Stress management and diet can have positive effects
By David Dunaief, MD

According to estimates, 10 to 15 percent of the population suffers from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms, although only five to seven percent have been diagnosed (1).
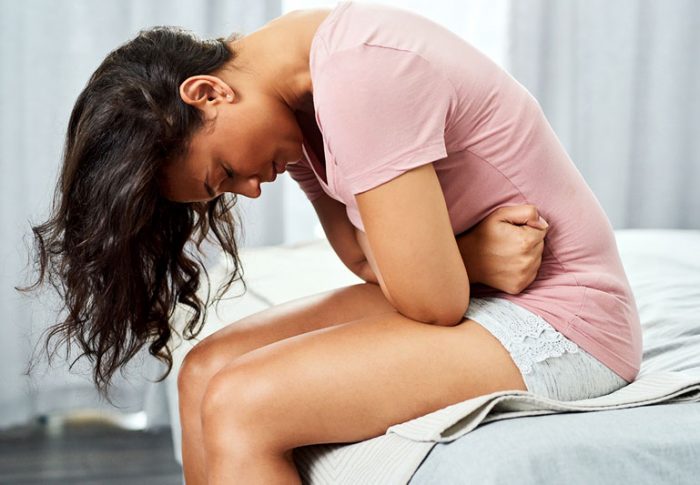
Symptoms can directly affect quality of life. They include abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, constipation and diarrhea.
Diagnosing IBS is challenging. While the general perception is that IBS symptoms are somewhat vague, there are discrete criteria physicians use to provide a diagnosis it and eliminate more serious possibilities.
The Rome IV criteria comprise an international effort to help diagnose and treat functional gastrointestinal disorders. Using these criteria in combination with a careful history and physical exam helps provide a diagnosis.
So, what can be done to improve IBS? There are a number of possibilities.
Mental state
The “brain-gut” connection is real. It refers to the direct connection between mental state, such as nervousness or anxiety, to gastrointestinal issues, and vice versa.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction was used in a small, but randomized, eight-week clinical trial with IBS (2). Those in the mindfulness group (treatment group) showed statistically significant results in decreased severity of symptoms compared to the control group, both immediately after training and three months post-therapy.
Those in the treatment group were instructed to do meditation, gentle yoga and “body scanning” — focusing on one area of the body for muscle tension detection. The control group attended an IBS support group once a week.
A preliminary study has suggested there may be a link between IBS and migraine and tension-type headaches. The study of 320 participants, 107 with migraine, 107 with IBS, 53 with episodic tension-type headaches (ETTH), and 53 healthy individuals, identified significant occurrence crossover among those with migraine, IBS and ETTH. Researchers also found that these three groups had at least one gene that was different from that of healthy participants. Their hope is that this information will lead to more robust studies that could result in new treatment options (3).
Gluten
In a small randomized clinical trial, patients who were given gluten were more likely to complain of uncontrolled symptoms than those who were given a placebo, 68 percent vs. 40 percent, respectively.
These results were highly statistically significant (4). The authors concluded that nonceliac gluten intolerance may exist. Gluten sensitivity may be an important factor in the pathogenesis of some IBS patients (5).
I suggest to my patients that they might want to start avoiding gluten and then add it back into their diets slowly to see the results.
Fructose
Some IBS patients may suffer from fructose intolerance. In a prospective (forward-looking) study, IBS researchers used a breath test to examine this possibility. The results were dose dependent. When patients were given a 10 percent fructose solution, only 39 percent tested positive for fructose intolerance, but when they were given a 33 percent solution, 88 percent of patients tested positive.
The symptoms of fructose intolerance included flatus, abdominal pain, bloating, belching and alternating bowel habits. The authors concluded that avoidance of fructose may reduce symptoms in IBS patients (6).
According to another study, about one-third of IBS patients are fructose intolerant. When on a fructose-restricted diet, symptoms appeared to improve (7). Foods with high levels of fructose include certain fruits, like apples and pears, but not bananas.
Lactose
Another small study found that about one-quarter of patients with IBS also have lactose intolerance. Two things are at play here. One, it is very difficult to differentiate the symptoms of lactose intolerance from IBS. The other is that most IBS trials are small and there is a need for larger trials.
Of the IBS patients who were also lactose intolerant, there was a marked improvement in symptomatology at both six weeks and five years when placed on a lactose-restrictive diet (8).
Though small, the trial results were statistical significant, which is impressive. Both the durability and the compliance were excellent, and visits to outpatient clinics were reduced by 75 percent. This demonstrates that it is most probably worthwhile to test patients for lactose intolerance who have IBS.
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics from a study that reviewed 42 trials shows that there may be a benefit to probiotics, although the endpoints were different in each trial. The good news is that most of the trials reached one of their endpoints (9).
Probiotics do show promise, including the two most common strains, Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteri, which were covered in the review.
All of the above gives IBS patients a sense of hope that there are options for treatments that involve modest lifestyle changes. I believe there needs to be a strong patient-doctor connection in order to choose the appropriate options that result in the greatest symptom reduction.
References:
(1) American College of Gastroenterology [GI.org]. (2) Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;106(9):1678-1688. (3) American Academy of Neurology 2016, Abstract 3367. (4) Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Mar;106(3):508-514. (5) Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Mar;106(3):516-518. (6) Am J Gastroenterol. 2003 June;98(6):1348-1353. (7) J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar;42(3):233-238. (8) Eur J Gastroen-terol Hepatol. 2001 Aug;13(8):941-944. (9) Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Feb;35(4):403-413.
Dr. David Dunaief is a speaker, author and local lifestyle medicine physician focusing on the integration of medicine, nutrition, fitness and stress management. For further information, visit www.medicalcompassmd.com.










 There was an inverse relationship between the amount of meat consumed and cataract risk. In other words, those who ate a great amount of meat were at higher risk of cataracts. “Meat” included red meat, fowl and pork. These results followed what we call a dose-response curve.
There was an inverse relationship between the amount of meat consumed and cataract risk. In other words, those who ate a great amount of meat were at higher risk of cataracts. “Meat” included red meat, fowl and pork. These results followed what we call a dose-response curve.




