By Daniel Dunaief
Joseph “Bob” Annunziata, a resident of Kings Park, wants you not to be like him.
An army veteran, Annunziata urges residents and, in particular, other veterans, to pay attention to their medical needs and to take action when they find out they have a problem.
A self-described “tough guy” who grew up in Bay Ridge, Brooklyn, Annunziata put off medical care for a partially blocked left carotid artery and it caused a medical crisis.
“My brother and sister vets, if you got a pain or the doctor tells you to do something, do it,” he said. “It almost cost me my life. I don’t want that to happen to anyone else.”
Annunziata, 80, was driving to the supermarket on Veterans Day when his right hand became limp and he was slurring his speech. Knowing he was in trouble, he turned the car around and drove 10 minutes to the Northport VA Medical Center.
The doctors evaluated him and rushed him to Stony Brook University Hospital, which is well equipped to handle stroke-related emergencies and is the only hospital in the state named one of America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Stroke Care for eight years in a row.
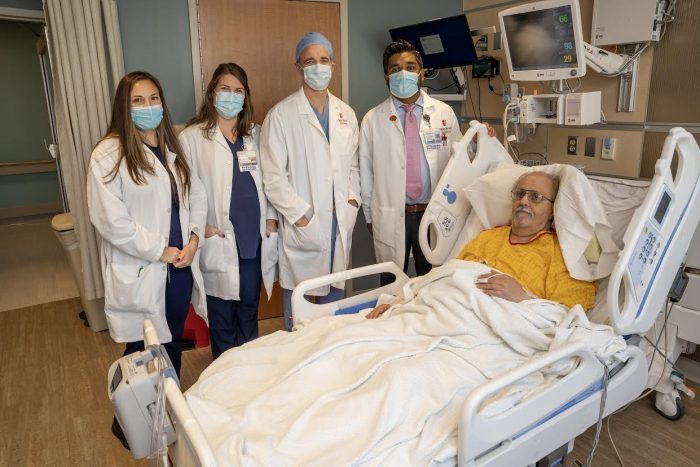
Several doctors evaluated Annunziata, including by Dr. David Fiorella, Director of the Stony Brook Cerebrovascular Center and Co-Director of the Stony Brook Cerebrovascular and Comprehensive Stroke Center, and Jason Mathew, stroke neurologist.
“We identified that there was a severe blockage in the left side of his brain,” said Dr. Mathew. “If blood flow is not returned to this area, the patient is at risk for a larger area of stroke.”
Indeed, a larger stroke could have caused right side paralysis and could have robbed Annunziata of his ability to speak or worse.
Performing emergency surgery could protect endangered brain cells, but also presented some risk. If not removed carefully and completely, the clot in the carotid artery could travel into the brain or the stroke could expand over time due to a lack of sufficient blood flow to the left side of the brain.
Time pressure
Stony Brook doctors discussed the particulars of the case together and explained the situation to Annunziata, who could understand what they were describing and respond despite symptoms that threatened to deteriorate.
The hospital, which does between 200 and 250 interventional stroke treatments per year and handles many more strokes than that annually, has a group of health care specialists who can provide accessible information to patients who are not experts in the field and who need to make an informed decision under time pressure.
Stony Brook has become adept at “conveying this complex information in a time-sensitive way,” Dr. Fiorella said. In those cases for which surgery is the best option, each minute that the doctors don’t open up a blood vessel reduces the benefits and increases the risk of longer-term damage.
Stony Brook sees about one to two of these kinds of cases per month. As a whole, the hospital, which is a large referral center, sees numerous complex and unusual cerebrovascular cases of all types, Dr. Fiorella said.
Annunziata and the doctors decided to have the emergency surgery.
Dr. Fiorella used a balloon guiding catheter, which is a long tube with a working inner lumen that has a soft balloon on the outside of it that is designed to temporarily block flow. He deploys these occlusion balloons in most all stroke cases.
The particular way he used it in these complete carotid occlusions is unique. The balloon guiding catheter makes interventional stroke procedures more efficient, safer, and the outcomes better, according to data for thrombectomy, Dr. Fiorella said.
The occlusion balloon enabled Dr. Fiorella to control blow flow the entire time, which makes the procedure safer. The surgery took under an hour and involved a small incision in Annunziata’s right wrist.

After the surgery, Annunziata was able to speak to doctors and call Rosemarie Madrose, his girlfriend of five and a half years. “He came out talking,” said Madrose. “I could understand him. I was relieved.” Four days after the emergency operation, Annunziata, who also received post operative care from Dr. Yuehjien Gu, Neurocritical Care Unit Director, left the hospital and returned to his home, where he spent the next morning preparing a welcome meal of a scrambled egg and two slices of toast.
The doctors attribute Annunziata’s quick recovery to a host of factors. Getting himself to the hospital as soon as symptoms started saved precious minutes, Dr. Fiorella said, as “time is brain.” He also advised against driving for people having stroke-like symptoms, which can include slurred speech, numbness, weakening of the arm or leg and loss of vision in one eye.
Dr. Fiorella urged people to call for help or to get a ride in an ambulance. Stony Brook has two mobile stroke unit ambulances, which are equipped with technology to assess patients while en route, saving time and alerting doctors in the hospital to patients who might need immediate attention and intervention.
These mobile units, which are available from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m., have helped reduce death and disability for stroke and have cut down the length of stays in the hospital.
People or family and friends who are observing someone who might be having a stroke can call 911 and indicate that the patient is having stroke-like symptoms. The emergency operator will alert the mobile stroke unit of a possible case if the unit is available and the patient is in range.
Helping a veteran
The doctors involved in Annunziata’s care were well aware of the fact that they were treating a veteran on Veterans Day.
“Oftentimes, we think about how we can give back more than just a thank you” to people like Annunziata, who “risked his life and helped his country the way he could,” said Dr. Mathew. “I’m helping him the way I can help.”
Dr. Fiorella added that he thought it was “wonderful” to “help someone who’s given so much to our country on Veterans Day.”
Army origin
Annunziata explained that he wound up in the Army through a circuitous route. “We watched all the war movies” when he was young and wanted to join the Marines, he said.
When he went to enlist in 1962, he was told there was a two and a half year wait. He and his young friends got the same reception at the Air Force, Navy and the Army. As they were leaving the Army building on Whitehall Street, he and his friends ran into a sergeant with numerous medals on his uniform. The sergeant urged them to go back up the hallway and enter the first door on the right and indicate that they wanted to expedite the draft. About a week later, Annunziata was drafted and got a 15 cent token in the mail for a train trip to Wall Street.
After basic training at Fort Dix, he was stationed in Greenland, where Annunziata operated a radar at the top of a mountain for two years. He participated in drills in which he had to catch American planes flying overhead.
Fortunately, he said, even during the height of the Cold War and just months after the Cuban Missile Crisis, Annunziata never spotted a Russian threat, even though the base was just 20 minutes from Russian air space.
Having gone through emergency surgery that likely saved his life, Annunziata urges residents to pay attention to any medical needs on their radar.
Dr. Fiorella was amazed at how quickly Annunziata expressed concern for his fellow veterans during his recovery.
“One of the first things he talked about was, ‘How can I use what happened to me to help other vets?’” Dr. Fiorella said.
Annunziata’s girlfriend Madrose, who is grateful that the procedure saved his life, said he “didn’t listen to me. He knew he had to do this. I kept saying, ‘When are you going to do it?’ He said, ‘I will, I will, I will.’ He learned the hard way.” She added that they both know he is “extremely lucky.”