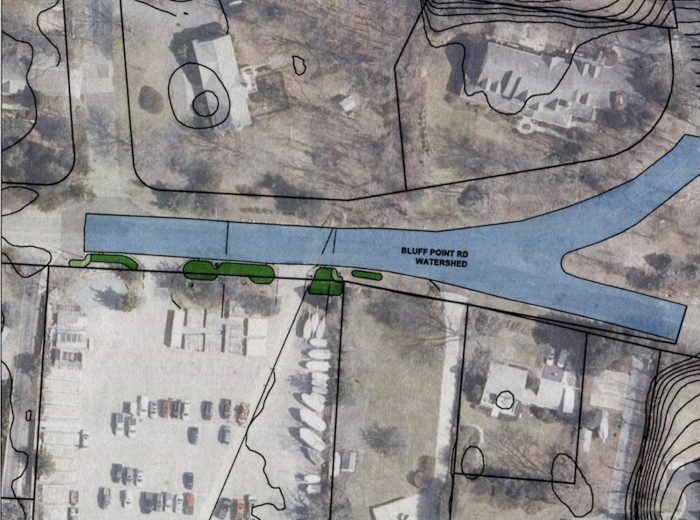
On March 16, environmental advocates met with public officials at the Northport Yacht Club to announce the addition of four rain gardens along Northport Harbor.
Adrienne Esposito, executive director of Citizens Campaign for the Environment, said her organization has partnered with the Village of Northport and the yacht club to address water pollution. According to her, rain gardens are a cost-effective and simple way to protect the harbor.
“In short, a rain garden is a nature-based solution to man-made pollution,” she said. “Stormwater runoff carries with it pesticides and fertilizers and other pollution and contaminants into our surface waters across Long Island. This rain garden is very important because it will be removing thousands of gallons of rain before it goes into the harbor.”
Nelson Pope Voorhis, a Melville-based engineering firm, is making this vision a reality. According to Rusty Schmidt, landscape ecologist at Nelson Pope, the proposed rain gardens will act as a filtration system, flushing out debris and other sources of pollution, to discharge stormwater safely into the harbor.
“A rain garden is a shallow bowl that we put into the landscape and that we direct water to on purpose,” Schmidt said. “In this case, the water is going to be coming from Bluff Point Road, and as the water comes down the street it will go into these gardens first. That water will soak into the ground in one day or less — in this case it will probably soak in in a few hours because the soils are sandy — and that water will be cleansed and cleaned and get to a drinkable quality.” He added, “It’s still going out to Northport Harbor, but through the soil and without all the garbage.”
We once had a thriving, billion-dollar shellfish industry here on the Island, and this is an important measure to bring back those types of species.
— Assemblyman Keith Brown (R-Northport)
According to a study conducted by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Northport Harbor and Northport Bay are both designated as priority waterbodies. Schmidt said that the proposed rain gardens would capture roughly 15,000 gallons of rainwater during a storm event, removing several harmful contaminants from the runoff before it reaches the harbor.
“Nitrogen is the number one pollutant to our bay, and we are eliminating a large volume of nitrogen from these rain gardens,” Schmidt said. “Nitrogen is the main component of growing the algal blooms, the red tides and the brown tides that are causing low oxygen and other problems in the harbor.”
The project is made possible by grants from the Long Island Sound Study and the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation’s Long Island Sound Futures Fund. Policymakers suggest this project will help to revitalize Northport’s decimated aquatic ecosystems.
“We once had a thriving, billion-dollar shellfish industry here on the Island, and this is an important measure to bring back those types of species,” said state Assemblyman Keith Brown (R-Northport). “I ran on a platform of cleaning up the Long Island Sound, the bays and the estuaries. The quality of them is a really important issue of mine, being from Northport.”
Ian Milligan, deputy village mayor and commissioner of Docks & Waterways, Police and Personnel, confirmed that the rain gardens near the yacht club will be the first of several planned to be installed throughout the village.

“We have a huge runoff water problem here in Northport and it all ends up in the harbor,” Milligan said. “This is the first rain garden that we’re doing in Northport and I’m also happy to say that the village, through other grants and other programs, has three more that are going to be coming out this year.”
According to Esposito, these projects will lead to a cleaner, safer Northport Harbor.
“The bottom line is that this rain garden really will be a simple solution to rainwater pollution,” she said. “We will be using native plantings and taking an area right now that floods and reimagining that area as a beautiful garden that will be absorbing the rain and filtering those pollutants, thereby protecting the harbor.”
Esposito added that construction of the proposed rain gardens near Northport Yacht Club will begin this spring.