Focus on nutritional options for improving outcomes
By David Dunaief, M.D.

Autoimmune diseases affect approximately 23.5 million Americans, most of them women. More than 80 conditions have autoimmunity implications (1). Among the most common are rheumatoid arthritis (RA), lupus, thyroid (hypo and hyper), psoriasis, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. In all autoimmune diseases, the immune system inappropriately attacks organs, cells and tissues of the body, causing chronic inflammation, the main consequence of immune system dysfunction, and it is the underlying theme tying these diseases together. Unfortunately, autoimmune diseases tend to cluster (2). Once you have one, you will likely acquire others.
Drug treatments
The mainstay of treatment is immunosuppressives. In RA where there is swelling of joints bilaterally, the typical drug regimen includes methotrexate and TNF (tumor necrosis factor) alpha inhibitors, like Remicade (infliximab). These therapies seem to reduce underlying inflammation by suppressing the immune system and interfering with inflammatory factors, such as TNF-alpha. The disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs may slow or stop the progression of joint destruction and increase physical functioning. Remicade reduces C-reactive protein (CRP), a biomarker of inflammation.
However, there are several concerning factors with these drugs. First, the side effect profile is substantial. It includes the risk of cancers, opportunistic infections and even death, according to black box warnings (the strongest warning by the FDA) (3). Opportunistic infections include diseases like tuberculosis and invasive fungal infections. It is no surprise that suppressing the immune system would result in increased infection rates. Nor is it surprising that cancer rates would increase, since the immune system helps to fend off malignancies. In fact, a study showed that after 10 years of therapy, the risk of cancer increased by approximately fourfold with the use of immunosuppressives (4).
Second, these drugs were tested and approved using short-term randomized clinical trials, but many patients are put on these therapies for 20 or more years.
So what other methods are available to treat autoimmune diseases? These include medical nutrition therapy using bioactive compounds, which have immunomodulatory (immune system regulation) effects on inflammatory factors and on gene expression and supplementation.
Nutrition and inflammation
Raising the level of beta-cryptoxanthin, a carotenoid bioactive food component, by a modest amount has a substantial impact in preventing RA. While I have not found studies that specifically tested diet in RA treatment, there is a study that looked at the Mediterranean-type diet in 112 older patients where there was a significant decrease in inflammatory markers, including CRP (5).
In another study, participants showed a substantial reduction in CRP with increased flavonoid levels, an antioxidant, from vegetables and apples. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid found in fish, was shown to significantly reduce a host of inflammatory factors in mice, including TNF-alpha (6).
Fish oil

Stock photo
Fish oil helps your immune system by reducing inflammation and improving your blood chemistry, affecting as many as 1,040 genes (7). In a randomized clinical study, 1.8 grams of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplementation had anti-inflammatory effects, suppressing cell signals and transcription factors (proteins involved with gene expression) that are pro-inflammatory, such as NFkB.
In RA patients, fish oil helps suppress cartilage degradative enzymes, while also having an anti-inflammatory effect (8). When treating patients with autoimmune disease, I typically suggest about 2 grams of EPA plus DHA to help regulate their immune systems. Don’t take these high doses of fish oil without consulting your doctor, since fish oil may have blood thinning effects.
Probiotic supplements
The gut contains approximately 70 percent of your immune system. Probiotics, by populating the gut with live beneficial microorganisms, have immune-modulating effects that decrease inflammation and thus are appropriate for autoimmune diseases. Lactobacillus salvirus and Bifidobacterium longum infantis are two strains that were shown to have positive effects (9, 10).
In a study with Crohn’s disease patients, L. casei and L. bulgaricus reduced the inflammatory factor, TNF-alpha (11). To provide balance, I recommend probiotics with Lactobacillus to my patients, especially with autoimmune diseases that affect the intestines, like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.
Fiber
Fiber has been shown to modulate inflammation by reducing biomarkers, such as CRP. In two separate clinical trials, fiber either reduced or prevented high CRP in patients. In one, a randomized clinical trial, 30 grams, or about 1 ounce, of fiber daily from either dietary sources or supplements reduced CRP significantly compared to placebo (12).
In the second trial, which was observational, participants who consumed the highest amount of dietary fiber (greater than 19.5 grams) had reductions in a vast number of inflammatory factors, including CRP, interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and TNF-alpha (13).
Immune system regulation is complex and involves over 1,000 genes, as well as many biomarkers. Dysfunction results in inflammation and potentially autoimmune disease. We know the immune system is highly influenced by bioactive compounds found in high nutrient foods and supplements. Therefore, bioactive compounds may work in tandem with medications and/or may provide the ability to reset the immune system through immunomodulatory effects and thus treat and prevent autoimmune diseases.
References:
(1) niaid.nih.gov. (2) J Autoimmun. 2007;29(1):1. (3) epocrates.com. (4) J Rheumatol 1999;26(8):1705-1714. (5) Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Jan;89(1):248-256. (6) Chem Biol Interact. 2011 May 20. (7) Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Aug;90(2):415-424. (8) Drugs. 2003;63(9):845-853. (9) Gut. 2003 Jul;52(7):975-980. (10) Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999 Jul-Nov;76(1-4):279-292. (11) Gut. 2002;51(5):659. (12) Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(5):502-506. (13) Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010 May 13;7:42.
Dr. Dunaief is a speaker, author and local lifestyle medicine physician focusing on the integration of medicine, nutrition, fitness and stress management. For further information, visit www.medicalcompassmd.com or consult your personal physician.


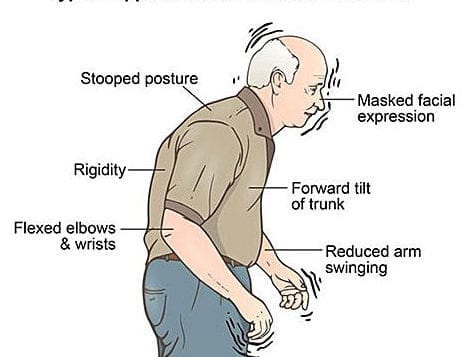
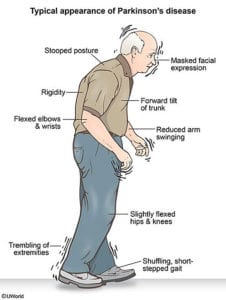 When we typically think of using CoQ10, a coenzyme found in over-the-counter supplements, it is to compensate for depletion from statin drugs or due to heart failure. Doses range from 100 to 300 mg. However, there is evidence that CoQ10 may be beneficial in Parkinson’s at much higher doses.
When we typically think of using CoQ10, a coenzyme found in over-the-counter supplements, it is to compensate for depletion from statin drugs or due to heart failure. Doses range from 100 to 300 mg. However, there is evidence that CoQ10 may be beneficial in Parkinson’s at much higher doses.








 Fiber has very powerful effects on our overall health. A very large prospective cohort study showed that fiber may increase longevity by decreasing mortality from cardiovascular disease, respiratory diseases and other infectious diseases (1). Over a nine-year period, those who ate the most fiber, in the highest quintile group, were 22 percent less likely to die than those in lowest group. Patients who consumed the most fiber also saw a significant decrease in mortality from cardiovascular disease, respiratory diseases and infectious diseases. The authors of the study believe that it may be the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects of whole grains that are responsible for the positive results.
Fiber has very powerful effects on our overall health. A very large prospective cohort study showed that fiber may increase longevity by decreasing mortality from cardiovascular disease, respiratory diseases and other infectious diseases (1). Over a nine-year period, those who ate the most fiber, in the highest quintile group, were 22 percent less likely to die than those in lowest group. Patients who consumed the most fiber also saw a significant decrease in mortality from cardiovascular disease, respiratory diseases and infectious diseases. The authors of the study believe that it may be the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects of whole grains that are responsible for the positive results.


