By Nancy Marr
Food is one of the more important factors in our lives. Food insecurity troubles many Americans, but for low-income consumers, especially, factors beyond their control affect their nutrition. Many low-income consumers can find lower prices, but consumers with very low incomes may not be able to get to stores that offer these low prices or fresh foods.
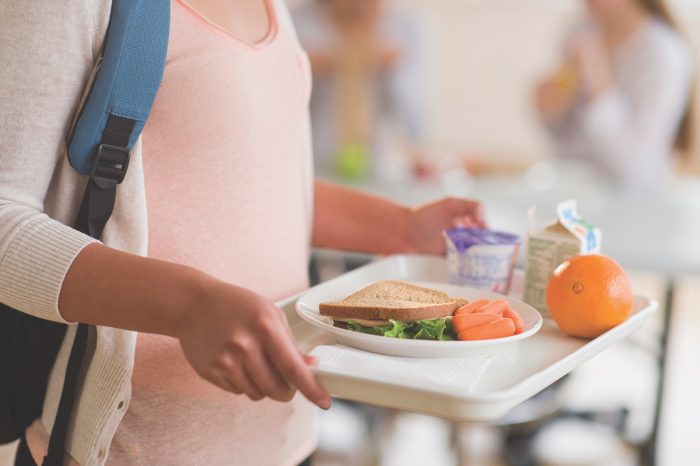
Here in Suffolk County, both school and summer feeding programs funded by the Department of Agriculture are making a difference by providing nutritious food for children from homes with food insecurity.
School lunch in America dates back to the late 19th century, when the passage of compulsory education laws and child-labor bans led to more kids in school for more hours per day than ever before. Health screenings in schools gave rise to concerns about malnutrition, which in turn sparked privately funded nutritious school meal programs in many cities. The programs were popular, but most were wiped out by the Great Depression.
In 1946, the federal government passed the National School Lunch Act which provided a way for the USDA to purchase surplus agricultural commodities for use by the schools in the feeding programs they agreed to fund.
The act created a three-tiered system: children in poverty received a free lunch, children whose families were above the poverty line but earning less than 130% of the federal poverty line got a price reduction, and everyone else paid full price. Millions of children have participated in the program.
The Federal USDA now funds the following child nutrition programs: the National School Lunch Program, School Breakfast Program, Summer Food Service Program, and After-School Snacks and Meals, using the same distribution system.
During the recent pandemic, when schools closed, the federal government funding made it possible for schools to continue the lunch program and changed it to one that served all the children at no charge. Schools arranged for the pick-up of lunches by the students. The USDA pandemic funding ended in June 2022, with an extension through the summer of 2022.
Schools and summer lunch providers then returned to the payment schedule that divided the children. The universal offering of free meals to all students had raised the level of participation by removing the stigma often associated with means-tested school meals and opened the program to children from families who would have struggled to pay the reduced-price copayment.
But so far, there’s no momentum in Congress to bring the free meals back, except for the CEP Program (Community Eligibility Provision) which provides breakfast and lunch free of charge to all the students who are enrolled. Eligible for CEP is any district or school with 25 percent of students who have been identified as in need, and children who are certified for free meals without an application because they are homeless, migrant, enrolled in Head Start, or in foster care.
Food policy councils, appointed by local government or organized independently of government, have proven to be effective in educating community members about local food and nutrition, as well as other issues related to health, such as walkability.
The funding during the pandemic showed how universal feeding encouraged children to participate in a nutritionally sound breakfast and lunch program which provided free food for all children. Federal or New York State funding would make that possible. For more information, go to www.schoolnutrition.org.
And write to Governor Hochul and your State Senator and Assemblyperson, and our United States senators, Senator Charles Schumer and Kirsten Gillibrand.
Nancy Marr is Vice-President of the League of Women Voters of Suffolk County, a nonprofit nonpartisan organization that encourages the informed and active participation of citizens in government and influences public policy through education and advocacy. For more information, visit my.lwv.org/new-york/suffolk-county or call 631-862-6860.