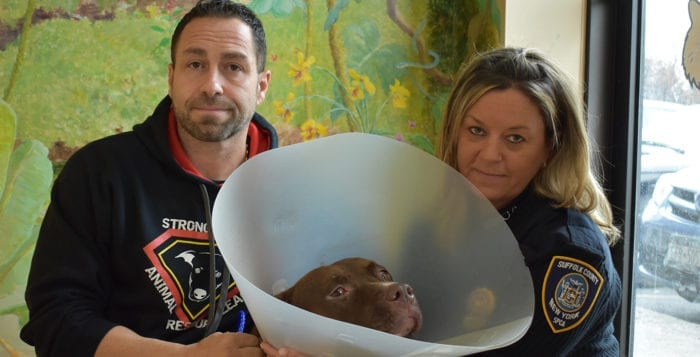
A dog who was maimed after a knife attack in Brentwood has found safety with a Centereach animal hospital and a North Shore-based animal rescuer.
At about 5:30 a.m. Nov. 20, Suffolk County police responded to a domestic dispute in Brentwood, according to a release put out by SCPD. Malik Fields, 25, was allegedly involved in a dispute with his girlfriend during which police said he stabbed two of the family’s six dogs. Detective Jennifer Pape of the Suffolk County Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals was also brought onto the scene by SCPD when it was discovered one pit bull named Storm had been stabbed and was bleeding profusely, according to Pape. Fields’ family brought Storm to a West Islip animal hospital where he was euthanized.
“Stabbing cases are rare, but in a year we investigate about 3,000 animal cruelty complaints,” Pape said. “It’s heart wrenching — it’s why I do what I do. They’re innocent, it’s why we need to protect them.”
Several hours after the initial disturbance, after authorities had already left, Fields’ family discovered another pit bull named Chocolate had also been stabbed, according to Pape. The family called Frankie Floridia, president of Sound Beach-based Strong Island Animal Rescue League, seeing if he could help take the dog to a veterinarian. Floridia called Pape, who rushed back to the scene. Soon after, the family brought the dog to the Animal Medical Hospital of Centereach at about 1:45 p.m. where Chocolate immediately went into surgery.
“I knew one dog had passed away and so we had to go fast to make sure everything was OK with the [other] dog, that was my main concern,” Floridia said.

Veterinarian Dr. Charles Greco said the dog had a 12-inch laceration deep along his shoulder that had cut into his left-side deltoid muscle. After being sedated, Chocolate was out of surgery after approximately 30 minutes. The veterinarian said he performed the surgery pro bono, yet this wasn’t the worst case he’s seen in his career.
“I had one case years ago where a dog was stabbed 40 times,” Greco said. “This dog had nothing to do with this [dispute], he just happened to be there.”
Chocolate is now in stable condition and is in the care of Floridia, who said he had been told by the family the dogs did not instigate or intimidate Fields. Despite the harm inflicted upon the young pit bull, Chocolate is still friendly and calm among strangers, willing to sniff their pants legs and walk around freely.
Fields was charged with two counts of aggravated cruelty to animals, according to the SCPD. He was arraigned Nov. 27, though Field’s lawyer could not be reached for comment. An order of protection was issued for the dogs by the Suffolk County District Attorney’s Office, which prevents Fields from interacting with the four other dogs, who were uninjured at the alleged incident and are still living with the family at the Brentwood house. In the meantime, Floridia did not want to give details on his plans for the dog, but he said he will work to make sure Chocolate goes to a caring home.
“We have good plans for him,” he said. “I’m going to do what’s best for the dog.”