For some of the residents of Comsewogue, now Port Jefferson Station, getting the mail once meant traveling from three to five miles to the post office in downtown Port Jefferson.
Tired of the inconvenience, a group of Comsewogue’s citizens petitioned the government in 1888 to establish a post office within their community.

The Postmaster General responded that so many places in the State ended in “ogue” that to avoid confusion Comsewogue would have to be renamed if a post office was to be considered for the area.
The name Comsewogue and its many variants was an Algonkian term meaning “a walking place,” had appeared in Brookhaven Town records as early as 1805 and was rich in etymology and history.
Nevertheless, the petitioners acquiesced and submitted several names as Comsewogue’s replacement: South Port Jefferson, Port Jefferson South, Maple Hill, Enterprise, Cedar Grove, and Jefferson Heights. Each was rejected, either for being too common or too long.
In the next round of proposals, William I. Wyckoff suggested Echo, the same name as a famous racehorse once owned by Comsewogue’s Nathaniel Dickerson. Echo — only four letters long — was accepted by the postal authorities and Charles A. Squires appointed as the office’s first postmaster.
A native of Good Ground (Hampton Bays), Squires had begun work as the depot agent at the Port Jefferson Railroad Station in 1886 and soon earned a reputation in Comsewogue for his competence and geniality.
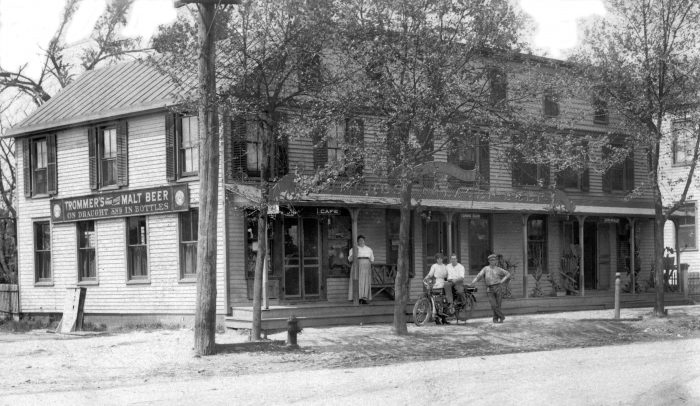
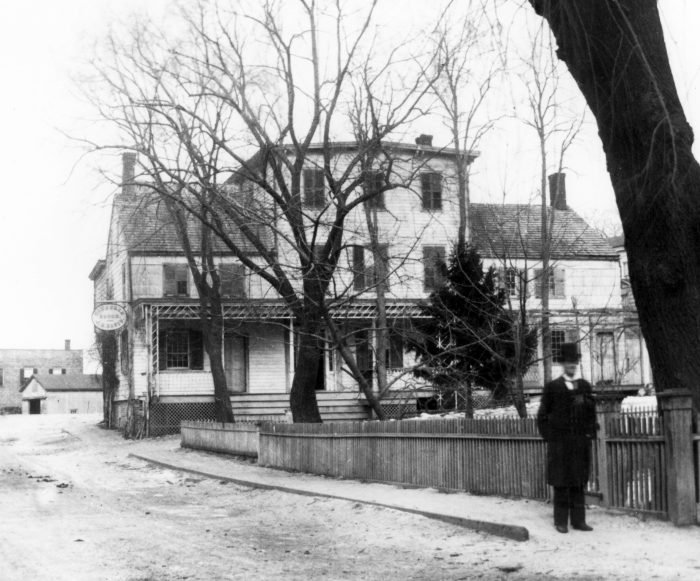
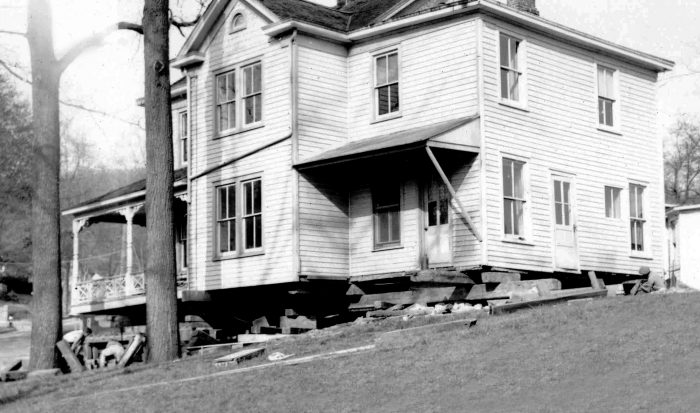
Under Squires’ able leadership, the Echo Post Office opened in a building on the west side of today’s Main Street (Route 25A), immediately north of the LIRR tracks.

Squires also championed his bailiwick in the Port Jefferson Echo, a newspaper that he had founded with G. Frederick Hallock in 1892. The “Republican journal” helped establish the uniqueness of Echo and operated out of the same building as the Echo Post Office.
Following A. Jay Tefft’s purchase of the Echo in 1899, Squires devoted his considerable energies to buying and selling real estate, developing several subdivisions in the area including Belle Croft, Norton Park, Fairview Place, and Bergen Estates.
In 1904, Echo’s post office and newspaper, along with Squires’ Real Estate Agency, resettled a few steps north on Main Street in the new Echo Building. Hugo Kreitzberg then transformed the unoccupied property resulting from the move into the Hotel Echo.
The Echo Post Office was renamed the Port Jefferson Station Post Office in 1910. Squires had led a popular petition drive in support of the change and later became known as the “father of Port Jefferson Station.”
Key among the reasons for the switch, it was argued that Echo was a “meaningless place name” and that the presence of the Port Jefferson Railroad Station best defined the area.
After being called home for 22 years, Echo just faded away.
Kenneth Brady has served as the Port Jefferson Village Historian and president of the Port Jefferson Conservancy, as s well as on the boards of the Suffolk County Historical Society, Greater Port Jefferson Arts Council and Port Jefferson Historical Society. He is a longtime resident of Port Jefferson.