Water, water everywhere and far too many drops were not clean.

That’s the conclusion of a recent summer water quality survey of Long Island conducted by Stony Brook University Professor Christopher Gobler, who is the endowed chair of Coastal Ecology and Conservation at the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences.
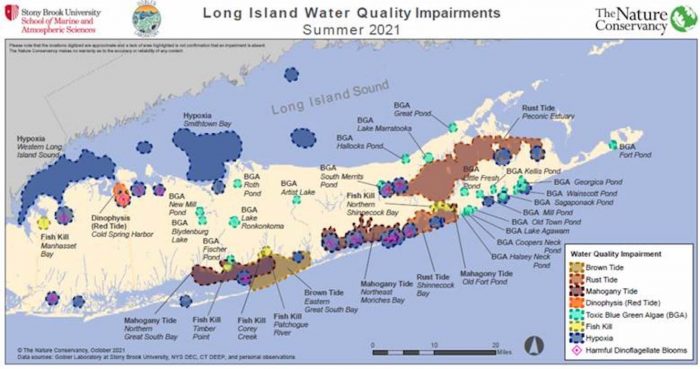
Every estuary and bay across Long Island had either toxic algal blooms and oxygen-starved dead zones this summer.
This trend threatened marine life including fish and shellfish.
Excess nitrogen from household sewage that seeps into groundwater and into bays, harbors and estuaries or, in some cases, is discharged directly into surface waters, causes toxic algal blooms.
Double the average annual rainfall, caused by storms like Hurricanes Henri and Ida, exacerbated the dumping of nitrogen from onsite wastewater into local waterways as well, Gobler explained.
Calling this the “new normal,” Gobler said the duration of the rust tide that continues across eastern Long Island is the longest since he started monitoring water quality in 2014. Additionally, the number of dead zones is near a maximum.
For the past six years before 2021, the incidence of blue-green algal blooms was higher than any of the other 64 counties in New York State, which is likely to continue in 2021.
Blue green algae produce toxins that can be harmful to people and animals and has caused dog illnesses and deaths across the United States.
“We’re the most downstate county and warmer temperatures are a driver,” Gobler explained in an email. “Excess groundwater discharge in Suffolk means more lakes and ponds here than in Nassau.”
Heavy rains, which are expected to become the new normal amid climate change that brings wetter and slower-moving storms, flush nitrogen contaminated groundwater out into the bays.
Brown and rust tides have had a severely negative impact on habitats in the area, including seagrass, and major fisheries such as scallops and clams and the coastal wetlands that protect waterfront communities from storms.
Homeowners can reduce nitrogen runoff by fertilizing their lawns less, Gobler suggested.
Onsite systems in Suffolk County are legal, but are also “quite polluting,” Gobler explained in an email.
Gobler said Suffolk County has been more aggressive than any other county in the nation in requiring advanced septic systems.
Additionally, Gobler suggests that the best way to combat these problems is to upgrade onsite septic systems.
Nassau and Suffolk completed subwatershed studies last year that identified wastewater as the largest source of nitrogen to surface waters. Excess nitrogen stimulates toxic algal blooms which can remove oxygen from bottom waters as they decay.
The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation recommends that marine waters should not have less than three milligrams of dissolved oxygen per liter to sustain fish life. Through the summer, however, more than 20 sites across the Island fell below that threshold, which, in several cases, caused fish kills.
“The research findings are conclusive,” Carl LoBue, senior scientist for The Nature Conservancy, said in a statement. “The longer we wait to fix our water quality problems, the longer it will take and the more expensive it will be.”