With a little under 600 wells in its system, the Suffolk County Water Authority has a big task ahead as it tries to comply with state mandates to remove the likely carcinogenic 1,4 dioxane from Long Island’s drinking water.
On a Zoom call with TBR News Media, water authority officials talked about the current progress on remodeling the county’s water infrastructure, including 76 wells. It’s a difficult task, and there are many years and millions of dollars more needed before many of the county’s wells are remediated. The authority has estimated 45% of its wells were detected with 1,4 dioxane, which Jeffrey Szabo, the CEO of the SCWA, called “frightening.”
For over a year, 1,4 dioxane has appeared in the news frequently . Gov. Andrew Cuomo (D) signed legislation at the end of last year banning 1,4 dioxane, which is normally found in some household cleaning products. At the tail end of July this year, New York adopted regulations for the chemical, setting the maximum contaminant levels, or MCL, of 1 part per billion. 1,4 dioxane has been found in 70% of Long Island wells found during a federal testing initiative back in 2013 through 2015.
The state has also set the MCL for PFOA and PFOS, both of which have been found to cause health issues in humans and animals, at a maximum of 10 parts per trillion. Perfluorooctane sulfonate, or PFOS, is a chemical often found in firefighting foams, and perfluorooctanoic acid, or PFOA, is used in nonstick and stain-resistant products.
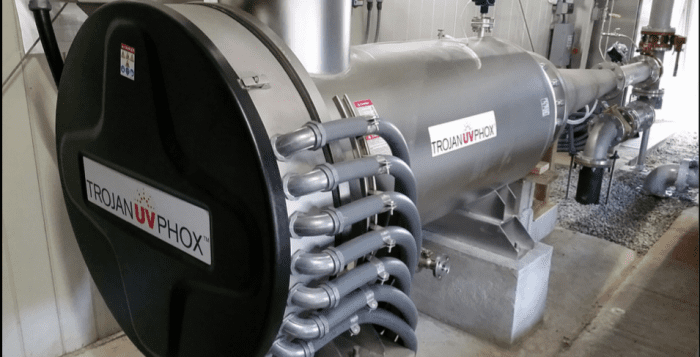
Szabo said they are on their way to establishing treatment for the PFOA and PFOS in all wells that need it. The water authority’s October report states that all wells with those chemicals above the MCL limit are either being treated to remove the contaminants or are being blended to below the MCL or have been removed from service. Szabo said the water authority has granular activated carbon, or GAC filters that help remove the PFAS chemicals, but such carbon-based filters have little to no effect on 1,4 dioxane. Instead, the SCWA started almost a decade ago developing technology to remove another similar chemical, 1,3 dioxane from drinking water. In 2017, SCWA engineers designed and piloted the first full-scale pilot 1,4-dioxane treatment system in state history. The authority’s Advanced Oxidation Process, or AOP treatment system is currently operational in only one location, Central Islip. That design process “took a long time and a lot of money,” Szabo said.
The water authority CEO said they now have 56 AOP treatment systems in construction in Suffolk, including in Farmingdale and Huntington. There are AOP treatment systems being designed for places on the North Shore such as Sunken Meadow Park, but in many cases it’s not as simple as installing a new filter, as it often takes reconfiguring and additional electrical work. Clearing and site work continues for future AOP sites and electrical upgrade work is beginning at sites such as Flower Hill Road in Huntington. In some cases it’s simply easier and cheaper to replace old wells, such as on Old Dock Road in Kings Park, which is replacing two wells on Carlson Avenue both of which need AOP systems.
Not only that, but there is an apparent year-long lead time from when the authority orders a new system to when it can be installed.
Despite recent efforts, funding continues to be the biggest issue. Each GAC system costs around $1 million to manufacture. An AOP system is closer to $2.5 million. At the end of last year, the SCWA estimated efforts to remediate such wells would cost $177 million over the next five years. The October report states the authority has spent close to $12 million to date for PFAS related work and $23,136,397 for emerging contaminant work.
The water authority passed a $20 fee added to residents’ quarterly water bills starting this year to help pay for this new water treatment.
Though even with that fee, it’s not likely enough to cover the full cost. The water authority has also filed lawsuits against several companies whose products contain PFOA, PFOS or 1,4 dioxane. Those suits are still ongoing. The SCWA has received $13.3 million in grants from New York State and has submitted additional applications for state grant funding for 14 of its wells.
The water authority is also waiting on a bill in the state legislature which could provide some extra financial assistance. A bill supported by state Sen. Jim Gaughran (D-Northport) and Assemblyman Fred Thiele (I-Sag Harbor) that would provide reimbursement for emerging contaminant grants by responsible parties has passed the state senate but currently remains in committee in the assembly.