Cases of whooping cough, which is caused by the Bordatella pertussis bacteria, have spiked in Suffolk County this year, raising concerns for the health of newborn babies who don’t have the kind of immunological tools to fight off the infection and its potential consequences.
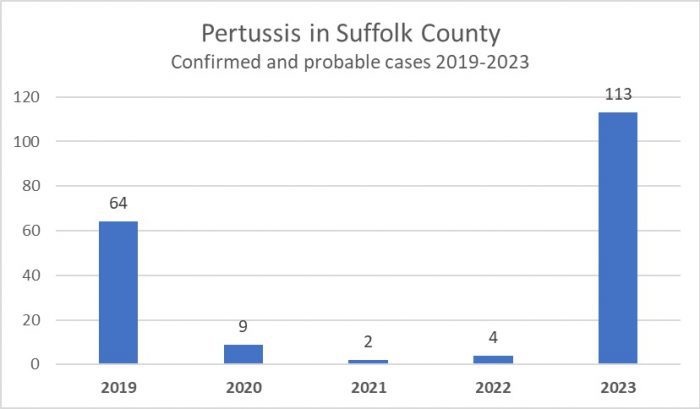
The Suffolk County Department of Health reported that 113 people had whooping cough, which is dramatically higher than the four people suspected of contracting this bacteria last year.
Whooping cough is “highly contagious,” explained Dr. Gregson Pigott, Suffolk County Health Commissioner in an email. “It is a cyclical disease with outbreaks occurring every three to five years.”
A large majority of people who have pertussis – 105 of the 113 – reported contracting the illness after November 28th, according to Dr. Pigott. Most of those who are sick are school aged children and their families, he added.
The surge in infections this year may be because immunity from the routine vaccination series, which is given between ages two months to six years, wanes over time.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that people receive the TDaP booster, which offers immunological protection from diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis, every 10 years.
Vaccination rates are “fairly high in Suffolk County, but we do know that some residents fell behind in their vaccinations during the height of the Covid pandemic,” Dr. Pigott added.
A preventable problem
Doctors urged residents, particularly those who might be interacting with young children or whose health is compromised, to check with their doctors on their vaccination status.
“Pertussis is a completely preventable disease,” said Dr. Adrian Popp, Chair of Infection Control at Huntington Hospital.
Indeed, doctors suggested that some of the people who aren’t receiving the vaccine may have pulled back from their normal inoculations amid the political discussion about the Covid vaccine.
“Covid has polarized our society in terms of vaccinations,” said Dr. Popp. Pertussis has “fallen prey” to this kind of thinking.
The pertussis shot has been around for over 50 years and can prevent bacterial infection, doctors said.
The vaccine is “completely safe and efficacious,” said Dr. Galinkin, infectious disease specialist at Port Jefferson-based St. Charles Hospital.
Dr. Galinkin, who has been practicing medicine in Suffolk County since 2004, said this is the highest level of whooping cough he’s seen in the county.
Indeed, even before the pandemic, the number of people infected with pertussis was 64 in 2019, according to the Department of Health.
The pertussis vaccine doesn’t completely prevent infection, but it does create a much milder case than it would for those who have no immunity, doctors said.
The incidence of pertussis can wax and wane, said Dr. Sharon Nachman, chief of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Stony Brook Children’s Hospital. The increase in cases this year likely means that “it won’t happen next year” as people do what they can to protect themselves, their family and their community when the numbers rise, as they have this year.
Indistinct early symptoms
Like other respiratory illnesses that are actively circulating among the Suffolk County population, whooping cough starts out as a cough and can include a runny nose and a low grade fever.
A whooping cough, however, often transitions into a more distinctive sound, as people who have it struggle to catch their breath after they cough.
Threat to infants
Health care providers suggested that pregnant mothers receive a booster for pertussis between the 27th and 36th week of pregnancy, which can not only reduce the risk of infection for the mom but can also provide some immunological benefit to the unborn child.
Doctors urged who are expecting a newborn to encourage anyone who has regular contact with the child in the first few months after birth to have updated immunizations, including for pertussis.
“The household of a newborn should consider being vaccinated,” said Dr. Popp. Infants who contract pertussis and who don’t have protection can develop complications such as encephalitis.
Pertussis is “an incredibly big problem for infants in the first year of life,” said Dr. Nachman.
Adults who contract pertussis can receive antibiotics, which generally eradicates the illness within five days. Untreated, however, pertussis symptoms and contagiousness can persist for weeks or even months.
Untreated pertussis can also lead to secondary pneumonia, added Dr. Nachman.
Respiratory illnesses climb
The combination of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), flu, and Covid continues to keep emergency rooms busy during the start of the new year.
Doctors urged adults who are immunocompromised or who are vulnerable to follow the same habits that reduced their risk during the worst of the pandemic, which includes washing their hands, keeping a safe distance from anyone who is sick, and wearing masks when they are in densely-populated indoor areas with less ventilation.
“You don’t necessarily want to isolate yourself to an extreme, but there are certain ways to decrease the chance of getting exposed to illnesses in general,” said Dr. Popp. People who are riding on crowded trains to and from work might want to search for cars that have fewer people when that’s an option, he suggested.
Hospitals are taking precautions to limit the likelihood of passing along infections. The staff in the emergency room at Stony Brook is wearing masks on rounds, said Dr. Nachman.
At this point, people who come to the hospital are offered masks, but are not required to wear them.