Most risk factors are modifiable
By David Dunaief, M.D.

Gout is thought of as an inflammatory arthritis. It occurs intermittently, affecting the joints, most commonly the big toe. The symptoms are acute (sudden onset) and include extremely painful, red, swollen and tender joints. In terms of symptoms, if you have ever had kidney stones, gouty arthritis is just as painful.
Uric acid (or urate) levels are directly related to the risk of gout attacks. As uric acid levels increase, there is a greater chance of urate crystal deposits in the joints. Although, and unfortunately, some patients can still experience gout attacks without high levels of uric acid.
This disease affects approximately 8.3 million people in the United States (1). This number has doubled since the 1960s. Men between 30 and 50 years old are at much higher risk for their first attack (2). For women, most gout attacks occur after menopause.
There are a number of potential causes of gout, as well as ways to prevent and treat it. The most common contributors include drugs, such as diuretic use; alcohol intake; uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure); obesity; and sweetened beverage and fructose intakes (3). Though heredity plays a role, these risk factors are modifiable.
The best way to prevent and treat gout is by modifying medications and lifestyle. One simple lifestyle change is to make certain, just like with kidney stone prevention, that those susceptible to gout attacks remain hydrated and consume plenty of fluids.
Just like there are medications that may cause gout, there are also medications that can treat and help prevent gout. If you do get a gout attack, NSAIDs such as indomethacin or steroids such as a Medrol pack help treat the symptoms. In terms of prevention, allopurinol helps to reduce the risk of a gout attack.
I thought we might look at gout by using a case study. I had a patient who had started a nutrient-dense, plant-based diet. Within two weeks, she had a gout episode. Initially, it was thought that her change in diet with increased plant purines might have been an exacerbating factor. Purines are substances that raise the level of uric acid. So, it is not surprising that foods with containing purines might substantiate a gout attack. However, not all purines equally raise uric acid levels.
Animal versus plant proteins
In a case-crossover (epidemiologic forward-looking) study, it was shown that purines from animal sources increase our levels of purines far more than those from plant sources (4). The risk of a gout incident was increased approximately 241 percent in the group consuming the highest amount of animal products, whereas the risk of gout was still increased for those consuming plant-rich purine substances, but by substantially less: 39 percent.
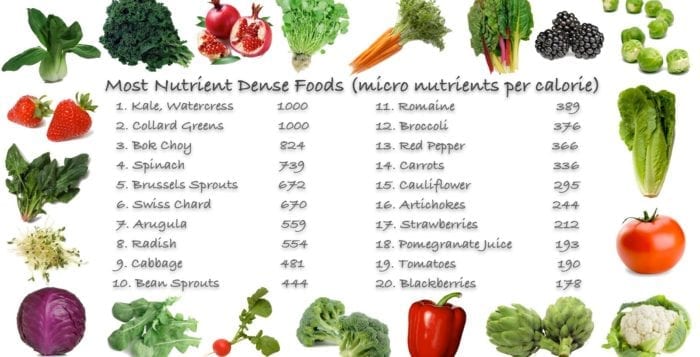
The authors believe that decreasing the use of purine-rich foods, especially from animal sources, may decrease the risk of incidences and recurrent episodes of gout. Plant-rich diets are the preferred method of consuming proteins for patients who suffer gout attacks, especially since nuts and beans are excellent sources of protein and many other nutrients.
In another study, meats — including red meat, pork and lamb — increased the risk of gout, as did seafood (5). However, purine-rich plant sources did not increase risk of gout. Low-fat dairy actually decreased the risk of gout by 21 percent. The study was a large observational study involving 49,150 men over a duration of 12 years.
There are several more studies indicating and reaffirming that plant foods do not increase the risk of gout attacks. The Mayo Clinic also suggests that plants do not increase the risk of gout. When considering my patient’s circumstances, it was unlikely that her switch to a nutrient-dense, plant-rich diet had increased her risk of gout.
Diuretics (water pills)
My patient was on a diuretic called hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension (high blood pressure). There are several medications thought to increase the risk of gout, including diuretics and chronic use of low-dose aspirin. In the ARIC study, patients who used diuretics to control blood pressure were at a 48 percent greater risk of developing gout than nonusers (6). In fact, nonusers had a 36 percent decreased risk of developing gout. This study involved 5,789 participants and had a fairly long duration of nine years. The longer the patient is treated with a diuretic, the higher the probability they will experience gout. It is likely that my patient’s diuretic contributed to her gout episode.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C may reduce gout risk. In the Physicians Follow-up Study, a 500-mg daily dose of vitamin C decreased levels of uric acid in the blood (9). However, be careful with vitamin C supplementation because it can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Medical conditions
There are a number of medical conditions that may impact the risk of gout. These include uncontrolled high blood pressure, diabetes and high cholesterol (7). My patient’s high blood pressure was under control, but she also had diabetes and high cholesterol. These disorders may have also contributed.
Obesity
Obesity, like smoking, seems to have its impact on almost every disease. In the CLUE II study, obesity was shown to not only increase the risk of gout but also to accelerate the age of onset (8). Those who were obese experienced gout three years earlier than those who were not. Even more striking is the fact that those who were obese in early adulthood had an 11-year earlier onset of gout. The study’s duration was 18 years. My patient was obese and had just started to lose some weight before the gout occurred.
Prevention
The key to success with gout lies with prevention. Patients who do get gout writhe in pain. Luckily, there are modifications that significantly reduce the risks. They involve very modest changes, such as not using medications called diuretics in patients with a history of gout; losing weight for obese patients; and substituting more plant-rich foods for meats and seafood. Increasing levels of uric acid may be a useful biomarker for indicating an increased risk of gouty arthritis attacks. However, gout attacks do occur without a rise in uric acid levels, so it is not a perfect. Although the cause of gout may be apparent to you, always check with your doctor before changing your medications or making significant lifestyle modifications, as we have learned from this case study of my patient.
References:
(1) Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Oct;63(10):3136-3141. (2) Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:Suppl 1:S2. (3) Am Fam Physician. 2014 Dec 15;90(12):831-836. (4) Ann Rheum Dis. online May 30, 2012. (5) NEJM 2004;350:1093-1103. (6) Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jan;64(1):121-129. (7) www.mayoclinic.com. (8) Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Aug;63(8):1108-1114. (9) J Rheumatol. 2008 Sep;35(9):1853-1858.
Dr. Dunaief is a speaker, author and local lifestyle medicine physician focusing on the integration of medicine, nutrition, fitness and stress management. For further information, visit www.medicalcompassmd.com or consult your personal physician.