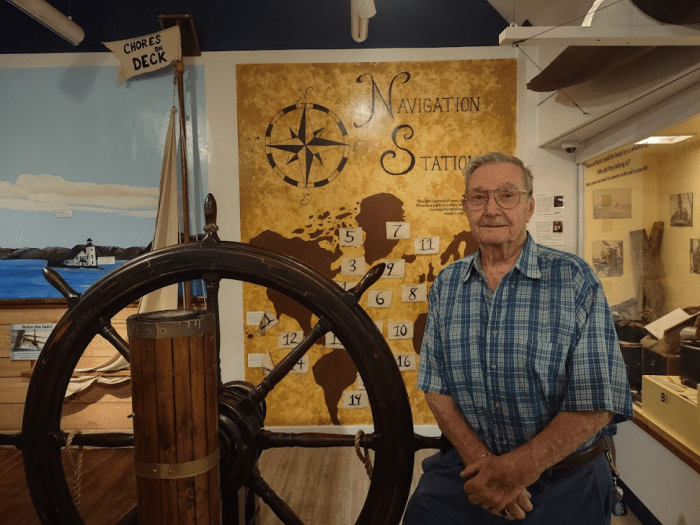
The Whaling Museum in Cold Spring Harbor welcomed special guest and Huntington resident Robert Archer to its museum last week. Bob’s great-great grandfather, Benjamin Archer (1825-1868), sailed as a greenhand, or an inexperienced crew member on Cold Spring Harbor’s whaleship, the Monmouth. According to FindAGrave, Benjamin was an immigrant from England, and he married Phebe Wall (1827-1898) from Ireland. At the young age of 17, he signed on as a greenhand on the bark Monmouth, as shown in the Museum’s archives.
The Monmouth was Cold Spring Harbor’s first and smallest vessel, built in Massachusetts at 100 feet long. John H. Jones, agent for the Cold Spring Whaling Company, purchased the Monmouth in 1836. The bark had a relatively long career with multiple whaling voyages for the Long Island village.
Benjamin sailed on the Monmouth from 1842-1843, which journeyed to the Indian, North Atlantic, and South Atlantic oceans. The captain of the voyage was the well-liked Hiram B. Hedges of East Hampton (1820-ca.1861), who himself started as a greenhand and worked his way up to captain. Although just a few years older than Benjamin, Hiram was known as “always kind to his men, and highly respected by them.” He was also “the handsomest captain who made port in the Sandwich Islands in his time.” Benjamin would have had to follow Hiram’s no-liquor regulation on the voyage.
Like all greenhands, Benjamin’s earnings were small – a cut of 1/150. As a whole, the voyage was comparatively short and profitable, yielding 75 barrels of sperm oil, 1,550 barrels of whale oil, and 12,400 pounds of baleen & whalebone. One voyage seems to have been enough for Benjamin, because we do not see record of him returning on a future voyage. However, he kept his connection to working on the waters, sailing as a local captain of several schooners and sloops in the 1850’s-60s in Cold Spring Harbor (you can check out his licenses in the museum’s digital collection).
1855 License for the sloop Dispatch
Benjamin had four children; all but one lived past childhood. Our last record of Benjamin’s maritime career was an 1865 license; he passed away just a few years later in 1868. Benjamin was only in his early 40s.
Interestingly, Capt. Hiram B. Hedges – like Benjamin – also retired from whaling. Although Benjamin and many of his descendants remained local to our area, 37-year old Hiram called it quits and moved to Oregon with his wife and son where he became a farmer before vanishing around 1861, possibly in a boating accident – or by committing suicide while facing onsetting Huntington’s disease, which ran in the Hedges family. He left behind three young children. (See “The Woman Who Walked Into the Sea.”)
Bob Archer noticed some of the museum’s recent Facebook posts, and he came to see the collection for himself in person. As an added connection to the museum, Robert’s wife, Kathleen, was a descendant of Captain James Wright, whose home is used today for the museum offices and collection storage.
Interestingly, Bob shared that years ago, Cold Spring Harbor was not loally regarded as the “well-off” location it is thought as today — Cold Spring Harbor residents were nicknamed humble “clammies”!
# # #
About The Whaling Museum & Education Center
The Whaling Museum & Education Center is the only museum in the world open year-round which explores the whaling history of the Long Island region. The Museum engages the community in exploring the diversity of our whaling heritage and its impacts to enrich and inform our lives. The museum is located at 301 Main Street, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724. Visit cshwhalingmuseum.org and follow The Whaling Museum on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter @cshwhalingmuseum