“Teaching to the test” is a concept that no longer computes in Comsewogue School District.
Administration and faculty in Comsewogue, for the last two school years, have experimented with a problem-based learning curriculum for small groups of interested ninth- and 10th-graders, an alternative to the traditional educational strategy of focusing assignments and assessments toward the goal of performing well on state-mandated standardized tests at the end of the year. Now, Superintendent Joe Rella has data to back up his notorious aversion to one-size-fits-all education and assessment.
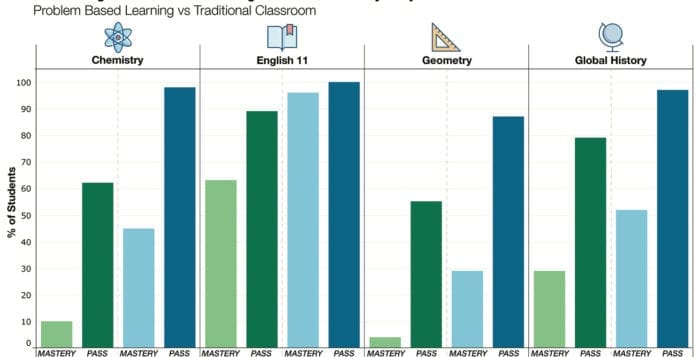
In all subjects, Comsewogue students in PBL classes passed 2018 Regents exams, scoring 65 or better, at a higher rate than those in traditional classrooms, according to data released by the district. On chemistry, geometry, algebra II, global history and English 11 exams, PBL students achieved mastery level, scoring 85 or better, at significantly higher rates than their non-PBL classmates.
“We played in your ballpark — we scored runs.”
— Joe Rella
“We played in your ballpark — we scored runs,” Rella said of how he interpreted the data, meaning students taught by alternative methods still displayed an aptitude on the state’s required tests.
Though Rella and the district have taken steps to try to have PBL assessments replace Regents exams, no avenue to do so has been greenlighted by the New York State Department of Education to this point for Comsewogue. Emails requesting comment on the significance of Comsewogue’s test results sent to the education department and Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s (D) press office were not returned.
During the 2017-18 school year, about half of Comsewogue’s ninth- and 10th-graders, roughly 300 students, took part voluntarily in PBL classes, which emphasize hands-on learning and real-world application of concepts as assessments — similar to a master’s thesis or doctoral dissertation — as opposed to the traditional “Regents model.” The students were still required by the state to take the Regents exams as all students are, and their performance has inspired the district in year three of the pilot to expand its PBL curriculum offerings on a voluntary basis for 2018-19 to its entire student body — kindergarten through 12th grade.
The superintendent said the impetus for the district to experiment with PBL started three years ago, when he and about 20 Comsewogue teachers spent a day at the New York Performance Standards Consortium in Manhattan. The organization was founded on the belief that there was a better way to assess student learning than dependence upon standardized testing, according to its website.
“In traditional settings, the teacher did most of the work, we listened, we copied notes and then we were tested on it,” Rella said. “The way the structure was, you spent a year learning stuff. At the end of the year, you took a test to see what you knew.”
In PBL classrooms, regardless of subject, Rella explained that a problem is initially presented, and students learn skills that are meant to help them practically find an answer to the problem. One group of PBL students during the 2017-18 school year decided to approach opioid addiction as a subject matter. Rella said chemistry students and English students worked on parallel tracks addressing that problem, with the science classes researching and presenting on the science behind addiction and the brain, and the English classes creating a public service announcement on the topic. The students presented and defended their findings and approach to the Suffolk County Legislature, with two students eventually being asked to join the county’s commission on substance addiction, according to Rella.
“It’s the problem that drives the learning rather than, ‘I learn to take an assessment at some future date.’”
— Joe Rella
“You have to acquire knowledge in order to solve the problem, so there is traditional teaching going on,” he said. “But right from the beginning, it’s the problem that drives the learning rather than, ‘I learn to take an assessment at some future date.’”
Rella credited District Administrator for Curriculum and Instruction Jennifer Polychronakos as the driving force behind professional development and empowering district faculty to embrace the district’s new approach.
“We’ve so far created about 20 units of study districtwide that are ready to go for next year and we’ve piloted some of them and worked out some of the kinks,” Polychronakos said. “We’re going to continue to really just take the standards that we have from the state and make them into more of a project-based, or problem-based, learning type of experience for the kids.”