Looking Back on the 79th Anniversary of Pearl Harbor
‘The attack yesterday on the Hawaiian Islands has caused severe damage to American naval and military forces. I regret to tell you that very many American lives have been lost. In addition, American ships have been reported torpedoed on the high seas between San Francisco and Honolulu.’ — President Franklin D. Roosevelt, Dec. 8, 1941

By Rich Acritelli
The above words were parts of the “Day in Infamy” speech that President Franklin Roosevelt presented to Americans directly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor some 79 years ago. As the United States is currently battling COVID-19, many decades ago, our citizens were fighting for a different type of survival. On that Sunday morning, Americans woke up to one of the most startling pieces of news that ever struck this country. As our people listened to their radios, they quickly realized that our powerful military in Hawaii was devastated by the Empire of Japan. In a matter of moments, a nation that was once hesitant to fight the Axis powers was now immediately engaged in a massive war.
The tropical paradise of Hawaii had its skies marred by the first wave of 183 Japanese Zero fighter planes that aggressively responded to their orders of “Tora, Tora, Tora.” Large numbers of Japanese aircraft took off from their carriers as they were cheered on the decks by the crews. In one of the largest national security blunders to ever harm the nation, the American intelligence system lost the Japanese fleet which sailed undetected from their home waters and emerged 230 miles off the coast of Oahu. While these waves were detected by radar, no alarm was issued due to the belief that these enemy aircraft were American B-17 Flying Fortresses that were traveling from San Diego. When military leaders in Washington D.C. feared that an attack was imminent, an American alert was finally issued to the senior military officers. Every Sunday morning, General George C. Marshall routinely rode his horse and this report sat at his home for almost two hours before he responded to this possible threat.
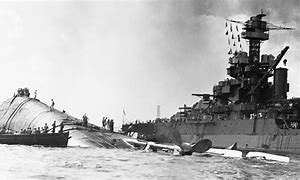
Within a short period, the beautiful skies overhead were darkened by the smoke of naval ships, aircraft, army equipment, and fuel dumps that were destroyed by bombs. Japanese planes accurately swarmed over “Battleship Row” to bomb the large American fighting ships. Again, another wave of Japanese organized 54 high level bombers and 78 dive-bombers, all of whom were escorted by 36 fighter planes. To make the strafing missions easier for the Japanese, many of the American military aircraft were situated extremely close together out of fears that Japanese agents would sabotage them. This same placement of planes was utilized by General Douglas R. MacArthur in the Philippines. Like in Hawaii, many of the planes and bombers were crippled on the ground, as the Japanese gained complete air superiority against American air, army and naval forces. The well-coordinated Japanese attack also presented the new fear that if they had landed their army forces in Hawaii, it was possible for them to take these islands.
During this surprise attack, Secretary of State Cordell Hull spoke with representatives from the Japanese Embassy in Washington D.C. As he spoke to his counterparts, Hull was informed by his aide’s that Pearl Harbor was being hit at that very moment. It was the task of these diplomats to give Hull a lengthy document of major grievances against the American government. They understood that the time to attack was near, and it was the goal of the Japanese officials to deliver this message to Hull before their planes struck Hawaii, but it took the Japanese Embassy longer to decipher and type this response and the delay caused them to hand Hull this response as their planes were devastating the headquarters of the American navy in the Pacific. For the rest of his life, Hull was bothered that as he was negotiating for peace, the Japanese deceived him through many phony meetings, where they were only interested in pursuing war.
Admiral Husband E. Kimmel and Lieutenant General Walter C. Short were the army and naval senior commanders that were responsible for the defense of Pearl Harbor. Short had 40 years of service under his belt, where he served with Marshall and was promoted by him to command the Department of Hawaii. Directly after this attack where Short was caught off guard, he retired from the service. When Kimmel saw the attack unfolding, a stray bullet forced him to fall to the ground. He realized that the Japanese were in the process of destroying the American military presence that he held the responsibility for protecting. With Pearl Harbor virtually defenseless, Kimmel eerily stated about almost being shot, “It would have been merciful had it killed me.” Both men were the scapegoats for “dereliction of duty” and their careers were terminated. Some 60 years later, Congress cleared Short and Kimmel’s names and stated that they were not solely to blame for 2,400 losses on Dec. 7, 1941.
Less than two weeks later, Kimmel was relieved of his command and Admiral Chester W. Nimitz ascended to the position of Commander in Chief. This historic officer was at the helm of many naval successes in the Pacific and he was warmly greeted by his wife who was pleased about his promotion. However, on Dec. 7, there was no joy, the fleet barely survived, and instead of searching for the Japanese carriers that caused this chaotic assault, his men were attempting to rescue their comrades who were trapped in sunken ships in and around Pearl Harbor. Nimitz could only respond to his wife, “all of the vessels are at the bottom.” On the USS Arizona alone, there were twenty-three sets of brothers that were serving together on this ship that were killed by the Japanese.
To make matters worse for the U.S., the Japanese attacked the American strongholds in the islands of the Philippines, Wake, and Guam. For years, the Japanese, as a growing military power, resented the deterrence of the United States navy held as they sought control the Pacific and Asia. The Japanese leadership understood that if they did not sink the aircraft carriers and battleships at Pearl Harbor, they were unable to match the military and economic might of the U.S. For a year, the Japanese lived up to their strength as the “Rising Sun” showed no signs of being halted. They controlled a tremendous land and sea empire that stretched north into China. They took two Aleutian Islands from Alaska, reached in opposite directions towards Australia and Burma, and they pushed towards the island of Midway.
Roosevelt was determined that the U.S. would fight in both the European and Pacific Theaters of Operation before the end of 1942. Immediately, FDR sought vengeance against the sneak attack that nearly destroyed the naval force at Pearl Harbor. While the “Doolittle Raid” did not hurt the Japanese war effort, it managed to show to this warring nation that America was able to quickly strike back. An aircraft carrier strike force sailed within four hundred miles of Japan and launched its bombers to hit their mainland. Fifteen out of the 16 American B-25 bombers crashed landed in China with a minimal casualties. And while this was a minimal raid, it was a psychological blow to the Japanese and it showed resilience to American citizens. For his efforts in leading and carrying out this assault, Dolittle was awarded the Medal of Honor by Roosevelt.
American boys from the inner cities, the rural areas, and communities like that of the North Shore were quickly trained and deployed for war. Both Americans and British landed in Morocco and Algeria to briefly fight the Vichy French troops and oppose the Germans. In the Pacific, American ground forces landed at Guadalcanal to prevent the Japanese from building an air strip that would attack the shipping lanes to Australia and New Zealand. Since this past March, our country has been severely hurt by the terror of COVID-19, but let the sacrifices and resolve that was shown by the United States during and after Pearl Harbor prove to our current citizens that there are no challenges that this nation is unable to overcome. May we always remember our past, present, and future veterans and those front-line workers today that are engaged within the “health defense” of this nation.
Thank you for members of the Rocky Point History Honors Society for contributing to this story.
Rich Acritelli is a social studies teacher at Rocky Point High School and an adjunct professor of American history at Suffolk County Community College.






