defined as citizens under the law until the ratification of the 14th Amendment in 1868.
African Americans took very big risks for mitigated reward when they sailed with whaling ships. When docking in harbors of the South, for example, they were subject to being jailed or captured and sold into slavery.
From Sea to Shining Sea features receipts for the imprisonment and release of Alfred Gall, an African American crew member on the Cold Spring Harbor Whaling Company’s Tuscarora, whose captain had to bail him out of jail. His crime? Being a free Black man in a Southern port.
Yet despite the marine and manmade dangers, whaling was considered to be a viable, even comparably steady trade. The sea offered a sort of freedom to men who might not find it on land as long as the voyage did not kill them.
“Whaling employed the most diversified workforce among all other occupations at the time. Many whalers of color who endured hard work, poor pay, awful living conditions, and serious danger, chose to work at sea because work options on land were limited,” Dayan said. “African American whalers who faced work discrimination on land were more likely than other racial groups to continue whaling.”
Whaling records indicate that rank prevailed over the color of one’s skin. Recruiters did not record race, just complexion, which was a subjective categorization. Herman Melville, the white author of Moby Dick was even listed as “dark.”
Light-skinned African American sailors had more opportunity for advancement. And while Black whalers did encounter barriers to advancing their ranks and were relegated to service-based positions, they usually earned the same rate of pay as other men of the same rank.
“On these voyages, your life and your counterpart’s life depended on how well you did you job. So in that way, you were equal in the sense of doing the work … tough, backbreaking work that was dangerous — you could lose your life but could achieve financial success,” Dr. Grier-Key said.
This made whaling unique to other industries. Whaling could provide a sort of networking opportunity for the African Americans and other people of color. Ancillary jobs associated with the sea were also available to them, such as being caulkers and coopers. Wives of BIPOC whalers might be seamstresses for the captains’ wives.
Such a utilization of community building is a trait understood by the team behind this exhibit, for whom From Sea to Shining Sea is a labor of love and longevity, part of the Whaling Museum’s ongoing efforts to share the whaling tales generally omitted from the history books.
Dr. Grier-Key and Dayan served together on the board for the Museum Association of New York, and Dr. Grier-Key knew of Waldroup through her work in the Southampton community. Together with Van Bell, they coordinated an exhibit that the stories of BIPOC whalers are no longer submerged in the murky annals of time.
RELATED PROGRAMS:
Black History: Whaleboat Chat
Join the special edition of a Whaleboat Chat highlighting the Whalers of the African Diaspora exhibition on Tuesday, Feb. 21 at noon. Gather around the star of the museum’s collection, the whaleboat, and listen as a staff member shares the tale of the dangerous Nantucket Sleighride and the brave whalers. Free with admission. No reservations necessary.
Black History: Build-A-Boat Workshop
Drop by the Museum any time on Feb. 21 and Feb. 24 from 1 to 3 p.m. to learn about African American whalers who designed, built and worked on whaling ships in the 19th century and then imagine, design and create unique wooden vessel models out of a variety of materials in this open-ended workshop. Entry: Admission + $10 participant.
Beyond the Book
Join the Whaling Museum’s new book club! Read Whaling Captains of Color by Skip Finley at home and go on new adventures through history. Then meet at the museum on Feb. 23 at 6:30 p.m. to dive deeper into the story through connections with the Museum’s collection. Adults only. $15 per participant. Registration required.
The Whaling Museum, 301 Main Street, Cold Spring Harbor is open Thursday to Sunday, 11 a.m. to 4 p.m. during the winter months, and Tuesday to Sunday, 11 a.m. to 4 p.m. in the summer. Admission is $8 for adults; $6 for seniors; $6 for children ages 4-17; free for children three years old and younger; and free for members. For more information, visit www.cshwhalingmuseum.org or call 631-367-3418.