Accessing medical treatment on Long Island has become easier for 9/11 first responders.
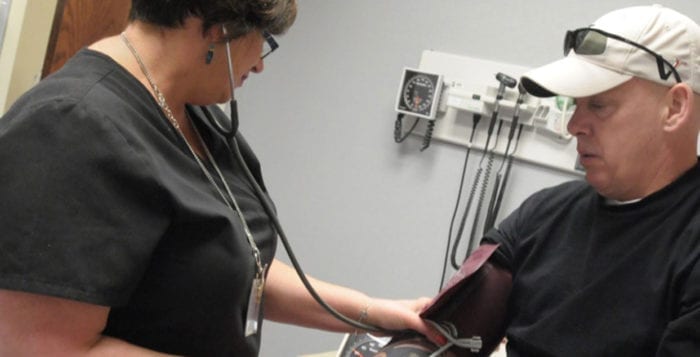
Stony Brook WTC Wellness Program celebrated the official opening of its new one-stop health clinic in Commack Nov. 28. The program relocated from Islandia to the Stony Brook Medicine Advanced Specialty Care building, located at 500 Commack Road. The move allowed the program to expand from a monitoring facility into a 20,000-square-foot, integrative clinic where World Trade Center responders can receive more comprehensive medical treatment under one roof.
Dr. Benjamin Luft, program director and principal investigator, said the clinic is dedicated to caring for approximately 10,000 patients suffering from illnesses after volunteering at Ground Zero after 9/11. He said the responders suffer from a wide variety of conditions and the new location will provide the medical staff more resources. Among the new services available will be blood testing and imaging, which weren’t available in Islandia and caused patients to have to go elsewhere.
“This is ideal for the World Trade responder patient population, and the reason why is these patients who have been so severely affected by the World Trade Center disaster have a compendium of various abnormalities and disorders which are directly related to 9/11,” Luft said. “These included diseases ranging from psychiatry diseases to respiratory and gastrointestinal problems, to cancer.”
“The program is now a state-of-the-art facility that not only monitors you, but treats you and gives you top-notch medical care all in one facility.”
— John Feal
The doctor said the program has a research team dedicated to studying neurocognitive problems, autoimmune issues and cancer-related illness. The new Commack location has an in-house laboratory that will make accessing patients’ samples and processing them easier. He said many of the illnesses related to the disaster were not initially recognized, and the number of patients has grown approximately 8 to 10 percent each year since the monitoring clinic first opened on the Stony Brook University campus shortly after 9/11.
The day of the Commack grand opening, the Stony Brook WTC Wellness Program honored John Feal, a first responder and founder of the Fealgood Foundation. A Nesconset resident and Commack native, he said having the clinic where he grew up is special to him. Feal and members of his organization worked tirelessly to get the James Zadroga 9/11 Health and Compensation Act passed in Dec. 2010 and again in 2015. The act enables first responders, volunteers and survivors of the Sept. 11 attacks to receive health monitoring and financial aid.
Luft said at first the program treated many patients who lacked medical insurance coverage. “So when they got sick, they didn’t have health insurance or have someone to take care of their acute problems,” he said. “We established our clinic to do that at no additional costs to the patients.”
Feal, who was a patient at the Islandia clinic and recently had his physical in Commack, said he was impressed with the new location.
“The program is now a state-of-the-art facility that not only monitors you, but treats you and gives you top-notch medical care all in one facility,” Feal said.
He said having a one-stop clinic is important to many, especially for those who have become too frail to travel. Aging is an issue as many are now in their mid-50s or older.
“As we get further away from 9/11, the illnesses are getting worse,” Feal said. “One, because of age and, two, because with these illnesses, some latency periods and manifestations in the body take this long.”
The first responder said it was humbling to be honored for his work Nov. 28.
“We’re talking about human life, and I’m never going to apologize for anything I ever said or did, because at the end of the day I only care about helping those who are sick from 9/11,” Feal said. “And so many people are getting sick. It’s not ending anytime soon.”