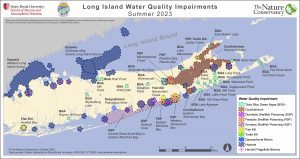
Peter Scully, Suffolk County deputy county executive and water czar, responds to questions from TBR News Media’s editorial staff:
1. You’ve been called Suffolk County’s water czar. Why does Suffolk County need a water czar?
The need for the county to have a high-level point person to advance the water quality agenda of County Executive Steve Bellone [D] is a result of two factors: The high priority that the county executive has placed on water quality issues, and the tremendous progress his administration has made over the past seven years in building a solid foundation to reverse decades of nitrogen pollution that has resulted primarily from the lack of sewers in Suffolk County and reliance on cesspools and septic systems that discharge untreated wastewater into the environment. The county executive succeeded in landing $390 million in post-Hurricane Sandy resiliency funding to eliminate 5,000 cesspools along river corridors on the South Shore by connecting parcels to sewers, and the county’s success in creating a grant program to make it affordable for homeowners to replace cesspools and septic systems with new nitrogen-reducing septic systems in areas where sewers are not a cost-effective solution, prompted the state to award Suffolk County $10 million to expand the county’s own Septic Improvement Program. These are the largest investments in water quality Suffolk has seen in 50 years, and the county executive saw the need to appoint a high-level quarterback to oversee the implementation of these programs.
2. Which groundwater contaminants are the highest priorities for Suffolk County?
In 2014, the county executive declared nitrogen to be water quality public enemy No. 1. The nitrogen in groundwater is ultimately discharged into our bays, and about 70 percent of this nitrogen comes from on-site wastewater disposal (septic) systems. Excess nutrients have created crisis conditions, causing harmful algal blooms, contributing to fish kills and depleting dissolved oxygen necessary for health aquatic life. They have also made it impossible to restore our once nationally significant hard clam and bay scallop fisheries, have devastated submerged aquatic vegetation and weakened coastal resiliency through reduction of wetlands. Nitrogen also adversely impacts quality of drinking water, especially in areas with private wells, although public water supply wells consistently meet drinking water standards for nitrogen.
Other major contaminants of concern include volatile organic compounds, known as VOCs. For example, there is perchloroethlyene, historically from dry cleaners; and petroleum constituents — most recently MTBE, a gasoline additive — from fuel storage and transfer facilities.
Then there are pesticides. Active ingredients such as chlordane, aldicarb and dacthal have been banned, but some legacy contamination concerns exist, especially for private wells. Some currently registered pesticides are appearing in water supplies at low levels, including simazine/atrazine, imidacloprid and metalaxyl.
Emerging contaminants include PFAS, historically used in firefighting foams, water repellents, nonstick cookware; and 1,4-dioxane, an industrial solvent stabilizer also present at low levels in some consumer products.
3. Are the chemicals coming from residential or industrial sites?
Contamination can emanate from a variety of sites, including commercial, industrial and residential properties. Many of the best-known cleanup sites are dealing with legacy impacts from past industrial activity. Examples include Grumman in Bethpage, Lawrence Aviation in Port Jefferson Station, Brookhaven National Laboratory in Upton and the Naval Weapons Industrial Reserve Plant in Calverton. There have been hundreds of Superfund sites on Long Island. Fortunately, most are legacy sites and new Superfund sites are relatively rare.
More recently, the use of firefighting foam has resulted in Superfund designations at the Suffolk County Firematics site in Yaphank, Francis S. Gabreski Air National Guard Base in Westhampton, and East Hampton Airport. The foam was used properly at the time of discharge, but it was not known that PFAS would leach and contaminate groundwater.
The county’s 2015 Comprehensive Water Resources Management Plan found that some chemicals, such as VOCs, continue to increase in frequency of detection and concentration. While some of this is attributable to legacy industrial plumes, experts believe that residential and small commercial sites are partially responsible for contamination. This is partly because any substances that are dumped into a toilet or drain will reach the environment, and because solvents move readily through our sandy aquifer. Septic waste is, of course a major of contamination. Residential properties can be also responsible for other pollution, such as nitrogen from fertilizers and pesticides.
4. Which industries currently generate the most groundwater pollution in Suffolk County?
The county’s Department of Health Services Division of Environmental Quality staff advise that, historically, the major contributors to groundwater pollution in the county were dry cleaners, and fuel storage and transfer facilities. However, current dry cleaning practices have minimized any possible groundwater discharges, and modern fuel facilities are engineered to more stringent code requirements that have substantially eliminated catastrophic releases. Low-level discharges are still a concern, and are the subject of the county’s VOC action plan to increase inspections and optimize regulatory compliance.
There are thousands of commercial and industrial facilities, most of which have the potential to pollute — for example, with solvent cleaners. Best management practices and industrial compliance inspections are key to minimizing and eliminating further contamination.
5. The word “ban” is often a dirty word in politics, but do you see benefits to banning certain products, and/or practices, for the sake of protecting the county’s drinking water supply? (The bans on DDT, lead in gasoline and HFCS, for example, were very effective at addressing environmental and human health concerns.)
Policymakers have not hesitated to ban the use of certain substances — DDT, lead in gasoline, chlordane, MTBE — in the face of evidence that the risks associated with the continued introduction of a chemical into the environment outweigh the benefits from a public health or environmental standpoint. Based on health concerns, I expect that there will be active discussion in the years ahead about the merits of restricting the use of products that introduce emerging contaminants like 1,4-dioxane and PFCs into the environment.
6. If people had more heightened awareness, could we slow or even eliminate specific contaminants? As consumers, can people do more to protect groundwater?
There is no question that heightened awareness about ways in which everyday human activities impact the environment leads people to change their behaviors in ways that can reduce the release of contaminants into the environment. A good example is the county’s Septic Improvement Program, which provides grants and low interest loans for homeowners who choose to voluntarily replace their cesspools or septic systems with new nitrogen-reducing technology. More than 1,000 homeowners have applied for grants under the program, which set a record in October with more 100 applications received.
If a home is not connected to sewers, a homeowner can replace their cesspool or septic system with an innovative/alternative on-site wastewater treatment system. Suffolk County, New York State and several East End towns are offering grants which can make it possible for homeowners to make this positive change with no significant out-of-pocket expense. Consumers can choose to not flush bleaches or toxic/hazardous materials down the drain or into their toilets. Consumers can also take care to deliver any potentially toxic or hazardous household chemicals to approved Stop Throwing Out Pollutants program sites. Homeowners can choose not to use fertilizers or pesticides, or to opt for an organic, slow-release fertilizer at lowest label setting rates.
7. Can you offer examples of products to avoid or practices to adopt that would better protect the drinking water supply?
Consumers can choose to not flush bleaches or household hazardous materials down the drain or into their toilets. Consumers can also take care to deliver any potentially toxic or hazardous household chemicals to approved STOP program sites. Homeowners can choose not to use fertilizers or pesticides, or to opt for an organic, slow release fertilizer at lowest label setting rates.
8. Aside from banning products or chemicals, and raising awareness, how do you address the issue?
Promoting the use of less impactful alternatives to products which have been shown to have a significant and/or unanticipated impact on public health or the environment, on a voluntary basis, is a less contentious approach than banning a substance or placing restrictions on its use through a legislative or rulemaking process. Such an approach should only be taken with the understanding that its success, value and significance will depend in large part on public awareness and education.
9. What about product labeling, similar to the U.S. Office of the Surgeon General warnings about cigarettes, or carcinogens in California, etc.? Can the county require products sold to include a groundwater contamination warning?
The question of whether the county Legislature has authority to implement labeling requirements could be better addressed by an attorney.
10. People, including some elected officials and people running for public office, sometimes say that sewage treatment plants remove all contaminants from wastewater. Can you set the record straight? What chemicals, including radioactive chemicals, are and are not removed from wastewater via sewage treatment?
Tertiary wastewater treatment plants are designed primarily to remove nitrogen, in addition to biodegradable organic matter. However, wastewater treatment is also effective at removing many volatile organic compounds. Some substances, such as 1,4-dioxane, are resistant to treatment and require advanced processes for removal. Evidence shows that the use of horizontal leaching structures instead of conventional drainage rings may facilitate removal of many pharmaceuticals and personal care products, known as PPCPs. Advanced treatment technologies, such as membrane bioreactors, are also being tested for efficacy of removal of PPCPs.
Staff advise that the mere presence of chemicals in wastewater in trace amounts does not necessarily indicate the existence of a public health risk. All wastewater treatment must treat chemicals to stringent federal and state standards. In some cases, such as for emerging contaminants, specific standards do not exist. In those cases, the unspecified organic contaminant requirement of 50 parts per billion is commonly applied.
11. Can you provide an example of a place where residential and industrial groundwater contamination concerns were reversed or adequately addressed?
There are numerous examples, mostly under the jurisdiction of U.S. Environmental Protection Agency or NYS Department of Environmental Conservation, in which groundwater concerns have been addressed through treatment to remove contaminants. Because health and safety are always the most important issues, the first priority is typically to make sure that people who live near an impacted site have a safe supply of drinking water. In areas served by public water suppliers — Suffolk County Water Authority or a local water district — this is not usually an issue, since public water suppliers are highly regulated and are required to test water supply wells regularly. In areas where people are not connected to a public water system, and rely instead on private wells, the Suffolk County Department of Health Services will work with the water supplier to identify properties that are not connected to a public water system and then contact homeowners to urge them to have their water tested at no charge to make sure that it is safe for consumption.
Over the past several years, Suffolk County, New York State and the Suffolk County Water Authority have worked together to connect hundreds of homes that had relied on private wells to the public water system, to make sure people have access to safe drinking water.
12. Are you hopeful about addressing the issues?
I am hopeful and optimistic about the success of efforts to reverse the ongoing degradation of water quality that has resulted from reliance on cesspools and septic systems. For the first time in Long Island’s history, environmentalists, business leaders, scientists, organized labor and the building trades all agree that the long-term threat that has resulted from the lack of sewers to both the environment and economy is so great that a long-term plan to address the need for active wastewater treatment is not an option, but a necessity. Experience shows that public awareness can be a significant factor in driving public policy.