By David Dunaief, M.D.

Many of us are starting to plan for Labor Day weekend, whether this means preparing for cookouts or getting ready for the new school year. It’s a good time to provide some food for thought — pun intended.
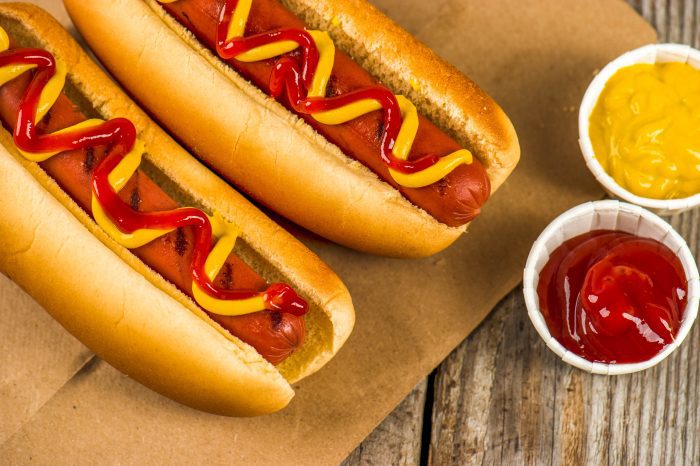
The barbecues associated with this weekend usually include hot dogs, hamburgers, sausages, bacon, poultry and fish. Sounds mouthwatering, doesn’t it? Unfortunately, there are more and more studies that implicate processed meats as a potential cause of diseases, including several cancers, heart disease, stroke and diabetes.
Processed meats are those that have been cured, salted, fermented or smoked. A short list of processed meats includes hot dogs, ham, pepperoni, bacon, sausages and deli meats, among others. While these are barbecue and picnic favorites, more importantly, deli meats are often used as sandwich staples for adults’ and school children’s lunches. Turkey and roast beef were typically in my lunch box when I was growing up. The prevailing thought at the time was that deli meats that were made without nitrates, nitrites and preservatives were healthy. Unfortunately, more recent studies show otherwise.
Does processed meat increase stroke risk?
In a large, prospective cohort study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition in 2011, results showed a 23 percent increased risk of stroke in men who consumed the most processed meats. Deli meats, including low-fat turkey, ham and bologna, considered healthy by some, were implicated. The 40,291 Swedish participants were followed for about ten years.
The increased risk could be attributed potentially to higher sodium content in processed meats. Another mechanism could be nitrates and nitrites. Interestingly, participants were mostly healthy, except for the processed meats. Thus, processed meats could interfere with the benefits of a heart-healthy diet, according to the authors.
How do processed meats affect cancer risk?
Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine has been aggressive about communicating the connection between processed meats and cancer. They’ve run television ads, including ones encouraging us to “break up with bacon,” and a billboard portraying a cigarette pack with hot dogs, not cigarettes, sticking out the top. The message read, “Warning: Hot dogs can wreck your health.”
Let’s look at some of the studies that have prompted these warnings.
In the large prospective Multiethnic Cohort Study, there was a 68 percent increased risk of pancreatic cancer in participants who ate the highest amounts of processed meats compared to the lowest (1). Participants were followed for seven years. The authors believe that carcinogenic substances in meat preparation, not necessarily fat or saturated fat, were probably the reason for increased risk. Pancreatic cancer is deadly, since most patients don’t have symptoms; therefore, it’s not discovered until its very late stages. It has destroyed the lives of some extremely physically fit people, like Patrick Swayze who died at the age of 57.
Processed meats also increase the risk of colorectal cancer. In a meta-analysis, there was an increased risk of 14 percent per every 100 grams, or 3.5 ounces (approximately one serving) of processed meat per day (2). Two slices of deli meat are equal to one serving. A deli’s turkey sandwich includes about five servings of processed meat in one meal.
In the EPIC trial, a prospective study with more than 420,000 participants, processed meats increased the risk of colorectal cancer by 35 percent (3). The absolute risk of developing colorectal cancer was 71 percent over ten years for those who were age 50. Interestingly, fish actually decreased the risk by 31 percent, making fish a better choice for the barbeque.
Other cancers implicated in processed meats include lung, liver and esophageal cancers, with increased risks ranging from 20-60 percent according to the NIH AARP Diet and Health study (4). A separate analysis of the EPIC trial showed that there was a greater than two times increased risk of esophageal cancer with processed meats (5).
Is there an association between type 2 Diabetes and processed meats?
In one of the most prestigious and largest meta-analyses involving the Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study and the Nurses’ Health Study I and II, results demonstrated a 32 percent increased risk of type 2 diabetes in participants who had a one-serving increase of processed meat consumption per day.
This data was highly statistically significant and involved over four million years of cumulative follow-up. Interestingly, the authors estimate that replacing processed meat with one serving of nuts, low-fat dairy and whole grains would reduce risk substantially (6).
I believe warning labels should come with processed meats; however, this is unlikely to happen. Therefore, you need to be your own best advocate and read ingredients. It is not just processed meats on the barbecue this Labor Day weekend that are concerning, but the long-term effects of eating deli meats that are even more worrisome.
References:
(1) J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97 (19): 1458-1465. (2) PLoS One. 2011;6 (6):e20456. (3) J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005 Jun 15;97 (12):906-16. (4) PLoS Med. 2007 Dec;4 (12):e325. (5) J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Mar 1;98 (5):345-54. (6) Am J Clinical Nutrition 2011;94 (4): 1088-1096.
Dr. David Dunaief is a speaker, author and local lifestyle medicine physician focusing on the integration of medicine, nutrition, fitness and stress management. For further information, visit www.medicalcompassmd.com or consult your personal physician.