Getting an annual eye exam is crucial
By David Dunaief, M.D.

If you have diabetes, you are at high risk of vascular complications that can be life-altering. Among these are macrovascular complications, like coronary artery disease and stroke, and microvascular effects, such as diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy.
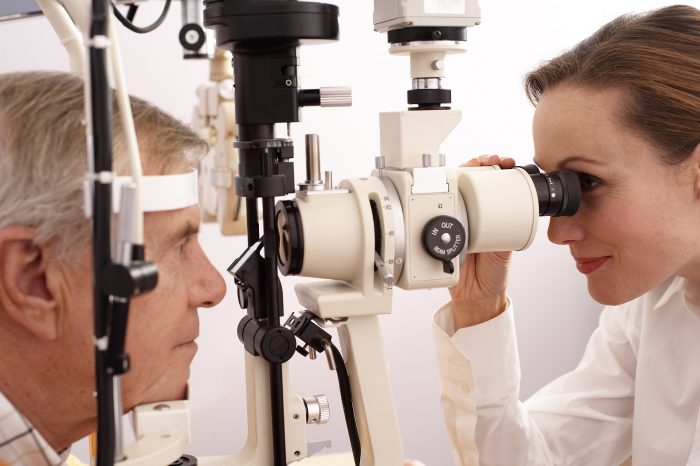
Here, we will talk about diabetic retinopathy (DR), the number one cause of blindness among U.S. adults, ages 20 to 74 years old (1). Diabetic retinopathy is when the blood vessels that feed the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye are damaged, and it can progress to blurred vision and blindness.
As of 2019, only about 60 percent of people with diabetes had a recommended annual screening for DR (2). Why does this matter? Because the earlier you catch it, the more likely you will be able to prevent or limit permanent vision loss.
Over time, DR can lead to diabetic macular edema (DME). Its signature is swelling caused by fluid accumulating in the macula (3). An oval spot in the central portion of the retina, the macula is sensitive to light. When fluid builds up from leaking blood vessels, it can cause significant vision loss.
Those with the longest duration of diabetes have the greatest risk of DME. Unfortunately, many patients are diagnosed with DME after it has already caused vision loss. If not treated early, patients can experience permanent damage (2).
In a cross-sectional study using NHANES data, among patients with DME, only 45 percent were told by a physician that diabetes had affected their eyes (4). Approximately 46 percent of patients reported that they had not been to a diabetic nurse educator, nutritionist or dietician in more than a year — or never.
Unfortunately, the symptoms of vision loss don’t necessarily occur until the latter stages of the disorder, often after it’s too late to reverse the damage.
What are treatment options for Diabetic Macular Edema?
While DME has traditionally been treated with lasers, injections of anti-VEGF medications may be more effective. These eye injections work by inhibiting overproduction of a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which contributes to DR and DME (5). The results from a randomized controlled trial showed that eye injections with ranibizumab (Lucentis) in conjunction with laser treatments, whether laser treatments were given promptly or delayed for at least 24 weeks, were equally effective in treating DME (6). Other anti-VEGF drugs include aflibercept (Eylea) and bevacizumab (Avastin).
Do diabetes treatments reduce risk of Diabetic Macular Edema?
You would think that using medications to treat type 2 diabetes would prevent DME from occurring as well. However, in the THIN trial, a retrospective study, a class of diabetes drugs, thiazolidinediones, which includes Avandia and Actos, actually increased the occurrence of DME compared to those who did not use these oral medications (7). Those receiving these drugs had a 1.3 percent incidence of DME at year one, whereas those who did not had a 0.2 percent incidence. This incidence was persistent through the 10 years of follow-up. Note that DME is not the only side effect of these drugs. There are important FDA warnings for other significant issues.
To make matters worse, those who received both thiazolidinediones and insulin had an even greater incidence of DME. There were 103,000 diabetes patients reviewed in this trial. It was unclear whether the drugs, because they were second-line treatments, or the severity of the diabetes itself may have caused these findings.
This contradicts a previous ACCORD eye sub-study, a cross-sectional analysis, which did not show an association between thiazolidinediones and DME (8). This study involved review of 3,473 participants who had photographs taken of the fundus (the back of the eye).
What does this ultimately mean? Both studies had weaknesses. It was not clear how long the patients had been using the thiazolidinediones in either study or whether their sugars were controlled and to what degree. The researchers were also unable to control for all other possible confounding factors (9). There are additional studies underway to clarify these results.
Can glucose control and diet improve outcomes?
The risk of progression of diabetic retinopathy was significantly lower with intensive blood sugar controls using medications, one of the few positive highlights of the ACCORD trial (10). Unfortunately, medication-induced intensive blood sugar control also resulted in increased mortality and no significant change in cardiovascular events. However, an inference can be made: a nutrient-dense, plant-based diet that intensively controls blood sugar is likely to decrease the risk of diabetic retinopathy and further vision complications (11, 12).
If you have diabetes, the best way to avoid diabetic retinopathy and DME is to maintain good control of your sugars. Also, it is imperative that you have a yearly eye exam by an ophthalmologist, so that diabetic retinopathy is detected as early as possible, before permanent vision loss occurs. If you are taking the oral diabetes class thiazolidinediones, this is especially important.
References:
(1) cdc.gov. (2) www.aao.org/ppp. (3) www.uptodate.com. (4) JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132:168-173. (5) Community Eye Health. 2014; 27(87): 44–46. (6) ASRS. Presented 2014 Aug. 11. (7) Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1005-1011. (8) Arch Ophthalmol. 2010 March;128:312-318. (9) Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:1011-1013. (10) www.nei.nih.gov. (11) OJPM. 2012;2:364-371. (12) Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:1588S-1596S.
Dr. David Dunaief is a speaker, author and local lifestyle medicine physician focusing on the integration of medicine, nutrition, fitness and stress management. For further information, visit www.medicalcompassmd.com or consult your personal physician.